This circuit can be used in various projects where we require the counting. Like in doctors’ clinic or hospitals, in restaurants, in customer care offices where long queue is there and we want to stop the rush at the counter. This system is very effective where man power is less. In this you have to provide a token to the person and the person has to wait for its turn which can be displayed on the 7 segment display. With the help of this counter circuit we can maintain the silence and the person will also be informed about their turn.
This circuit is based on 4026, a Johnson counter IC commonly used in digital display. It has a 5 stage Johnson decade counter with decoder which convert the Johnson code to a 7 segment decoded output. This means it will convert the input into numeric display which can be seen on 7 segment display. It can be used for displaying analogue value, such as temperature with pic microcontroller, used for counting objects. It can be used in various applications like in 7 segment decimal display circuit, in clocks, timer etc. Advantage of 4026 counter–
* It contains counter and 7 segment decoding in one package.
* It can be easily interface with 7 segment types.
* Ideal for low power display.
* Operated at wide range of temperature from 5V to 20V.
* The big advantage of the 4026B counter IC is that it can drive a 7-segment display without eeding a decoder driver IC
Description
To understand its working how we can interface 4026 with 7 segment display, first have to look on its pin diagram –

Now let us understand the working of individual pins-
1. Pin 1 or clock pin- It receives clock signals, and at every positive clock and counter advances one by one. You can provide clock with the switch, 555 timer or with the help of logic gates. In short high pulse on this input increments the counter.
2. Pin 2 or disable clock (clk inhibit) pin- 4026 counter advances one by one by receiving positive pulse at this time for this clock inhibit pin should be grounded. If it is connected to supply than counter advancement will be inhibited means there will be no meaning of clock pulse.
3. Pin 3 or enable display (En in) pin- It enable the 7 segment display to display the numeric value. It should be kept high for enabling the display. Mean output goes high when only when display enable is high.
4. Pin 4 or enable out- It Enables the carry out pin. In our circuit we have left this pin unconnected.
5. Pin 5 or divide by 10 output- It is used to complete one cycle for every 10 clock input cycle and it also used to cascade more IC’s.
6.Pin 6, pin7 and Pin9 to pin 13 – These are 7 decoded output from a to g used to illuminates the corresponding segment of 7 segment display to display the digit from 0 to 9.
7. Pin 14 or not 2 output (UNGATED “C” SEGMENT) signals- They are not gated by the Display clock and therefore are available continuously. This feature is a requirement in implementation of certain divider function such a as divide by 60 and divide by 12.
8. Pin 15 or Reset pin- It is used to reset the counter. When it receives high it clears the counter and counting again starts from zero. One important thing reset pin should again made low to start the counter once again.
9. Pin 8 or ground pin and Pin 16 known or Vdd it should be connected to power supply.
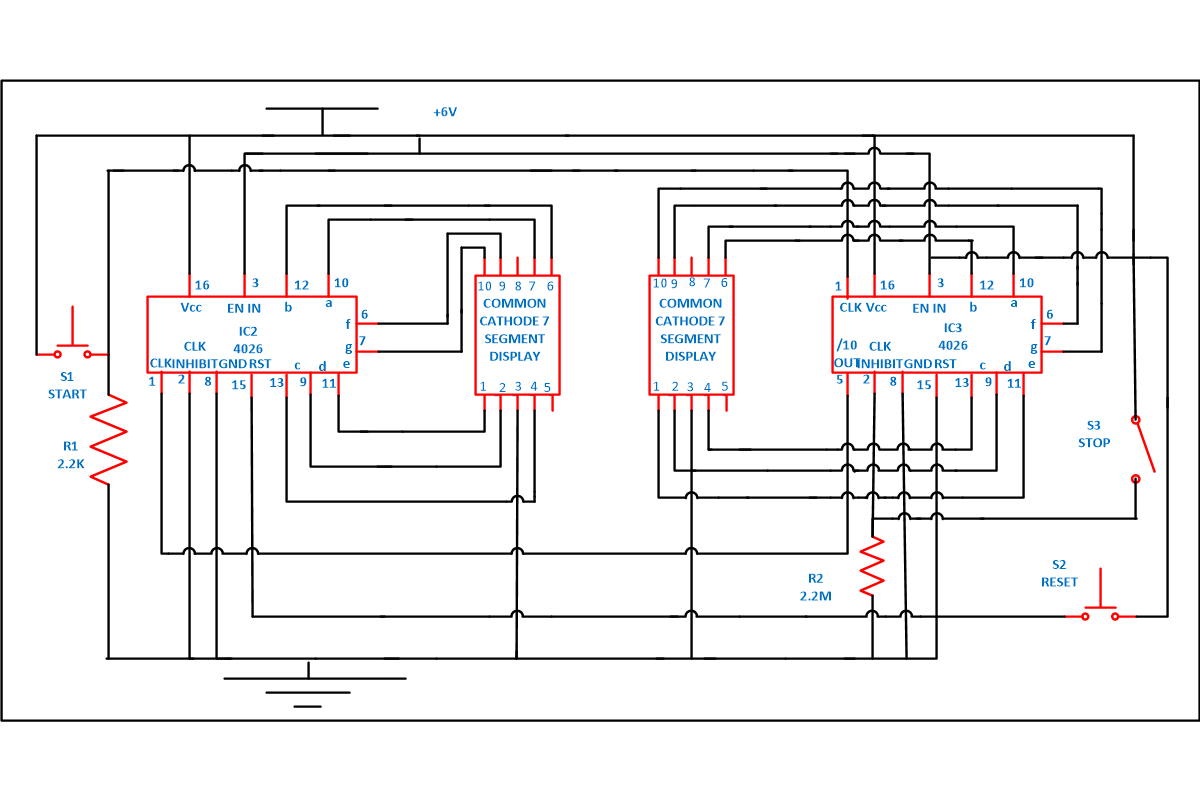
To understand its working assemble the circuit as shown in circuit diagram –
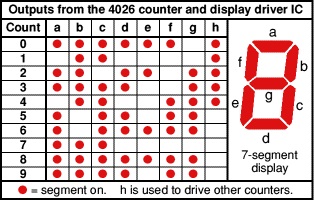
It uses a 4026 combined counter and display driver IC which is designed to drive 7 segment display. When you press the switch S1 counter starts from zero and it advances one each time whenever pin 1 receives a positive pulse. When you press the switch for first time numeric 1 will display. Then you again press the switch numeric 2 will display, giving you second output. In similar manner 3 and 4 will display. When count reaches to 9 after that it again starts it counting from zero.
For resetting the counter to zero at any point press switch S2. For this pin 15 must be taken high and then taken low again. The table below shows sequence of how each segment glows after receiving clock signal.
Working
Working of the counter circuit–

Assemble the circuit properly. Connect the pin 3 of both the IC 1 and 2 to supply, to on the display. If pin 3 is connected to ground we will get a blank display on 7 segment output.
And also connect the pin 15 which is a reset pin of the both the IC together so that when counting reaches to 99 it will reset the counter to zero. When you on the switch S3 counter will not progress irrespective of clock signal at pin 1 because this is connected to pin 2 that is disable clock (clk inhibit) pin and it goes high when it is on . As 4026 counter advances one by one by receiving positive pulse at this time clock inhibit pin should be grounded.
Now whenever a customer arrives in restaurant, hospital or customer care office, you can provide them with token number. Now apply power supply. Zero will be displayed on both the 7 segment display. As soon as switch S1 is pressed, a clock pulse is provided to pin 1 (which is a clock input pin) of IC1. After receiving the clock pulse 4026 IC counter advances and 1 will be displayed on common cathode 7 segment display. When second customer enters, same phenomenon occurs till count reaches 9. When it reaches 9 one cycle is completed. As you can see from circuit diagram pin 5 of IC1 is connected to pin 1 of IC2 to cascade another IC, after every 10th pulse it will go high to provide a clock pulse to IC2 to advance its counter that’s why we will receive a 1 on 7 segment common cathode display 2 .
Provide switch S1 and S3 to doctor or chef so that when they are done with one patient or customer they can press the switch and the next customer can go. Now people can see their number on display and go according to their token number.
Unit place number are displayed on display 1 and tens place numbers are displayed on display 2. After completion of each cycle tens place advances one. Now you can cascade more 4026 IC to increase the number of display according to your requirements. Play around it by adding and removing some more components. So now can start your own project.
Video
Circuit Diagrams
Filed Under: Electronic Projects


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.