Difference between graphical and ordinary lcds.
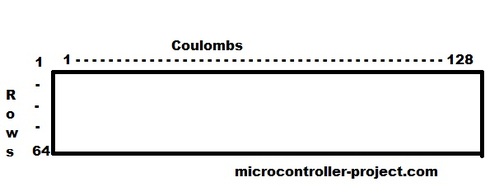 Graphical Lcd Rows(64) and Coulombs(128)
Graphical Lcd Rows(64) and Coulombs(128)
Graphical lcds are different from the ordinary character lcds, like 16×1 16×2 16×4 20×1 20×2 etc. They (ordinary) can print\display only characters or custom made characters. They display characters in a fixed size matrix normally 5×7 or 5×8. Where as in graphical lcd’s e.g 128×64 we have 128×64=8192 dots or 8192/8=1024 pixels. We can display a character in a size which we need. More over we can make a picture on a graphical lcd as well. If the size of graphical lcd is 1024 pixels we can display a picture on it covering 1024 pixels. More over we can also display video(animated or doted) an video on graphical lcds.
Normally graphical lcd which is easily available in the market and is best to getting start in the field of graphical lcds is 128×64. It has 128 coulombs and 64 rows. You can display your data in 128×64 dot matrix.
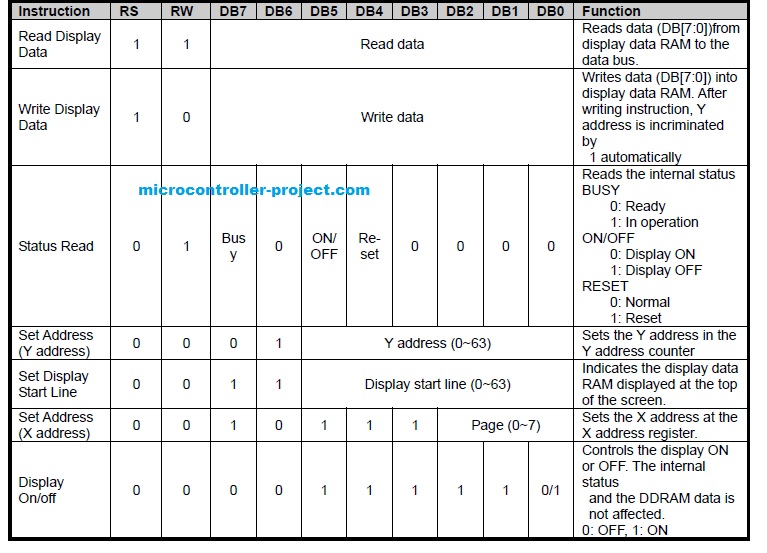
Graphical Lcd controller
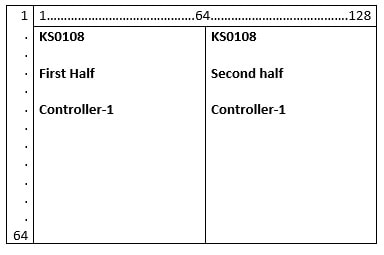
Graphical lcd is controlled by two KS0108 controllers. A single KS0108 controller is capable of controlling 4096 dots or 512 pixels. So for controlling a graphical lcd we need two KS0108 controllers.
Lcd is further divided in to two equal half’s. First half from 1 to 64 coulombs in controlled by first KS0108 controller. The second KS0108 controls the second half from 64 to 128 coulombs. The figure on the left explains about how the controller’s are dedicated for half’s.
Further graphical lcd half’s division
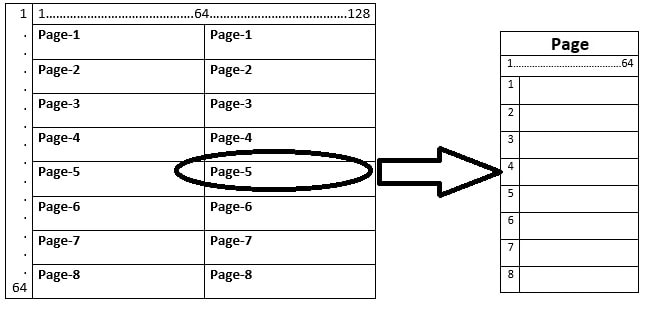
Page distribution in Pixels
Each page contains 64 pixels(64 coulombs and 8 rows). You can create your desired output on these pixels. Each pixel lights up when it is 0 and becomes off when it is 1. Each pixel contains 8 dots.
The figure on the left shows a single pixel of graphical lcd. Each pixel is built up by 8 dots. 1 coulomb and 8 rows constitute a pixel.
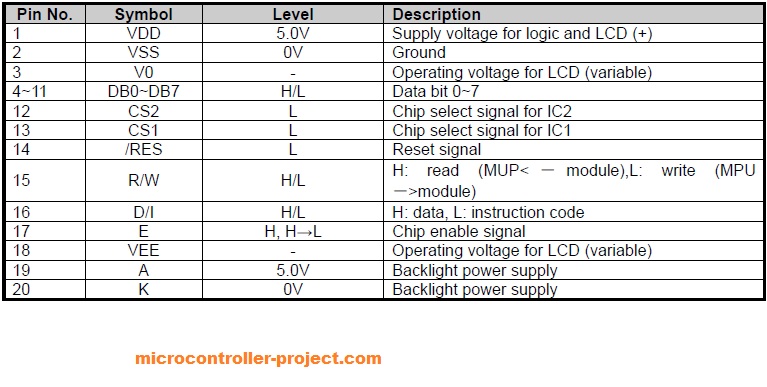
Graphical Lcd (128×64) Pinout
Graphical Lcd pins are same as other character lcds. Only two new pins are introduced with the graphical lcd. These are CS1 and CS2. CS1 is chip select 1 it selects the first half or first KS0108 controller of lcd. CS2 is chip select 2 it selects the second half or second KS0108 controller of lcd. Both CS1 and CS2 are active low. By active low I mean for selecting a first or second half, make its associated pin (CS1 , CS2) low 0. All the other pins E (enable) R/W (read/write) RS or D/I (register select) works in the same way like for normal lcds.
Like other lcds we also first have to initialize graphical lcd. By initializing I mean in which format we want to use our lcd. Like which half I want to use. Which page of which half I want to use. What is my x-address? What is my y-address?
|
Filed Under: Featured Contributions
Tagged With: 128x64, description, graphical lcd, pinout


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.