If you take a stroll outside today, you’ll see a lot of people with mobile phones, phablets or tablets in their hands making calls, using the internet to catch up on the news, watch videos, or interacting with others via Facebook, Tumblr or Twitter including you. In doing so, we all are using a mobile data network. Many of these applications particularly video consume a lot of bandwidth, so telecommunications companies across the world always try to talk about upgrading to the latest generation of mobile data to help speed things up.As we approach 2020 it is likely that there will be more than 50 billion connected devices worldwide and The Internet of Things will no longer be something we think about but will be all around us. Everything from home appliances to our cars will be connected to the network, and 5G is being designed and built with this in mind.5G is not just a mobile technology, its ubiquitous access to high & low data rate services.The technology is still a long way from becoming a reality, but it has the potential to completely change the way we interact with wireless devices, from the smartphones in our pockets to the cars we drive.
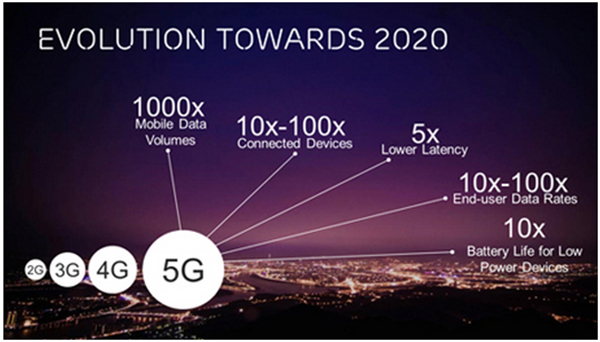
Fig. 1: Representational Image Showing Features of 5G Network
Not only will more devices be connected to the 5G network than we’ve ever imagined, but the network will do everything better than 4G. This includes providing the capability and capacity for high resolution video streaming such as ultra-high definition 4K video. Privacy and security are also key considerations, so 5G will include extra capabilities to ensure that customer information is protected and our devices are harder to hack.
Battery life is essential aspect of our mobile connectivity. The target for 5G networks is handsets, phablets, tablets and other devices with five times the battery life of existing 4G devices. Imagine not having to recharge for a couple of days or being able to watch a couple of movies without having to find a power outlet to plug into.
FEATURES OF 5G TECHNOLOGY–
Fig. 2: Graphical Presentation of 5G Network
1.5G technology offer high resolution for crazy cell phone user and bi-directional large bandwidth shaping.
2.The advanced billing interfaces of 5G technology makes it more attractive and effective.
3.5G technology will be also providing subscriber supervision tools for fast action.
4.The high quality services of 5G technology based on Policy to avoid error.
5.5G technology will be providing large broadcasting of data in Gigabit which supporting almost 65,000 connections.
6.5G technology offer transporter class gateway with unparalleled consistency.
7.The traffic statistics by 5G technology makes it more accurate.
8.Through remote management offered by 5G technology a user can get better and fast solution.
9.The remote diagnostics is also a great feature of 5G technology.
10.The 5G technology will be providing up to 25 Mbps connectivity speed.
11.It will be globally accessible.
12.It will be having 6th sense technology.
13.The 5G technology also support virtual private network.
14.The new 5G technology will take all delivery service out of business prospect.
15.The uploading and downloading speed of 5G technology will be touching the peak.
16.The 5G technology network offering enhanced and available connectivity just about the world.
SPECIFICATIONS – Although the standards bodies have not yet defined the parameters needed to meet a 5G performance level yet, other organizations have set their own aims, that may eventually influence the final specifications.
Typical parameters for a 5G standard may include:
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
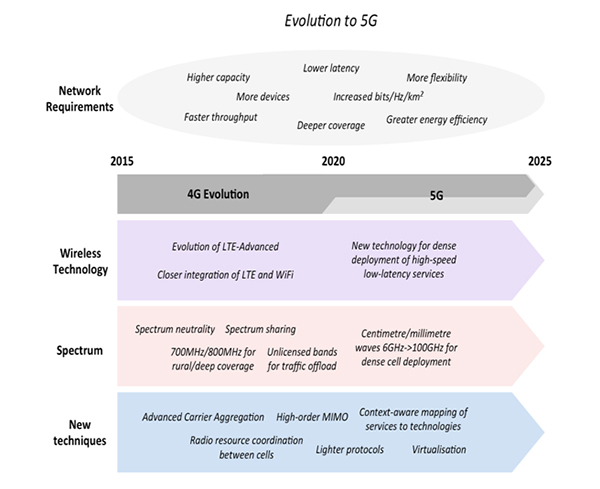
Fig. 3: Block Diagram Showing Evolution Of 5G Network and its Close Comparison With 4G Network
|
4G |
5G |
| · It is the fourth generation of mobile communication technology. | · It is the revolution in 4G mobile communication technology. |
| · It provides dynamic information access, wearable devices. | · It provides dynamic information access, wearable devices with AI capabilities. |
| · It supports data band width in Mbps. | · It supports data band width inGbps. |
| · Speeds for 4G are further increased to keep up with data access demand used by various services. | · 5G will provide very high speed as well as efficient use of available band width to the consumers. |
| · 4G provide high definition streaming and some additional features such as multimedia Newspaper and ultra-broadband internet access which were not present in 3G. | · 5G includes large phone memory, dialing speed, and much more and also we can hook our 5G cell phones with laptop to get broadband internet access. |
| · Band width per frequency channel is up to 100Mhz. | · Band width per frequency channel is up to 28Ghz. |
| · CDMA multiple access. | · CDMA & BDMA multiple access. |
| · In 4G concatenated codes are used for error detection. | · The high quality of service of 5G technology based on policy to avoid error. |
What will 5G allow us to do that we can’t right now with 4G? To provide a little more context around how much faster 5G speeds will be compared to 4G, let’s go back to the video example I mentioned at the beginning. According to Huawei, 5G will allow us to download an eight gigabyte HD movie in six seconds versus the seven minutes it would take over 4G or more than an hour on 3G.
But 5G is much more than just faster data speeds on our mobile devices. It also opens the door to a lot of different consumer and industrial applications and uses, some of which seem unbelievable now because they’re so futuristic.
For example, Ulrich Dropmann, head of industry environment networks at Nokia, gave a scenario where we might be cruising in our driverless car when, unbeknownst to us, a crash has just occurred up the road. With 5G, sensors placed along the road would be able to instantly relay that information back to our car (this is where having low latency is important), so it could brake earlier and avoid another accident.At MWC (MWC is an annual event in Barcelona where the wireless industry comes together to show off the latest devices and technologies.), Ericsson showed how 5G could be used to control heavy machinery from a remote location. Inside the booth, attendees strapped on an Oculus Rift headset and were able to remotely control one of two real diggers to move dirt either outside the conference hall or one thousands of miles away in Sweden.
CHALLENGES FOR 5G–
· Standardization– One of the big challenges facing 5G is standardization. There are already multiple groups working to come up with standards around interoperability, backward compatibility with older technologies (4G, 3G), and making sure the network will be future-proof. While many companies agree that a global standard is needed, whether they’ll be able to come together and agree on one is another story.
· Infrastructure – Building the infrastructure for 5G is also a huge task, with issues around spectrum and installing new antennas. 5G is likely going to rely, at least in part, on higher-frequency bands. There is more space in those airwaves available, but at such high frequencies, signals can’t travel nearly as far as they can over the frequencies used for 4G, resulting in a poor connection.
One major enabler for 5G will be the release of frequency spectrum and this need to be managed on a global scale to ensure commonality and also the reduction of interference between services, especially those operating globally. This process is managed under the auspices of the International Telecommunications Union, ITU.Obstacles like buildings and trees and even bad weather can also cause interference, according to Nokia’s Dropmann. To offset that, carriers will need to install more base stations to ensure better coverage, and use antenna technologies like MIMO (multiple-input and multiple-output).
Filed Under: Articles


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.