Basic of AND Gate
AND gate gives high at the output only when all the inputs are high otherwise, it gives low.
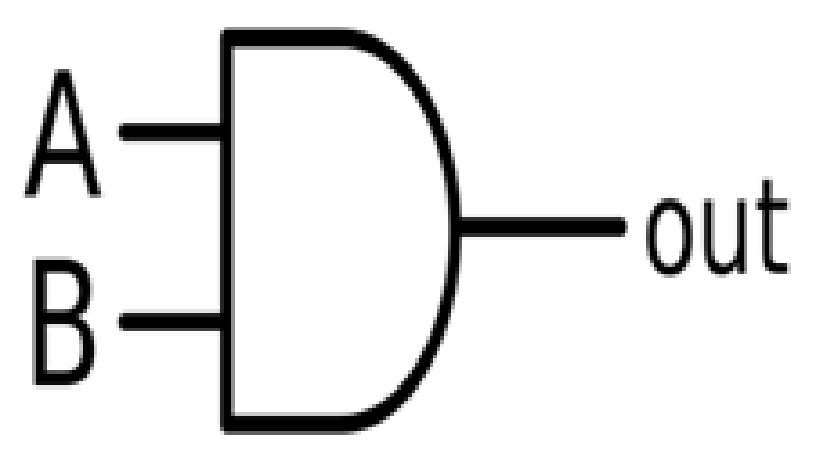
Fig. 1: Symbol of AND Gate
| INPUT 1 A | INPUT 2 B | OUTPUT A.B |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
The TRUTH TABLE OF AND GATE
The use of transistor for AND gate operation depends on the transistor switching speed. For AND gate operation we use transistor as a switch.
Components Required
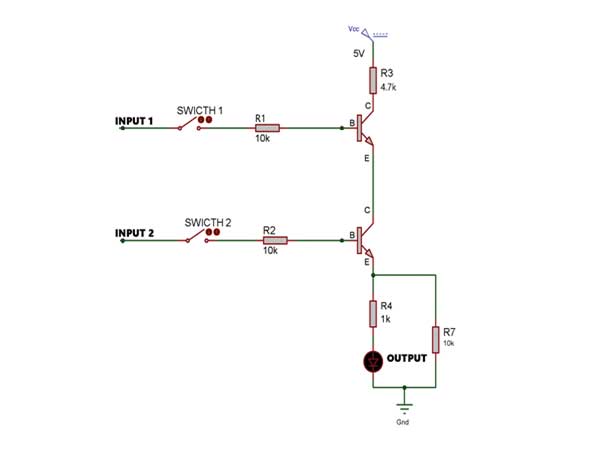
The transistors are connected in series and their bases are used as input. The base of both the transistors act like inputs and one of the emitter of either of the transistors is used to derive the output. Initially, both the switches are in OFF state so none of the transistor bases get a power supply. The base to emitter junction and base to collector junction of both the transistors have a voltage lower than 0.65V, which is the practical threshold voltage of the diode.
Both junctions are in reverse bias hence both the transistors turn off and go into their cutoff state. Therefore, the transistors act like an open switch. Since all the current coming from the collector through resistor R3 blocks by the transistor. Hence at the output, we get a low voltage which turns off the LED.
In next case when we press switch 1 then the base of the first transistor gets a positive value of voltage but its emitter is connected to another transistor collector. As the second transistor is still in its cutoff state, the emitter of the first transistor is disconnected. The base to emitter junction and base to collector junction of both the transistors have a voltage lower than the threshold voltage and again they reach their cutoff state. All the current is again blocked by the transistor and we get low voltage at the output, which turns OFF the LED.
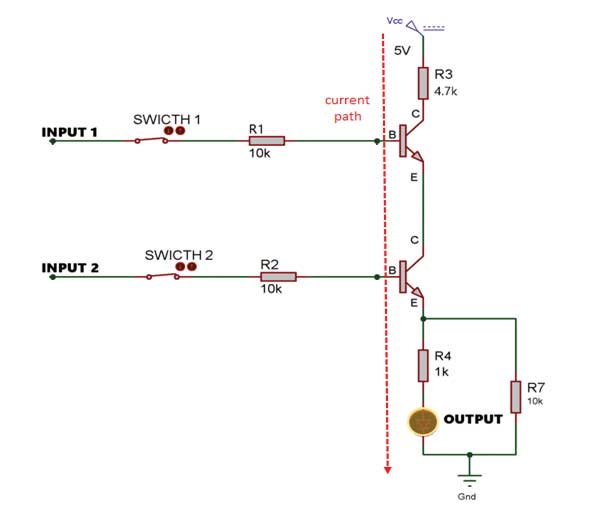
Fig. 3: Circuit Diagram showing working of Transistor based AND Gate


Filed Under: Electronic Projects


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.