File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a standard protocol for transferring files between a client and server over an internet network. The FTP protocol was written by Abhay Bhushan (IIT Kanpur) in 1971. In 1980, a TCP/IP version of the protocol as RFC 765 was introduced which became the de facto standard worldwide. in 1998, the protocol stack was updated for IPv6 support. Within this protocol, the security features were enabled by a TLS/SSL layers called FTP Secure (FTPS). A new secured version of FTP is also widely used called SSH File transfer protocol (SFTP). The SFTP is quite different protocol than the traditional FTPS.

Fig. 1: Representational Image of FTP Protocol
The FTP protocol is based on Client-Server model, so device at one end request files while the device at other end responds to the request. There are separate control and data connections between the client and the server. The FTP clients need to authenticate themselves to the server by a sign in the protocol. The sign in is usually in the form of username and password. An FTP client can also sign in as anonymous user if it is allowed by the server. Earlier FTP client applications used to be command line programs, though now client utilities with graphic UI are commonly available.
FTP Connection
An FTP client can communicate with an FTP server in either of two modes – Active or Passive mode. In active connection, the client listens to a port (PORT M) and while making connection to server it sends (PORT M) FTP commands to inform the server which port it is listening. Then the server initiates a data channel to client on that port (PORT M) using port number 20 where port 20 is the FTP server data port and the data transfer starts.
In passive connection, the FTP client send a PASV command to the FTP server using a control connection. The server responds to the command by sending its IP address and port number. The client then can open a data connection using an arbitrary port number to the received IP address and server port number. The passive mode was introduced to allow communication with clients that fall behind a Firewall and so, cannot accept a TCP connection.
In passive mode, the FTP server responds to the client in the form of three-digit codes over the control connection. The response includes a number and an optional text. The number (three-digit number) represents the response code while the optional text is a human readable explanation of the response code. The first digit in the response code denotes the kind of response and can range from 1 to 6. The first digit in the response code has the following significations –
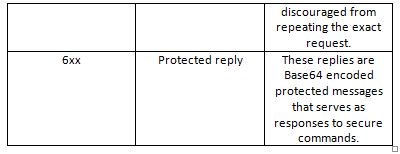
Fig. 2: Table Listing Significations of First Digit in Response Code of FTP Server

Fig. 3: Table Listing Significations of First Digit in Response Code of FTP Server
The second digit in the response code specifies the type of data transfer as follow –

Fig. 4: Table Listing Significations of Second Digit in Response Code of FTP Server

Fig. 5: Table Listing Significations of Second Digit in Response Code of FTP Server
Some of the common response codes are as follow –


Fig. 6: Table listing common response codes of FTP Server Fig. 7: Table listing common response codes of FTP Server
Once the client and server are connected, they can transfer the following four data representations –
1) ASCII mode – It is used for text transferring, data is converted into “8-bit ASCII” before or after transferring if necessary, but it is not suitable for the data other than plain text.
2) IMAGE mode – It is called binary mode, used in transferring images, the data is sent in binary form byte by byte, the receiver receives that byte-stream and stores it as sync with receiving.
3) EBCDIC Mode – It is used for plain text between hosts using the EBCDIC character set
4) Local Mode – It allows two machines that has identical setup, transfer data without converting into ASCII (in a proprietary format).
The data transfer can happen in either of the following three modes –
1) Stream Mode – In this mode data is sent as continuous stream without any processing at the FTP. Instead, the processing of data is done at the TCP layer.
2) Block Mode – In this mode, FTP breaks data into blocks and pass those blocks to the TCP layer.
3) Compressed Mode – In this mode, the data is first compressed using a compression algorithm before passing to the TCP layer.
FTP Login –
FTP client first has to login to FTP server in order to transfer data. The client can authenticate using username, password if server allows. The commands to authentication can be sent on port 21 for login. The username can be sent using USER command and the password can be sent using PASS command. This sequence is in plain text form and is venerable to sniffing attacks (Network traffic capture).
Anonymous FTP access –
A FTP server is sometimes allowed to login without username and password. Client can login to server using an anonymous account, when asked for username user can type “anonymous” and then server asks for an email address instead of password (No verification of data is performed). This can be seen in an update server which just provides only updates.
FTP Features –
1) Web Browser Support – FTP supports web bowser logins and data surfing. The most common and new web browser can retrieve files hosted on FTP server. Using FTP in web browser, most of the advance web applications are using ftp to provide downloads and updates. A user can login to FTP server using web browser and surf data there. The syntax to login from browser looks like the following – [ftp://[user[:password]@]host[:port]/url-path]
2) Security – The security in FTP is not provided in the traditional version. The logins credentials and commands transferred to server are in plane text without any encryption. Thus, any network sniffer can read the data. Common attacks FTP is venerable to are as follow –
• Brute force attack
• FTP bounce attack
• Packet capture
• Port stealing (guessing the next open port and usurping a legitimate connection)
• Spoofing attack
• Username enumeration
The Solutions to these security weaknesses are as follow –
1. Use secure version of FTP – FTPS instead of traditional FTP, like instead of TELNET use TELNETS.
2. Use a more secure protocol for data transfer that can handle encryption like SSH file transfer protocol.
3. Use a secure connection to server like use VPN instead of directly connecting to the server.
There are some variants of FTP that provides secured data communication like FTPS, SFTP, TFTP, SSH File Transfer Protocol, which can also be used.
In the next tutorial, FTP protocol will be implemented in an IoT application. In the next tutorial, a Raspberry Pi will be configured as a FTP client and will be made to download files from a FTP server.
Filed Under: IoT tutorials, Tutorials

