Previously, I have given arduino library for unipolar type stepper motors. It perfectly controls speed, direction, a number of revolutions, motor angle etc all the parameters of unipolar type stepper motors. But it was for only unipolar type stepper motors. As we know the stepper motor may be bipolar type also. But this library cannot control bipolar type stepper motor. So I have decided to develop another arduino library to control bipolar type stepper motor.
So, here I present Bipolar Stepper motor library in Arduino for all bipolar type stepper motors. The library has 9 different functions that can be used to rotate and control motor as per the requirements. The library is designed as per the industrial motion control requirements. Here are some of the features of this library.
1. Controls any bipolar stepper motor
2. Controls direction of rotation of motor
3. Accurately controls the number of revolutions of the motor like 1, 2, 3, 4, …..
4. Accurately controls motor speed in RPM with 95% accuracy
5. Accurately rotates motor to desire angle between 0 – 360o with 80-100% accuracy
6. Compatible with all arduino boards
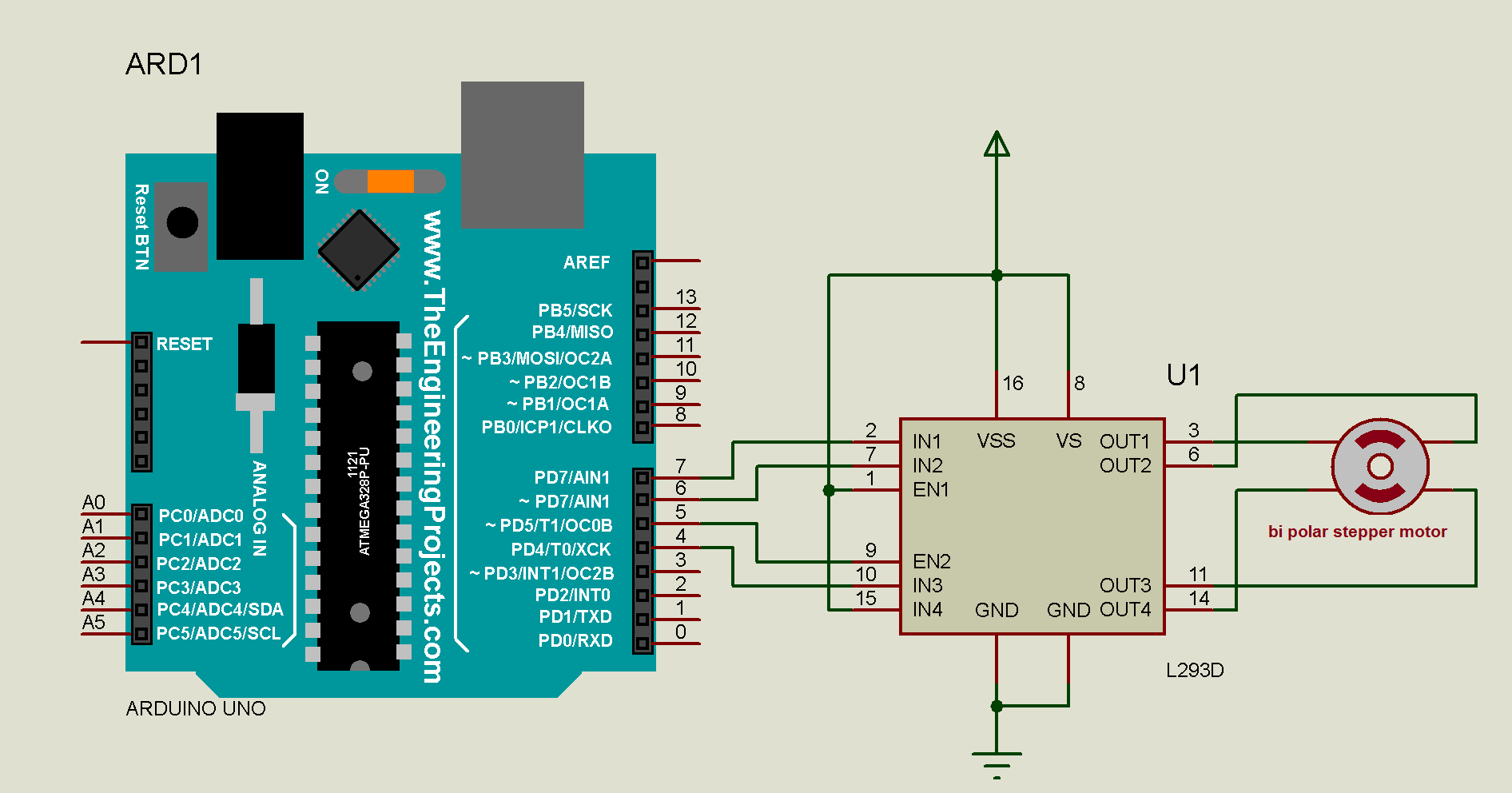
The brief descriptions of all library functions are given here. Some examples are given afterward that explains how the motor is controlled using this library. One video is also given that shows the demonstration of these examples. At last, the circuit is suggested that uses L293D chip – widely used as H-bridge driver for DC motors as well as bipolar stepper motors.
To use this library in your arduino sketch, just copy the bi_polar_Stepper folder into the root directory of arduino library folder like C:arduino-1.6.7libraries.
DESCRIPTION OF LIBRARY FUNCTIONS
1) bi_polar_Stepper(int pin1,int pin2,int pin3,int pin4) – this will create an instance of bi_polar_Stepper in the arduino sketch with stepper motor driver pins. Means one has to specify arduino board pins that are used to drive stepper motor
2) set_step_per_rev(int steps) – this function will set the number of steps required by the stepper motor to complete 1 revolution. Means it will set the step angle (step resolution) of the motor. One must enter step angle of motor for accurate control
3) set_RPM(int rpm) – this function will set the speed of motor in RPM and motor will rotate at selected speed with up to 95% accuracy
4) rotate_CW() – this function will start rotating motor clockwise. To rotate motor clockwise continuously one has to use this function in continuous loop
5) rotate_CCW() – this function will start rotating motor counter clockwise. To rotate motor counterclockwise continuously one has to use this function in continuous loop
6) rotate(int dir) – this function will rotate motor as per selected direction. If direction is given as 1 then motor will rotate clockwise and vice versa
7) rotate_one_rev(int dir) – this function will rotate motor exact 1 revolution in selected direction
8) rotate_n_rev(int dir,int num) – this function will rotate motor required number of revolutions in selected directions
9) rotate_x_deg(int deg) – this function will rotate motor to desire angle from 0 – 360o in either direction with 80 – 100% angle accuracy
EXAMPLES
1) Rotate motor continuously in any one direction at 60 RPM
2) Rotate motor one revolution clockwise and one revolution counter clockwise continuously
3) Rotate motor clockwise at 100 RPM and counter clockwise at 50 RPM continuously
4) Rotate motor 4 revolutions clockwise at 20 RPM and 2 revolutions counter clockwise at 10 RPM continuously
5) Rotate motor 90o clockwise and 90o anticlockwise continuously at 30 RPM
Note:- If the stepper motor is of higher current and voltage ratings then instead of L293D chip, we can use L298 chip or set of 4 separate Darlington transistors like TIP122, TIP142 etc can be used to drive stepper motors.
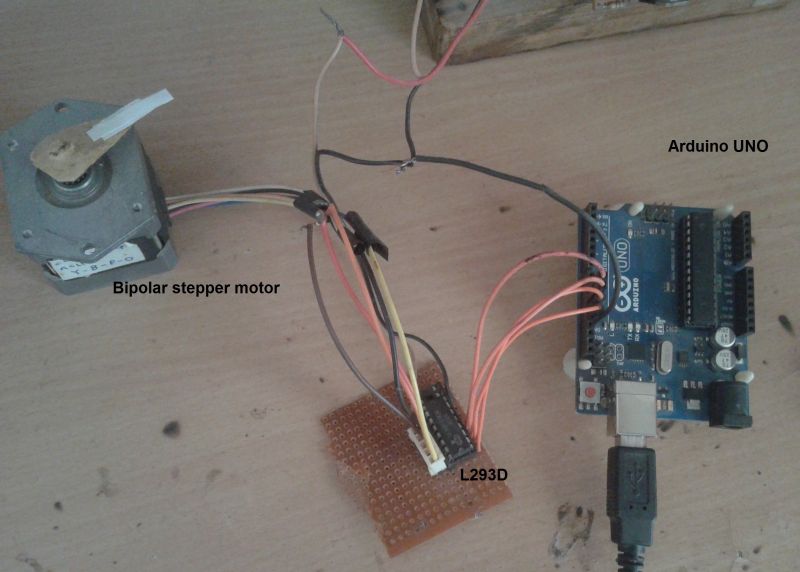
Here is the snap of above circuit arrangement.
Fig. 1: Prototype of Bipolar Type Stepper Motor Controller
The given library and example programs along with above circuit are tested with following stepper motors.
1) 2 phase bipolar motor with 5V, 100 RPM (MAX), 200 steps/rev (1.8o step angle)
2) 2 phase bipolar motor with 5V,60 RPM (MAX), 200 steps/rev (1.8o step angle)
Just go through the videos given here for demonstration.
You may also like:
Circuit Diagrams
Project Video
Filed Under: Electronic Projects
Filed Under: Electronic Projects






Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.