ASK means Amplitude Shift Keying (also known as ON-OFF keying). It’s one of the Modulation Scheme used to transmit Digital Data using High Frequency carrier signal. It’s very simple and popular method. It transmits 1’s and 0’s of Digital Data by transmitting carrier or no carrier like
· Bit 1 (logic high) is Transmitted with carrier frequency Fc
· Bit 0 (logic low) is Transmitted with no carrier
Means series of bits – bit stream is transmitted as carrier ON and carrier OFF. That’s why it is also known as ON-OFF keying.
The figure given below shows Waveforms for ASK Modulation.
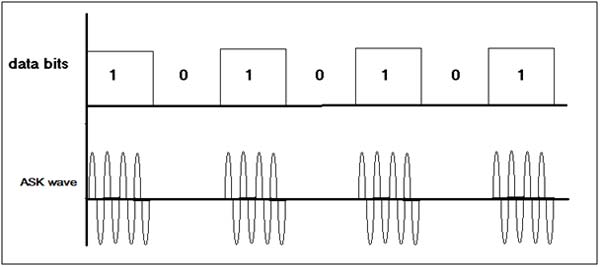
Fig. 1: Image Showing Waveforms for ASK Modulation
The first Waveform is bit pattern – data bits. 2nd Waveform shows ASK Modulation – for data bit 1 carrier signal (with frequency Fc) present but for data bit 0 there is no carrier signal. Usually carrier frequencies are higher than (100s of KHz) data rate. So in Single bit period several cycles of carrier are transmitted.
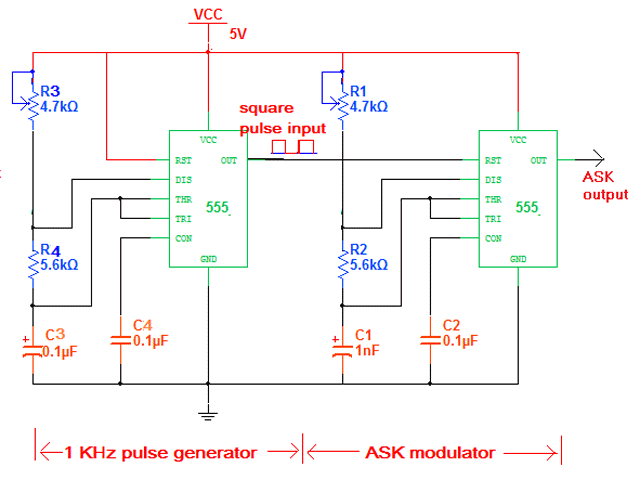
Here given Circuit demonstrates how ASK Modulated wave can be generated. The Circuit is build using IC555. The bit stream can be given as input, and as an output IC555 generates ASK Wave. In this experiment instead of bit-stream, Square pulses are applied as input that can represent Logic High and Logic Low as bit 1 and bit 0. To generate Square pulses one more IC555 is used.
Circuit Description
There are two sections in the circuit
1. ASK Modulator
2. 1 KHz Pulse Generator
Please refer Circuit Diagram Tab
Pulse Generator
IC555 is connected in Astable mode. It will generate continuous pulses at 1 KHz frequency. The frequency is determined by RC components R4, R5 and C3 as
F = 1.44 / (R4 + 2×R5) × C3
This 1 KHz pulse output is connected to reset pin (4) input of 2nd IC555 that works as ASK Modulator.
ASK Modulator
As shown in figure IC 555 is configured as Astable Multi vibrator. When its reset pin is high it generates continuous Square pulses with frequency
F = 1.44 / (R1 +2×R2) × C1
And when its reset pin is low its output is also low. The values of R1, R2 and C1 are selected as to get desire carrier frequency. The carrier frequency is selected as 100 KHz. Let us see how values of R1, R2 and C1 are calculated.
Circuit Designing
Assume C1 = 1 nF = 1 × 10-9 F
Substituting this value in to above equation
F = 1.44 / (R1 + 2×R2) × 10-9
Because desired frequency is 100 KHz
100 × 103 = 1.44 / (R1 + 2×R2) × 10-9
R1 + 2×R2 = 1.44 /( 105 × 10-9)
R1 + 2×R2 = 14400
Now to get around 50% duty cycle R2 > R1, so let us take R1 = 3.3 K.
So
2×R2 = 14400-3300 = 11100
So R2 = 5550 = 5.5 K
The nearest practical value can be 5.6 K.
Thus finally R1 = 3.3 K, R2 = 5.6 K and C1 = 1 nF. Instead of selecting fixed value of R1, a Potentiometer is used to tune the frequency and get exact value of 100 KHz.
Similarly we can determine values of R3, R4 and C3 to generate 1 KHz frequency. To find out these values start with assuming C1 = 0.1 µF. So from equation
F = 1.44 / (R4 + 2×R5) × C3
1000 = 1.44 / (R4 + 2×R5) × 10-7
(R4 + 2×R5) = 1.44 /( 103 × 10-7)
(R4 + 2×R5) = 14400
Again we can select same R4 and R5 values as 3.3 K and 5.6 K respectively. And to get exact 1 KHz frequency we can use Potentiometer instead of fix value resistor for R4.
Circuit Setup
The Circuit can be built on Bread Board or on general purpose PCB.
· On Bread Board, place all the components and make necessary connections as shown in Circuit Diagram
· On general purpose PCB, mount and solder all the components and connect components as per Circuit Diagram
Next, apply 5 V to the Circuit through power supply and connect output of Pulse Generator and ASK Modulator to both the channels of DSO (or CRO) using CRO probes.
Image of Circuit Setup

Fig. 2: Image Of Circuit Setup for ASK Modulation
Circuit Operation
1 KHz pulse input is given to reset pin 4 of IC555. When reset pin is given low logic the internal flip flop resets and IC555 gives low output. When reset pin is high IC555 works normal and generates Square Wave of Frequency determined by RC components in the output. So when bit 1 or logic high is given as input to reset pin a 100 KHz carrier is generated in the output and when bit 0 or logic low is given IC555 gives low output as requirement of ASK Modulated output.
Here is the Output Image of given Circuit

Fig. 3: Image showing Output Result of ASK Modulation
Circuit Diagrams
Project Components
Filed Under: 555 Timers, Electronic Projects


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.