Have you ever noticed a black magnetic stripe at the backside of our credit card? A number of thoughts run through your mind. For what purpose magnetic stripe is used? What information this stripe contains? Is the information only being read or the encoded information is copied? And, if information is saved, what could be the consequences?

Fig. 1: An Represenational Image of Automatic Identification and Data Capture (AIDC) Technology
A thought like this inspire us to take a closer look at the card technologies and the family to which they belong- Automatic Identification and Data Capture technologies (AIDC).
Answers to all these above mentioned questions are simple. The purpose for using magnetic stripe technology and in general, AIDC technologies, is to identify people or objects through machine automated process.
Now again the question arises, why are these technologies cropping up in the most routine tasks of our everyday lives?
This machine automated reading of magnetic stripe makes the job easier and, therefore, more efficient. The clerk does not have to tally the information needed, all by himself, a machine quickly does it for him. It also helps in making fraudulent IDs easier to detect. Both efficiency and fraud prevention ultimately save the business money.
What is AIDC?
Automatic identification and data capturing is a method of automatically identifying objects, collecting data about them and entering data directly into the computer system. All this process is done automatically without any human involvement. Human involvement is confined to a user scanning an AIDC equipped item which is bar coded.
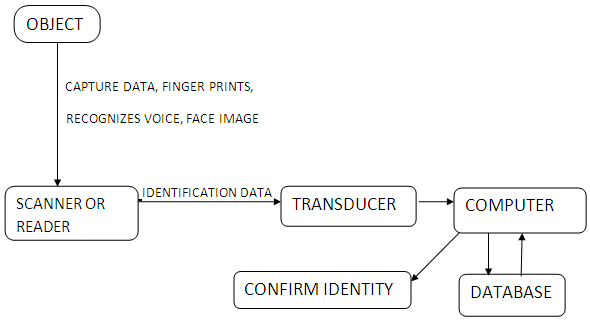
Fig. 2: Typical Block Diagram Showing Working of AIDC
The information associated with the object is called identification data. This data may be in the form of images, sounds or videos. Before feeding the data into the computer system, this data is converted into a digital file. Hence, a transducer is employed to fulfill this task i.e. to convert actual data into digital file. Now, in computer system a database is fed. The stored data file is analyzed by a computer or is compared with other files in a database to verify or to provide authentication to enter in a secured system.
AIDC technologies mainly consist of three principle components namely-
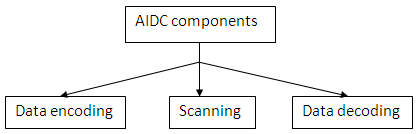
Fig. 3: Figure Showing Classification of AIDC Technology
Data encoding– alphanumeric characters are translated into the form that can be read by machine.
Machine scanning– scanner reads the encoded data and converts in electric signals.
Data decoding– electrical signals is transformed into digital data and then finally into alphanumeric characters.
AIDC Technologies:
Following are the various AIDC technologies:
· Barcodes
· Radio Frequency Identification (RFID)
· Biometrics
· Magnetic Stripes
· Optical Character Recognition (OCR)
· Smart Cards
· Voice Recognition
· Electronic Article Surveillance (EAS)
· Real Time Locating Systems (RTLS)
Barcodes & RFID
1. Barcodes:
You must have seen bar-coded items in supermarkets. There are about 250 types of barcodes that have been designed till now. They may be 1D or 2D. Those which you observed on the goods are referred to as linear barcode. Standard of these barcode are published by AIM and are currently in progress at ISO.
Barcodes consist of small images of lines (bars) and spaces affixed to retail store items, ID cards and postal mail to identify a particular product number, person or location. A barcode reader uses a laser beam that is sensitive to the reflections from the line and space thickness and variation. The reader translates information from the image to digital data and sends it to the computer for further process.

Fig. 4: Representational Image Showing Barcode Reader
2. Radio Frequency Identification (RFID):
This technology acts as the base in automated data collection, identification and analysis systems worldwide. RFID obtains information on an item without making direct contact with the item. Depending on the technology variation used, reading and writing distances can vary from few millimeters to several meters.
RFID systems comprises of three components: an antenna, a transceiver and a transponder (the tag). The application area of RFID includes livestock identification and Automated Vehicle Identification (AVI) because of its capability to track moving objects.

Fig. 5: Representational Image Showing Inside of RIFD Card
Biometrics & Magnetic Stripes
3.Biometrics:
Biometrics system consists of a scanning device or a reader, software that converts the scanned biological data, like finger prints, voice characteristics etc, into digital format and compares captured biological data with the stored data of that individual.
Application of biometric verification in corporate and public security systems, consumer electronics and point of sale is becoming increasingly common.

Fig. 6: Representational Image of Biometric Recognization
4.Magnetic Stripes:
Almost every individual carry cards like credit cards, IDs, ATM cards etc. All these cards are cropped with magnetic stripe. The technology has been with us for many years. These stripes contain information about the owner of the respective card. The information in magnetic stripes is read by magnetic stripe reader.

Fig. 7: An Image of Magnetic Stripe Reader and Card
OCR & Smart Cards
5.Optical Character Recognition (OCR):
Optical character recognition is the electronic or mechanical translation of scanned images of text that may be handwritten, typewritten or printed, into machine encoded text.
Use of OCR is to digitize documents and books, publish text on website, sort mails, and process checks and mail based payments by credit cards to computerize so that a record can be maintained in an office, instead of bulks of papers.
OCR is a field of research in pattern recognition, artificial intelligence and computer vision.

Fig. 8: Representational Image Showing Optical Character Recognition
6.Smart Cards:
A smart card, a chip card or integrated circuit card (ICC), is any pocket-sized plastic card with embedded integrated circuits. It is an electronic recording device. Most smart cards looks like a credit or debit card, but smart cards can function on at least three levels (credit-debit-personal information).
Smart cards may provide strong security authentication for single sign on (SSO) within large organizations. Information such as withdrawals, sales, and bills can be processed immediately and if/when necessary; those records can be transmitted to a central computer file updating.

Fig. 9: Representational Image Showing Smart Card with Embedded Contactless Chip and Antena
Voice Recognition, EAS & RTLS
7.Voice Recognition:
Voice or speech recognition is the ability of a machine or program to receive and interpret dictation or to understand spoken commands. Voice based security systems store a record of speech traits and patterns, which are difficult to counterfeit. Applications of voice recognition include voice user interfaces such as voice dialing, call routing, search, simple data entry, preparation of structured documents etc.
Fig. 10: Represenational Image of Voice Recognization
8.Electronic Article Surveillance (EAS):
When you go to any showroom in malls or library, you have to pass through gated area. This is where Electronic Article Identification technology is used.
EAS is a technology used to identify items as they pass through a gated area. Mainly this identification is used to alert someone of the unauthorized removal of items from a store, library or a data center. When an item is purchased, the EAS tag is deactivated. The gate is able to sense if the tag is active or de-active when the item is passed through it and sounds an alarm if necessary. Hence, theft can be countered.

Fig. 11: An Image of Electronic Article Surveillance
9.Real Time Locating Systems (RTLS):
RTLS is a wireless radio frequency solution that continuously monitors and reports real time locations of tracked resources. RTLS tags transmit IDs and status information at frequent intervals via low power radio signal to a central processor which computes the location of up to thousand of tagged assets within yards and remote sites. The result is completely automated inventory of all tagged yard equipment all the time.

Fig. 12: Simple Figure Showing Working of Real Time Locating Systems
Sensors
Sensors:
Sensors play a key role in any automation and control systems. Sensor is a device that measures a physical quantity and converts into a signal that can be easily read by the instrument used. It gives a detailed description of the given object. There are uncountable application of sensors which includes aerospace, medicine, manufacturing, robotics, machine and cars.

Fig. 13: An Image Showing Various Sensors
Newly designed sensors utilize advanced techniques making it more efficient and smaller in size. In addition to this, these sensors collect information much more than the capability of traditional sensors. Traditional sensors were wired but these newly designed sensors are wireless which adds one more key feature of such sensors.
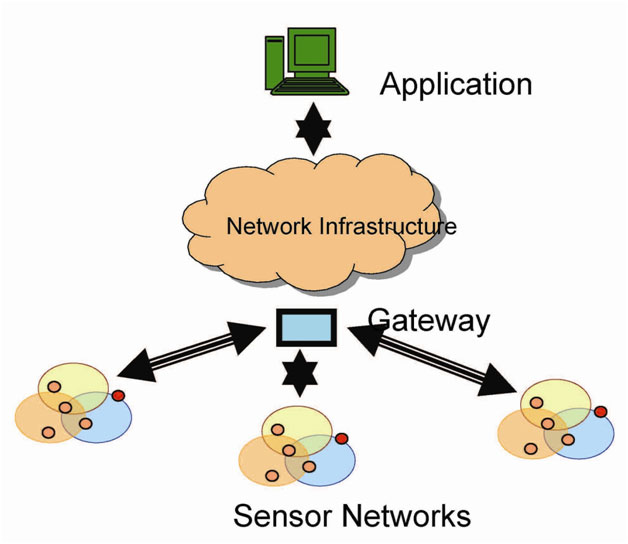
Fig. 14: Figure Showing Simple Application for Newly Designed Sensors
Benefits
Benefits of AIDC:
Through automation you can save valuable time and resources by reducing dependency on manual labor. By utilizing AIDC technologies, identification of objects or people has become much more efficient and accurate.The correctness in identification reduces the need for repeated verifications for assurance.
In industries like banking and insurance, by automating the documents, accurate processing of paperwork is achieved.
Utilizing the biometric data in AIDC system will ensure access to restricted facilities are granted to the right person and access rights are not easily transferred to other unauthorized person.
In mobile telecommunication industry, international mobile equipment identity served the purpose to protect the consumers from stolen mobile phones by disallowing stolen mobile phone to utilize mobile network services.
In retail industry, workers are often being equipped with mobile computing devices that function both as electronic readers and basic computing devices to process data before channeling it to backend system for processing.
Conclusion:
Automatic Identification and Data Capture technology comprises a diverse group of technologies and systems that capture the item related data for use within system context. It encompasses a wide range of data carrier technologies including barcodes, magnetic stripe cards, smart cards and the rapidly expanding technology such as RFID. Feature extraction technologies are also an important part of AIDC, where biometric techniques such as finger print scanning, retinal scanning, face recognition or voice recognition techniques can be used to identify individuals.
AIDC has advanced greatly over the years and it is now possible for users around the world to interact with millions of business processes and systems using AIDC equipped electronic devices. AIDC is no doubt a competitive threat to those who tend to avoid it and are unaware of its potential. AIDC is most important because it saves great amount of time when entering digital data and its accuracy which ultimately results in reliability.
Other digital data entry keyboard methods do not always work for image, video or audio data, which make AIDC the only method of entering data for further digital processing.
Filed Under: Articles


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.