At times we come across applications or situations wherein we need to generate square waves with the microcontroller. The square wave can be generated by programming a pin which toggles between 0 and 1 with a certain time delay. Alternatively, the inbuilt feature of AVR timers can be used in square wave generation. The advantage of using AVR timers in wave form generation is that the output pin toggles automatically when the timer condition are fulfilled. This article focuses on usage of AVR timer for simple square wave generation.
There are four specified pins in ATmega16 for waveform generation. Each pin can be operated by their corresponding timer only. The following table provides information about it.
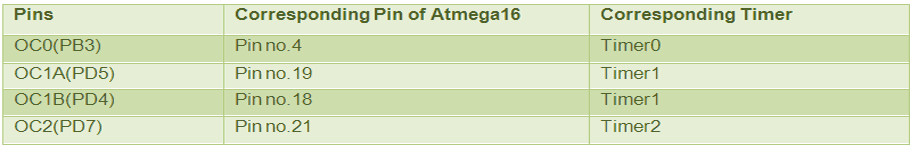
Fig. 2: Pin Numbers in ATmega16 for waveform generation
Modes in Timers:
The AVR Timers work in different modes of operation. There are following modes of operation:
1. Normal mode
2. Clear timer on Compare (CTC) match mode
3. Phase Correct PWM mode
4. Fast PWM mode
Delay generation using Normal and CTC mode has been described in previous articles. These two modes are also used in square wave form generation. Phase correct PWM and Fast PWM modes are used for PWM generation.
Wave form generation:
It is better to use CTC mode instead of Normal mode because in CTC mode, frequency can be easily adjusted. ?
When the Timer is triggered, register TCNTn counts the value constantly as timer started. Each timer has an OCRn (Output Compare Register), which is continuously compared with TCNTn register. In CTC mode whenever match occurs, OCFn (Output Compare Flag) will set to 1. If continuous wave form generation is required, OCFn must be reset again. Alternatively, if OCIEn (Output Compare interrupt) and Global interrupt flags in SREG are set, OCFn will reset automatically after interrupt execution.
In the earlier article, Timer register TCCR0 is explained. The bits WGM0 [1:0] are programmed to select waveform generation mode. The following table shows the combination of bits to select modes of operation:
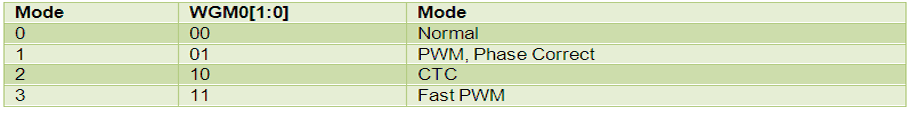
Fig. 3: Bit Value of WGM0 to select waveform generation mode in AVR
The Register TCCR0 also consists COM0 [1:0] bits. These bits are used to select functionality of OC0 pin. Following table shows function of COM 0[1:0]:

Fig. 5: Bit Value of COM0 to select functionality of OC0 pin in AVR
Objective- To generate square wave form of 5 KHz frequency by using timer 0.
Calculation for frequency

Fig. 5: Equation For Frequency Calculation of Square Wave
Programming steps:
1. Select CTC mode by programming WGM0 [1:0] bit.
2. Program COM0 [1:0] bits and select “toggle OC0 if compare match”.
3. Set OC0 (PB3) pin as output pin.
4. Set OCIE0 bit of TIMSK register.
5. Enable global interrupt by “sei ()” command.
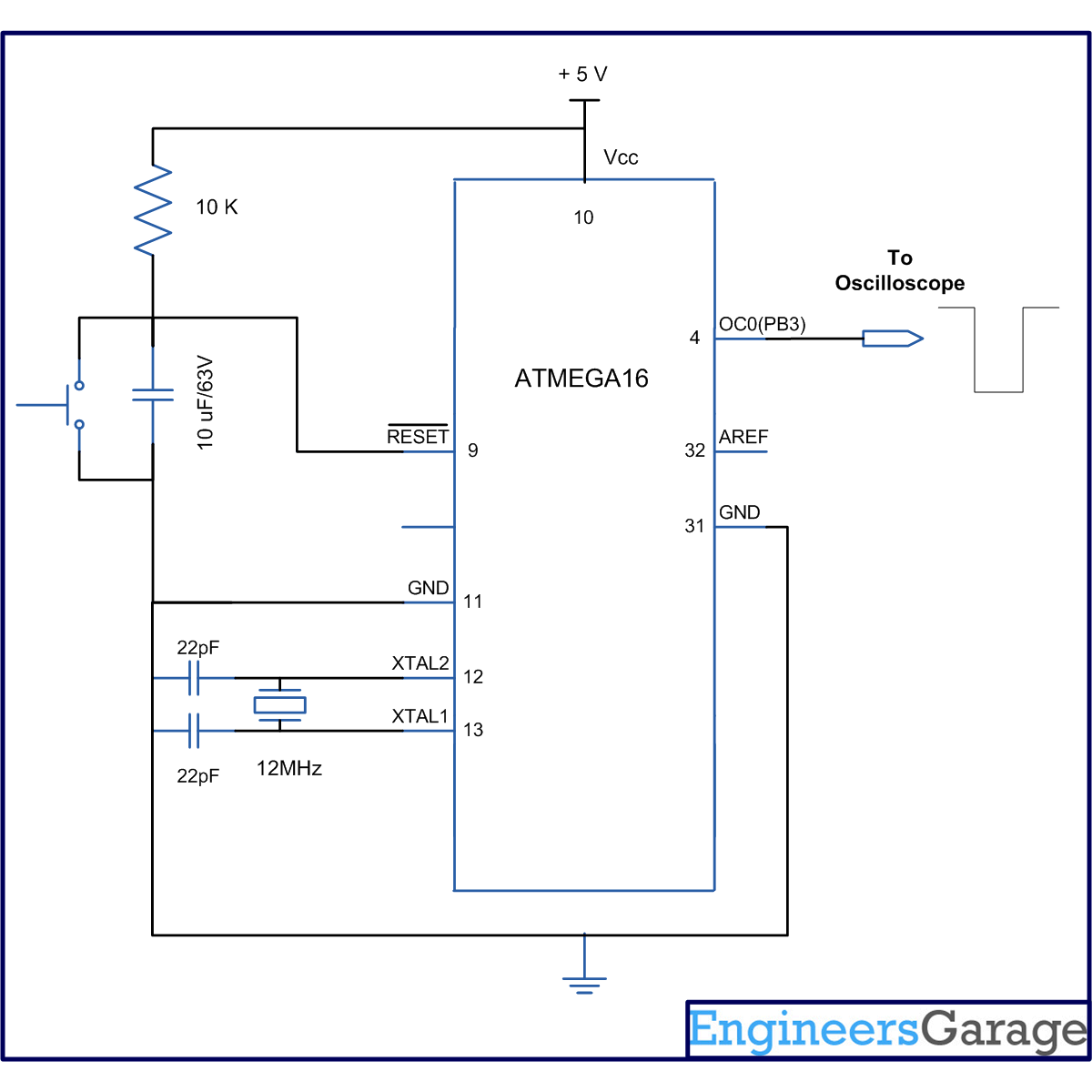
Circuit description:
The connection of ATmega16 for this experiment is shown in circuit diagram. Since timer0 is used, hence the OC0 pin is connected to C.R.O to observe wave form.
Output wave form:
The following picture shows the output wave form which is received on CRO. The measured frequency of wave is 5 KHz.
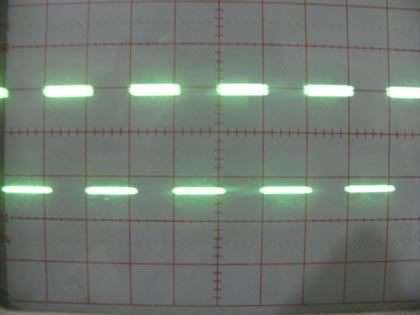
Fig. 6: Output Square waveform on CRO using AVR Timer
Project Source Code
###
// Program to Generate waveform using AVR Microcontroller (Atmega16) Timers#include<avr/io.h>#include<util/delay.h>#include<avr/interrupt.h>void t0_init(void);#define FREQ 12000000 // crsytal freqeuncy#define PRECSALER 8#define F_OUT 5000 // output frequency#define OCR0_VALUE ((((FREQ/2)/PRECSALER)/F_OUT)-1)int main(){t0_init(); // timer initializesei(); // enable global interruptswhile(1);}void t0_init(){// WGM0[1:0]= 10, for CTC mode// COM0[1:0]= 01, to toggle OC0 on compare match// CS0[2:0] =010. for prescaler 8TCCR0=(1<<WGM01)|(1<<COM00)|(1<<CS01);DDRB|=(1<<PB3); // select as output pinTIMSK|=(1<<OCIE0); //enable output compare interrupt}ISR(TIMER0_COMP_vect) // interrupt subroutine{OCR0=(uint8_t)OCR0_VALUE; //put OCR value}###
Circuit Diagrams
Project Components
Project Video
Filed Under: AVR.
Filed Under: AVR.


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.