Brain Waves: Introduction & Basic Concept
Brain wave is a common term that can be easily found in Science books/newspapers or can be heard from doctors and researchers. Have you ever thought what exactly Brain waves are? How are they produced? What is their role in day-to-day life and how do they affect us?
Let me take you through a roller coaster ride exploring Brain Waves alongside its features, types, characteristics, and other details.
What is Brain Wave?
Brain Wave is among the few technologies the world is researching these days. There are a lot of potential techniques in this field and it may solve many of our future problems.
Brain waves are definitely attachedwith and are produced in our brain. Our emotions, chemical activities, thoughts are communicated through the neurons. Neurons, which are the brain cells and building block of central nervous system, communicate with each other in the form of electrical pulses and signals. Millions of signals communicate with each other producing electrical activity in our brain. This in turn produces Brain waves around our scalp and can be measured by measuring electrical activities near the scalp. These electrical activities are called waves as these have wave type shape and nature.
Brainwaves are subject to change depending upon the changes of our thoughts and feelings and are essential because their patterns tell a lot about a person. Any imbalance in brainwaves can severely affect our emotional or neuro-physical health. Any kind of instability in the brainwaves can cause conditions like obsessive-compulsive disorder, panic attacks, explosive behaviour, and migraines and among others. There are two conditions of instability in brainwaves
• Over-arousal- This leads to sleep disorders, impulsive behaviour, spasms, anxiety disorders, anger and aggression.
Under-arousal- This leads to insomnia, depression, lack of attention span and chronic pain. Brainwaves can be detected through sensors that are placed on the scalp through a procedure known as electroencephalogram (EEG).
Present Studies
Study on Brain wave has been a major part of all the Research Institutes and Education Centers across the globe including MIT , Yale etc . Many Researchers/ companies are also working on it and it is not far when we will see brain wave technology coming as a tsunami. Few companies working in this field are Mettl, MindFlex, Emotiv, NeuroSky, etc. The EEG module of NeuroSky has brought a major breakthrough in the research and many companies working presently on Brain Waves are using the Neurosky’s EEG module for research. This EEG module contains 6 filters which are used to filter noise and extra signals produces by brains and is used to give attention, meditation, delta, theta, alpha, beta, and gamma.
Types of Brainwaves
The Brainwaves contain a spectrum of frequencies mainly between 1Hz – 100Hz. A picture of the spectrum, which I had taken while studying about the Brain wave, is shared below.
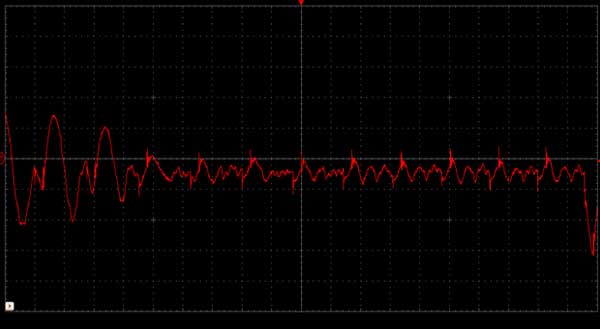
The spectrum is divided in 5 major types named as:
1. Delta Wave
2. Theta Wave
3. Alpha wave
4. Beta Wave
5. Gamma wave
Let me explain you about each of the brain wave types. All the types are inter- linked and overlapped with one another.
• DELTA WAVES
Delta Waves were first discovered in early 1900s by W. Grey Walter. He improved the work of Dr. Hans Berger’s electroencephalograph machine (EEG) to detect alpha and delta waves. Delta waves are generally produced in the thalamus or cortex region of brain. Thalamus is present in the right half of our brain. Delta activities in our body also stimulate the release of growth hormones like prolactin and GHRH.
The frequency of these waves is between 0.5 to 3 Hz. The properties of delta waves are:
o They are slowest and loudest of all the brainwaves.
o They are generated in deep sleep and in a state of deep meditation.
o Delta waves are produced when all external awareness is absent.
o They cause healing and regeneration.
o They are involved in bodily processes when we are sleeping such as heart beat, breathing, kidney and digestive functioning.
o Females generally tend to have higher delta activity than the male.
Delta Waves activity in infants is much more than adults. This can also be seen practically as infants spend much time in sleeping. Study shows that delta wave is in fact the most dominating brain wave in children till 5 years of their birth. Delta wave declines with a drop rate of 25% from 11 – 14 years and keep declining whole life span and at the age of 75, they are almost absent.
Change in nutrient metabolism, physiological damage, chemical alteration can be a cause of interruption in delta waves. Proper amount of delta waves results in less anxiety, improved sleep and headache relief.
So next time you have a headache, try to increase your DELTA WAVE.
Interesting fact:
Whenever we have an intuition regarding an incident or experience, it is generally a response from our body naturally and a result of slow wave activity in delta or theta region of Brain waves.
• THETA WAVES
The first indication of theta waves came in 1938 in a research paper published by Jung and Kornmüller. Further study on theta waves was continued by John D. Green and Arnaldo Arduini.
Scientists believe that all the spiritual connections of our body are experienced due to theta waves. Theta waves are responsible for our deep memories and visions. It is the place where we experience learning, inspiration, memory, etc.
Theta waves are basically the inner sense of body instead of external factor. It occurs mainly when we are about to sleep or when we just wake up. In theta we are in dream and it is the same place where we hold our fears, history and nightmares. It is also involved in restorative sleep and short term memory.
Theta has its benefits of helping us improve our intuition, creativity, and makes us feel more natural but at the same time excess of theta waves can bring depression and stress.
The frequency of theta waves lies between 3 to 8 Hz.
o Theta waves occur in light meditation and in sleep when we are dreaming.
o They are dominant during learning processes.
o Theta waves help us focus on signals coming from within.
o They hold our fears, nightmares and troubles.
• ALPHA WAVES
Alpha waves were discovered by Hans Berger, the famous German neurologist who is famous for his invention of EEG. Berger also discovered delta waves along with alpha. Alpha waves arise from constructive/in phase electrical activity of thalamic pacemaker cells. They originate from the occipital lobe of the brain.
Alpha comes in between the beta and theta and bridges the gap between conscious and subconscious mind. It’s associated with tranquil, pleasant and almost floating feeling and is co-related with relaxed wakefulness and creative thoughts.
It helps us calm down when needed and promotes feelings of deep relaxation. If we get stressed, a phenomenon called “alpha blocking” may occur which involves excessive beta activity and very little alpha. Essentially the beta waves “block” out the production of alpha because we become too aroused.
Alpha brainwaves are dominant during quietly flowing thoughts, and in some meditative states. Alpha waves aid overall mental coordination, calmness, alertness, mind/body integration and learning.
The frequency range of alpha waves is between 8 to 12Hz.
o They occur during the thinking process
o They signify the resting state of brain
o Alpha waves are responsible for the mental coordination and mind body integration
• BETA WAVES
Now comes the wave associated with highest attention level. Whenever our brain is actively engaged in highly participatory mental activities, it generates beta waves. These waves are of low amplitude and high frequencies. The frequency of beta waves ranges from 15 to 40 cycles a second. Generation of beta wave is a characteristic of highly engaged mind. Whenever we are in any conversation, or whenever we write, read, debate, teach, etc. we are in beta state of mind.
Beta waves are symbol of alertness, reasoning, logic and waking consciousness of ours.
While Beta brain waves are important for effective functioning throughout the day, they also can translate into stress, anxiety, and restlessness.
The beta waves are further subdivided into three bands:
• Low Beta (12-15Hz) – These brainwaves are characterized as fast, idle or musings.
• Beta (15-22Hz) – These brainwaves are defined as high engagement.
• Hi-Beta (22-38Hz) – These brainwaves are highly complex and characterize anxiety or excitement.
• GAMMA WAVES
The Gamma waves were earlier ignored in analog EEG where frequencies less than 25Hz were used. Scientist and researchers at that time thought of gamma waves as a noise. One of the early hints of Gamma waves came while recording the waves of cortex of awaked monkeys.
A very little have been known about these waves but it is very clear that these waves are used in high speed information processing and are associated with the processing of visual , auditory stimulus.
From the context of EEG, they are mostly present when the person is awake, though gamma waves are always being supported by other waves such as alpha, theta, and delta.
Gamma waves are also associated with our ability to adapt and learn. They are bound without perception for new things. Studies show that people who are mentally challenged tend to have low gamma activities.
With the frequency ranges of 38 to 42 Hz, Gamma waves have the following characteristics:
o They are fastest of all brainwaves
o They pass information at a rapid rate
o They occur in states of high activity like love and altruism
o They disappear under anesthesia.
o They have been noted in Buddhist meditation and some music experiments.
In a nutshell, we can say that the frequency of brain wave is directly proportional to the attention of the brain. For ex, lowest frequency Delta state occurs when we are in deep sleep and highest frequency Gamma State occurs when we are highly cautious.
Brain wave sensors
As per my internet search, there are many commercial sensors available in the market for hobbyists. Let us have a look at few famous and worldwide used sensors and analyze them.
1. Official Headsets from Neurosky – Neurosky is all up with a collection of EEG Headsets ranging from $80 – $150. These modules can provide us Meditation/Attention values, EEG signals power band values and raw wave data also. It communicates wirelessly and neurosky provides free developer tools also. It is a good option as per present technicalities.
2. Open EEG – Open EEG means building your own EEG module from scratch. This method is more complex and expensive as we need to build everything from starting including filters, analyser, etc. It adds up the development cost and incurs around $200.
3. Force Trainer Ball Game – Neurosky provides their chips to Force Trainer and they are cheap too. These are easily available at the cost of $80. Though Force trainer is cheap but it does not allow us to access raw EEG data. Also, we cannot extract power band values from Force Trainer.
4. Mindflex Ball Game – Neurosky also provides their chips to Mindflex and we can say that Mindflex, ForceBall, Neurosky all have nearly same silicon chip with different firmwares. Mindflex allow us to access raw EEG values and also EEG power band values in the range of $100.
5. Emotiv Brainwave sensor – Emotiv sensors are among the most famous brain wave sensors and are used for research applications worldwide. They provide us 10 – 12 EEG channels from nearly 15 – 20 locations of our brain. They range from $300 – $500. These sensor interpret 3 mental states, 13 conscious thoughts, facial expression, head movements (by using gyroscope). Emotiv also provides Bluetooth interfacing.
6. MyndPlay BrainBand : MyndPlay provides us data of 8 EEG channels with 12 bit ADC resolution . MyndPlay senses data from only one brain location with single electrode and costs around $158. Bluetooth interfacing and SDK is provided by the MyndPlay and they use some conductive gel for ear clip .
There are many more sensors like AuroraDream Band , Melon Headband , Hi Brain, iFocus Band, Mindwave, MindSet, Mindball, Xwave headset, Muse, OPenBCI all ranging from $60 – $400 and provides different features, different interfacing and performance. You can choose according to your requirement and budget. Also, please note that the prices I have mentioned are according to my search at some particular time. You may find variations in the price when you search for them. Keep surfing internet for their latest prices and availability.
For our study I have chosen Mindflex Brain wave sensor as I found it bit less complex, it senses data from one location with one electrode exactly above the right eye. Moreover it’s suitable as per our budget (less than $100) and it provides raw EEG data and power band values which is the prime requirement for our study.
Mindflex Sensor Detailing
Though there is complete gamewhich we need to purchase but presently we are only dealing with the HeadBand part of the game. So here is the partlist of the parts present in Mindflex Brainwave HeadBand.
1. ForeHead Sensor – A small circular 40mm radius Stainless Alloy electrode to sensor our Brain Wave signals coming of our scalp or forehead. It is directly connected with the main processing board of Mindflex.
2. Ear Clips – There are two ear clips in the MindFlex headband. My assumption is that these ear clips are also made of the same material of which the electrode is i.e. Stainless Alloy. These are connected to our ears, while we measure Brain waves, providing EEG shielding and a reference to the processor inside the circuit.
3. On/Off Switch – This is a simple two way ON/OFF switch to make the headband processing unit ON or OFF. This switch will enable if wireless data is being transmitted or not.
4. Power Light – A small red colored LED is used as a power indicator. This LED will indicate if proper power is being provided to the board or not. There are two reasons when the LED is off. Either the switch is OFF and there is no supply to the board, or the switch is ON but there is insufficient power left in the battery.
5. Adjustable Buckle – This adjustable Buckle is to make sure that the user comfortably wears the HeadBand. This is also to make sure that the band is such tight the electrode/sensor is in direct contact with human forehead.
These 5 components can be easily seen from outside.
Now for our Study, we have opened the Brain wave sensor. There are two closed plastic rectangular shaped box parts in the sensor. Lets us open both the parts and see one by one what is inside them.

So, this is the interior of first part. There are three 1.5V AAA alkaline batteries for the power. These three batteries constitute a total of 4.5 V and supplies power to our main board.

Now lets us come to the main board part. Let me open it and see what is inside this part. Above picture is what we get to see inside the second part.

This particular board is the NeuroSky EEG chip, used by MindFlex for processing.
Now the processed data from the EEG chip goes to the micro controller and later the micro controller sends the wireless data at 2.4 Ghz. This frequency is used because it is the free RF wireless range.
Except the NeuroSky board, there is the main board of Mindflex, which have the micro controller with 12 Mhz crystal oscillator. Below the PCB there is RF antenna for wireless transmission. Also, there is glue-like non conductive substance put on ICs to prevent short circuit or accidental contact.
Many a times when the manufacturer does not put the IC in thermal protection kit, which is the black outer body of any IC, he just places the wafer on the PCB which is many times anti static is nature. Still, I will not play or touch with this part and let it be like it is.
In the next article in the series, we will see more about the Neurosky EEG chip in detail. Stay tuned to know more about it.
Filed Under: Articles, Brainwave, Tutorials


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.