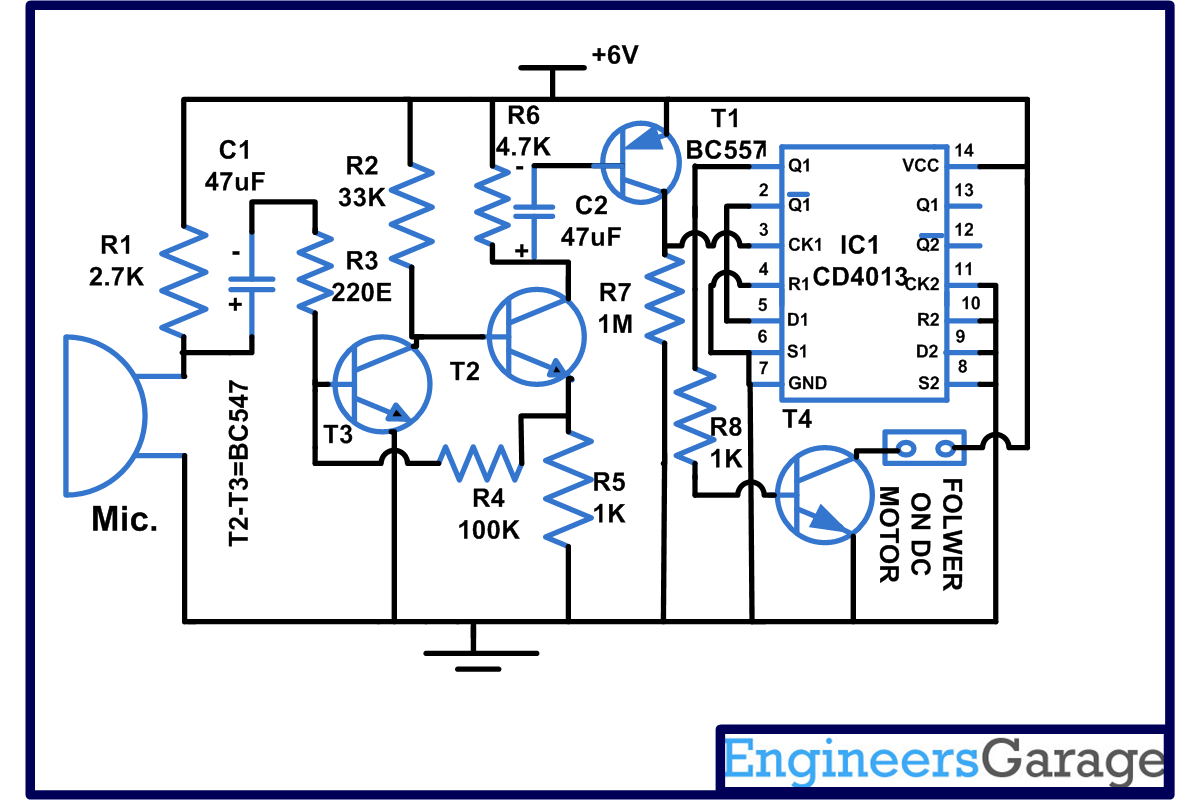
In this circuit when you clap or whistle in front of a Mic, a flower connected in the output starts rotating. For making this sound sensor circuit, we have used CD4013 IC, DC motor and few more components. IC CD4013 contains two independent D type flip flop which exist in one of two states and can store information. Each module is further equipped with a group of pin outs assigned as data, set, reset, clock input and a couple of complementary outputs Q and
To put in simple words, this circuit describes movement of a DC motor based on the voice sensing capabilities provided to it through a microphone. The DC motor can be accessorized using a variety of attachments such a miniature flower (in this case), a small fan etc. Accessorizing can get more diverse when power of DC motor is increased but this might make the circuit bulkier in terms of power requirements and power handling capacity of the IC might get tested too.
CD 4013 comes in 14 pin dual inline package. To understand the working of circuit first we have to understand its pin lay out.

Fig. 1: Pin Diagram Of CD 4013 IC
1. Pin no1, 2, 13 and 12 are complimentary outputs. This set of output changes state while setting and resetting the IC producing opposite logic level at any instant when operated in bistable mode.
2. Pin 5 and 9 are called Data pins and are generally connected to one of the outputs for the purpose of lengthening the applied input clock for square wave. For other waves, they may be terminated to any other logic level or they may be connected either connected to supply or to the ground of the circuit. In this circuit we have connected {C}{C}{C}{C}{C}{C}{C}{C}{C}{C}
and Data pin 5 together.
3. Pin 3 and 11 are called as Clock input. These are input pins which are used to receive clock signals generally in the form of square wave. These signals may be provided by the transistor in the form of astable multivibrator or with the help of NAND or NOR gate. This input will produce effect on any of the output pins, the other being connected to Data pin as explained above. In our circuit we are providing clock signal through transistor circuit.
4. Pin 4, 6 and 10, 8 are called as set and reset pins. Whenever any of the pin goes high, we will get the output. When set and reset are low, output shows that data at input at the time of last low to high clock transition means output is held till the next transition. For safety, these are also assigned to a logic level generally they are grounded with a high value resistor. Once this is done, the input can be made to alternately respond to positive peak pulses to toggle the logic stage of the Q and {C}{C}{C}{C}{C}{C}{C}{C}{C}{C}
output alternately.
5. Pin 14 and 7 are called supply and ground pin respectively. Pin 14 receives the positive supply input which should not exceed 15V otherwise it will destroy the IC and pin 7 is ground or connected to negative supply input of IC.
Now you can also see this in truth table-
|
CLK |
D |
R |
S |
Q |
Q- |
|
low-hi |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
|
Low-high |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
|
Hi- low |
X |
0 |
0 |
Q |
Q |
|
X |
X |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
|
X |
X |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
|
X |
X |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
Now working of this sound sensing circuit is very simple: when you clap in front of the Mic, signals are amplified by the transistor and clock input of the IC makes its transition from low to high. We will receive a high at output Q, transistor connected to it will conduct and a DC motor connected to it will start rotating. At this time we will receive low at{C}{C}{C}{C}{C}{C}{C}{C}{C}{C}
. We have also connected pin 2 and 5 together for the purpose of lengthening the clock pulse as explained above. Pins 9, 10, 11 are also connected to ground so that will not produce any false pulse.
Circuit Diagrams
Project Components
Filed Under: Electronic Projects


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.