DS12C887 is a real time clock (RTC) IC from Dallas Semiconductors. The RTCs provide precise time and date information. This article explains the making of a digital clock with alarm setting functionalities. RTC has been interfaced with AT89C51 to perform desired operations. This project is an improvement over Digital clock using RTC DS12C887 and 8051 microcontroller (AT89C51) with time set and has the alarm setting function also. The alarm setting function allows user to set the alarm. The clock time is displayed on the LCD. The free source code for the program is available in C.
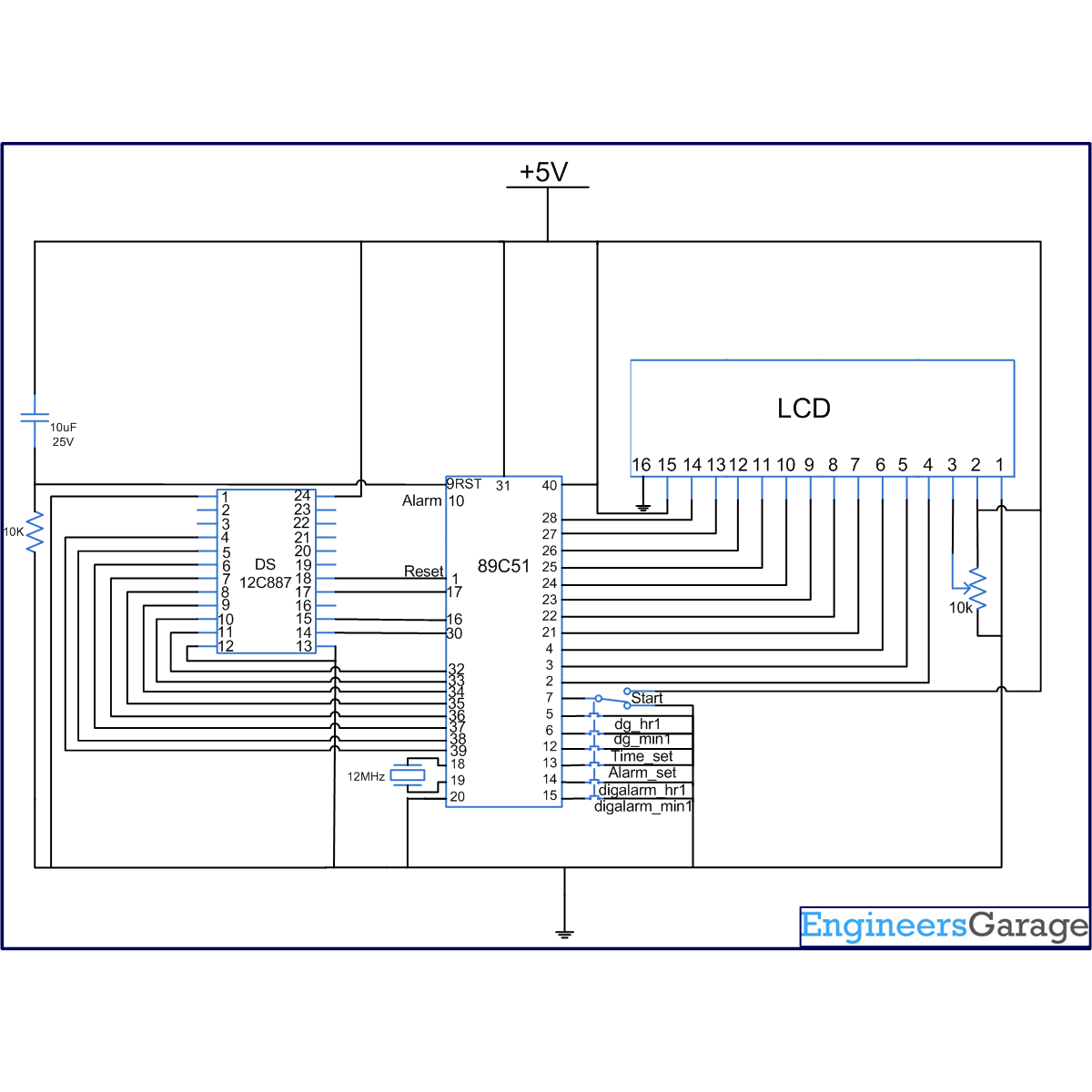
The circuit for interfacing the RTC and 16×2 LCD with the microcontroller 8051 is shown in the circuit diagram. Port P2 is set as data port for LCD to send the data on the LCD while port P0 is set as data port for the RTC DS12C887. This is used to extract the time, date and other information from the RTC. The pins of port P1 and P3 of the controller AT89C51 are used to provide the input signals for setting the time, alarm etc. They also provide control signals for the RTC and the LCD.
Project Source Code
###
//Program for Digital Clock using RTC DS12C887 & 8051 microcontroller (AT89C51) with alarm set function /*24 hr clock set p3^3=0,then start=0 them set time by dig_hr1 & dig_min1, then remove p3^3 & start */ #include<reg51.h> #include<absacc.h> #define dataport P2 // Dataport for LCD #define port P1 #define alarm P3 sbit reset = port^0; sbit rs = port^1; sbit rw = port^2; sbit e = port^3; sbit dig_hr1=port^4; sbit dig_min1=port^5; sbit digalarm_hr1=alarm^4; sbit digalarm_min1=alarm^5; sbit alarmport=alarm^0; sbit start=port^6; int min1=0,hr1=0,alarmmin1=0,alarmhr1=0; int min0=60,hr0=25; unsigned char sec0=60,min00,hr00,hr,min,sec,alarmmin,alarmhr; void delay(unsigned int msec ) { int i ,j ; for(i=0;i<msec;i++) for(j=0; j<1275; j++); } unsigned char num(int d) { switch(d) { case 0:{ return 0x00; break; } case 1:{ return 0x01; break; } case 2:{ return 0x02; break; } case 3:{ return 0x03; break; } case 4:{ return 0x04; break; } case 5:{ return 0x05; break; } case 6:{ return 0x06; break; } case 7:{ return 0x07; break; } case 8:{ return 0x08; break; } case 9:{ return 0x09; break; } case 10:{ return 0x10; break; } case 11:{ return 0x11; break; } case 12:{ return 0x12; break; } case 13:{ return 0x13; break; } case 14:{ return 0x14; break; } case 15:{ return 0x15; break; } case 16:{ return 0x16; break; } case 17:{ return 0x17; break; } case 18:{ return 0x18; break; } case 19:{ return 0x19; break; } case 20:{ return 0x20; break; } case 21:{ return 0x21; break; } case 22:{ return 0x22; break; } case 23:{ return 0x23; break; } case 24:{ return 0x24; break; } case 25:{ return 0x25; break; } case 26:{ return 0x26; break; } case 27:{ return 0x27; break; } case 28:{ return 0x28; break; } case 29:{ return 0x29; break; } case 30:{ return 0x30; break; } case 31:{ return 0x31; break; } case 32:{ return 0x32; break; } case 33:{ return 0x33; break; } case 34:{ return 0x34; break; } case 35:{ return 0x35; break; } case 36:{ return 0x36; break; } case 37:{ return 0x37; break; } case 38:{ return 0x38; break; } case 39:{ return 0x39; break; } case 40:{ return 0x40; break; } case 41:{ return 0x41; break; } case 42:{ return 0x42; break; } case 43:{ return 0x43; break; } case 44:{ return 0x44; break; } case 45:{ return 0x45; break; } case 46:{ return 0x46; break; } case 47:{ return 0x47; break; } case 48:{ return 0x48; break; } case 49:{ return 0x49; break; } case 50:{ return 0x50; break; } case 51:{ return 0x51; break; } case 52:{ return 0x52; break; } case 53:{ return 0x53; break; } case 54:{ return 0x54; break; } case 55:{ return 0x55; break; } case 56:{ return 0x56; break; } case 57:{ return 0x57; break; } case 58:{ return 0x58; break; } case 59:{ return 0x59; break; } } } void lcd_cmd(unsigned char item) { dataport = item; rs= 0; rw=0; e=1; delay(1); e=0; return; } // DATA SENDING FUNCTION void lcd_data(unsigned char item) { dataport = item; rs= 1; rw=0; e=1; delay(1); e=0; return; } void lcd_data_string(unsigned char *str) { int i=0; while(str[i]!='�') { lcd_data(str[i]); i++; delay(1); } return; } void lcd_data_int(int time_val) { int int_amt; int_amt=time_val/10; lcd_data(int_amt+48); int_amt=time_val%10; lcd_data(int_amt+48); } void lcd() // Function to initialize LCD { lcd_cmd(0x38); delay(5); lcd_cmd(0x0C); delay(5); lcd_cmd(0x80); delay(5); } void set_rtc_time( int q) { XBYTE[10]=0x20; XBYTE[11]=0x82; XBYTE[0]=0x00; if(q==1) { XBYTE[2]=min; XBYTE[4]=hr; } XBYTE[7]=0x01; XBYTE[8]=0x01; XBYTE[9]=0x10; XBYTE[1]=0xff; if(q==2) { XBYTE[3]=alarmmin; XBYTE[5]=alarmhr; } XBYTE[11]=0x22; } //function to set hours void set_hr1(char a,int b) { if(b==1) { hr1++; if(hr1>23) hr1=0; lcd_cmd(a); lcd_data_int(hr1); lcd_data(':'); } else { alarmhr1++; if(alarmhr1>23) alarmhr1=0; lcd_cmd(a); lcd_data_int(alarmhr1); lcd_data(':'); } } //function to set minute void set_min1(char a,int b) { if(b==1) { min1++; if(min1>59) min1=0; lcd_cmd(a); lcd_data_int(min1); } else { alarmmin1++; if(alarmmin1>59) alarmmin1=0; lcd_cmd(a); lcd_data_int(alarmmin1); } } void set_time() interrupt 0 { reset=0; lcd_cmd(0x01); if(start==0) { lcd_data_string("SET TIME"); lcd_cmd(0x8A); lcd_data_int(hr1); lcd_data(':'); lcd_data_int(min1); lcd_cmd(0xc0); while(start==0) { delay(10); if(dig_hr1==0) set_hr1(0X8a,1); if(dig_min1==0) set_min1(0X8d,1); } } lcd_cmd(0x01); hr=num(hr1); min=num(min1); set_rtc_time(1); lcd_cmd(0x01); lcd_cmd(0x80); lcd_data_string("TIME:"); hr0=25; min0=60; } void set_alarm() interrupt 2 // Time set function { reset=0; lcd_cmd(0x01); if(start==0) { lcd_data_string("SET ALARM"); lcd_cmd(0x8b); lcd_data_int(alarmhr1); lcd_data(':'); lcd_data_int(alarmmin1); while(start==0) { delay(10); if(digalarm_hr1==0) set_hr1(0X8b,2); if(digalarm_min1==0) set_min1(0X8e,2); } } lcd_cmd(0x01); alarmhr=num(alarmhr1); alarmmin=num(alarmmin1); set_rtc_time(2); lcd_cmd(0x01); lcd_cmd(0x80); lcd_data_string("TIME:"); hr0=25; min0=60; } bcdconv(unsigned char mybyte) { unsigned char x,y; x= mybyte & 0x0F; x=x | 0x30; y= mybyte & 0xF0; y=y>>4; y=y | 0x30; lcd_data(y); lcd_data(x); } void alarm1() // Function to check alarm { reset=0; reset=1; lcd_cmd(0xc3); lcd_data_string("alarm"); delay(100); lcd_cmd(0xc3); lcd_data_string(" "); } void read_rtc_display() //Function to read RTC { hr00=num(hr0); min00=num(min0); XBYTE[11]=0x22; hr=XBYTE[4]; lcd_cmd(0x87); min=XBYTE[2]; sec=XBYTE[0]; if(hr!=hr00) { lcd_cmd(0X87); bcdconv(hr); lcd_data(':'); hr0=hr; } if(min!=min00) { lcd_cmd(0X8A); bcdconv(min); lcd_data(':'); min0=min; } if(sec!=sec0) { lcd_cmd(0x8D); bcdconv(sec); sec0=sec; } } void main() { reset=1; lcd(); XBYTE[10]=0x20; lcd_cmd(0x01); IE=0x85; lcd_cmd(0x80); lcd_data_string("TIME:"); while(1) { read_rtc_display(); if(alarmhr ==hr && alarmmin ==min ) { alarm1(); } } }###
Circuit Diagrams
Project Components
Project Video
Filed Under: 8051 Microcontroller.
Filed Under: 8051 Microcontroller.


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.