It’s time and again now that my buzzing fingers do not stop boasting about this very internet-prevalence to this day. Who, in his best dream would have ever thought that he would lend data from a remote cloud one day as he does water and electricity from the supply line? Goodness! It’s pragmatically visible now..!! Cloud Computing is nothing less than a dream come true with the evolution of Information and Communication Technology (ICT). Its rightly said; “Every cloud has a silver lining”, but wait, here we have a silver cloud available at our service 24 x 7. Cloud Computing is the fifth generation of computing after Mainframe, Personal computer, Client-Server computing and the Web. A cloud is a model for enabling convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources.

Fig. 1: A Representational Image of Cloud Computing Technology
What is Cloud Computing technology?
Cloud computing is a technology that puts your entire computing infrastructure both hardware and software, applications, etc online. It uses internet and remote, central servers to maintain data and applications. Gmail, Yahoo mail, Facebook, Hotmail, Orkut, etc are all the most basic and widely used examples of cloud computing. One does not need his own PC or laptop to check some stored mail/data/photos in the mailbox but any computer with an internet connection since the data is stored with the mail service provider on a remote cloud. The technology in essence is a geographical shift in the location of our data from personal computers to a centralized server or ‘cloud’. Typically, cloud services charges its customers on usage basis. Hence it is also called Software as a Service (SaaS). It aims to provide infrastructure and resources online in order to serve its clients; Dynamism, Abstraction and Resource Sharing.
History and Evolution:
The term “cloud” was actually derived from telephony. The telecommunication companies offered Virtual Private Network with good quality at cheaper rates. The symbol of the cloud represented the demarcation point which was the sole responsibility of the provider. Cloud computing manages the servers and network infrastructure. In 1977, Ramnath Chellappa first coined the word cloud computing.
It is actually difficult to quote the exact history of cloud computing, it being a concept evolved from many other prevalent techniques of the digital world. It has essentially evolved from various computing technologies like grid computing, utility computing, parallel computing, and virtualization. The most recent development of cloud computing has evolved from the Web2.0 technology which caters to web applications that facilitate participatory information sharing, interoperability, user-centered design etc. Examples of Web 2.0 include wikis, blogs, social networking sites, video sharing sites etc.
The evolution of cloud computing can be bifurcated into three basic phases:
The Idea Phase – This phase incepted in the early 1960s with the emergence of utility and grid computing and lasted till pre internet bubble era.
- The Pre-cloud Phase – The pre-cloud phase originated in the 1999 and extended to 2006. In this phase internet as the mechanism to provide Application as Service got developed.
- The Cloud Phase – The much talked about real cloud phase started in the year 2007 when The classification of IaaS, PaaS and SaaS got formalized. The history of cloud computing has witnessed some very interesting breakthroughs launched by some of the leading computer/web organizations of the world. The following picture exhibits the significant applications which triggered the growth of cloud computing.

Fig. 2: A Figure Illustrating Significant Applications of Cloud Computing Technology
This discussion flouts without firm mention to Amazon’s S3 and EC2. Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) is an online storage web service which provides storage through web service interface. It was launched in March 2006. Similarly, Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) is a web service that provides resizable compute capacity in the cloud. It is designed to make web-scale computing easier for developers.Amazon played a major in the field of cloud computing. In 2008, Eucalyptus emerged as the first open-source AWS, API-compatible platform for deploying private clouds. The bourgeoning cloud computing technology fetched further hype when leaders like Google, IBM and Microsoft entered the arena. IBM’s ‘Blue Cloud, Google online ‘App Engine’ (for ex. online spreadsheets), Microsoft’s Azure and Apple’s icloud are some other energy boosters.
Varieties of Cloud Computing
Varieties of Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing is classified under various heads. On the basis of the type of usage or the location, it is classified under following heads:
1. Public Cloud – When a cloud is available to the general public on a pay-per-use basis, that cloud is called a ‘Public Cloud’. The customer has no visibility over the location of the cloud computing infrastructure. It is based on the standard cloud computing model. Examples of public cloud are Amazon EC2, Windows Azure service platform, IBM’s Blue cloud.
2. Private Cloud – The internal datacenters of business organizations which are not made available to the general public are termed as private cloud. As the name suggests, the private cloud is dedicated to the customer itself. These are more secured as compared to public clouds. It uses the technology of virtualization. A private cloud is hosted on the company’s own servers. Example of private cloud technology is Eucalyptus and VMware.
3. Hybrid Cloud – A combination of private and public cloud is called a hybrid cloud. Companies use their own infrastructure for normal usage and hire the cloud at events of heavy network traffic or high data load.
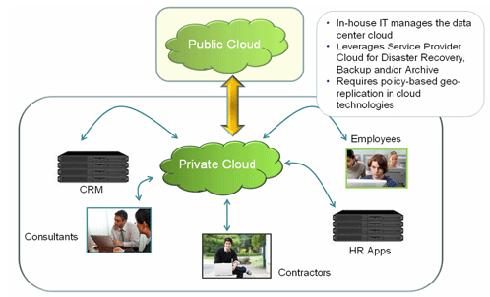
Fig. 3: A Diagram Illustrating a Public Cloud and Private Cloud
4. Community Cloud – In community cloud computing the cloud is shared between organizations of the same community or group. For example, government agencies of the same city can share the same cloud meant for the city however, agencies of other cities work on different cloud.
Cloud computing offers a wide range of applications and services to its users. Cloud services are offered on demand to the users on pay per use basis. The services offered ranges from processing and application integration and storage to communication services. The next classification of cloud computing is based on the type of service offered. These services can also be observed as different layers of cloud computing.
1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) – This is the primary and the bottom most layer of the cloud stack. This layer includes servers, networks and hardware appliance delivered as either infrastructure web services (for ex. AWS) or ‘cloud centers’ (for ex. Go Grid). The cloud provides an infrastructure including platforms (virtual), networks etc, on which applications can be placed. The consumers of IaaS could be system developers, system administrators, IT managers who deal in creating, installing, managing and monitoring IT infrastructure operations.
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS) – This being the second layer of the stack provides clouds platforms. At this layer, the cloud facilitates hardware resources, typically virtual machines which can be loaded with users’ OS and software. This environment contains development language or framework like Java, .Net, Python, Ruby on Rails, etc. For example Google App Engine supports the Python framework, Microsoft Azure runs on .Net framework. PaaS consumers can use the tools and execution resources provided by cloud providers for developing, testing, deploying and managing applications serviced in a cloud environment.
3. Software as a Service (SaaS) – This is the top most layer of cloud stack. It refers to services that directly used by end users. At this layer, cloud provides software applications. You don’t need to buy any software to use; instead of you can just use this from the SaaS provider’s server through your browser. And you have to pay for the software as you make use of. The software applications are deployed as hosted services which the users can access via a network connecting SaaS providers and consumers.
Cloud Computing Framework
Cloud Computing Framework
Let us now take a glimpse as to what all comprises the cloud computing environment. The cloud computing environment is managed by five major performers or actors namely
· Cloud consumer; consumers (consumers, organizations) at the front end.
· Cloud provider; cloud service providers.
· Cloud auditor; party that can conduct independent assessment of cloud services, information system operations, performance, and security of the cloud implementation.
· Cloud broker; party that negotiates relationships between cloud consumers and providers.
· Cloud carrier; intermediary for the transport of services between consumers and providers.
Acting and co-coordinating with each other these perform work in a three-layered framework as shown in the picture below:
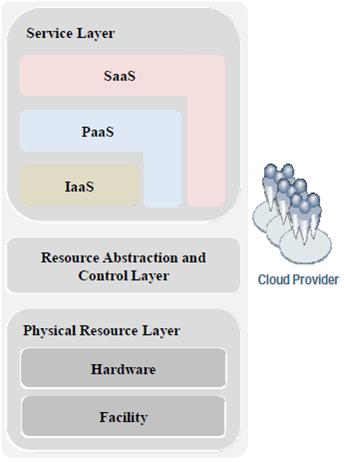
Fig. 4: A Diagram Illustrating Three-Layered Cloud Computing Framework
The topmost layer is the service layer where the consumers consumes all the services being offered to them; SaaS, PaaS, IaaS. The middle layer is the resource abstraction and control layer. With this layer the consumers are provided with system elements to manage access to physical computing resources through software abstraction. The commonly used technology at this layer is the virtual machine technology. The lowest layer in the cloud computing framework is the physical resource layer which contains all the physical computing resources such as computers (CPU and memory), networks (routers, firewalls, switches, network links and interfaces), storage components like hard disk, power, etc.
Applications
Applications
Cloud computing can perform all operations possible on a normal computer of supplemented with the right middleware at the right time. This makes it a judicious technology with myriad applications.
- Unlimited access of data and applications from any part of the world.
- A cloud computing system reduces your cost of hardware. You can enjoy the access to fastest speed and processing without actually purchasing this hardware on your own. Moreover, no issues with the limited memory on your hard drive or flash drive. The cloud computing system manages it all.
- Cloud computing systems provide the organization to access the computer applications. The company needs to pay a metered fee to a cloud computing company instead of purchasing set of software licenses for each employee.
- Data back-up on the cloud
- Google’s new chrome OS has used the concept of cloud computing, wherein users will be able to store their data online which can further be accessed and recovered from anywhere in the world from their cloud. It is integrated with applications like Google Docs, Google Calendar, Google Weather, Google Calculator, etc.
- Microsoft also headed the league with the launch of Windows Azure in 2009; an Operating System solely designed to allow developers to provide users with “Cloud Computing” technology and products to use, on the fly.
- icloud is a cloud storage and cloud computing service introduced by Apple Inc. on June 6, 2011. It allows users to store data such as music files, videos etc on remote clouds (remote servers) which can later be downloaded into multiple Apple devices like iphones, ipads, iphones, and computers running Mac OS or Microsoft Windows.
Filed Under: Articles


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.