In this tutorial, I will explain how server-client communication uses TCP/IP. I have already explained about socket and How to create Socket in Linux. Before explanation, let’s see some basic views of terminology.
Three main things are needed to establish connection between server-client models:
1) Transport protocol (TCP or UDP)
2) Socket
3) IP address and port
Transport protocol (TCP)
TCP is a connection oriented protocol which stands for transfer control protocol. It is a reliable and secure protocol. In TCP, the receiver can generate the acknowledgement of received packet so sender (client) does need to wait for the acknowledgement and if the back response doesn’t come or any packet error is generated, it will resend to the client.
Socket
The socket is end point connection for communication between two machines. It is like data connectivity path between two wireless terminals. The socket is required at both sides of server and client. You can refer to the tutorial socket and How to create socket in Linux.
IP address and port
IP address is a unique numerical address of each computer and device. It plays an important role in networking domain with Internet protocol. In server – client model, the server needs to know about which device is connected with it and with whom server establishes the connection. IP address plays an important role in communication between server-client models.
In terms of networking, the port is the location where information is sent. Various protocols assign a different port number. The specific port number is required to communicate between server-client according to which protocol is used.
Let’s check how to get user’s IP address. Enter the following command from command terminal:
ifconfig
It displays network information like address, data packet etc. Be sure which type of Internet connection is in your system.
The IP address of the system is located by “inet addr”. It is your system IP address.
For example, inet addr: xxx.xx.xx.xx
Here, x represents numerical value.
Server – Client Communication using TCP/IP
Server-client model is communication model for sharing the resource and provides the service to different machines. Server is the main system which provides the resources and different kind of services when client requests to use it.
Let’s see, server –client communication through socket programming using TCP/IP. I thought you know the basic C programming and socket. Kindly refer to the tutorial socket and How to create socket in Linux before learning this tutorial.

Fig. 1: Overview of Server – Client Communication using TCP/IP
Server-client communication using TCP/IP
The following tasks are done at client side:
· Create a socket for communication
· Configure TCP protocol with IP address of server and port number
· Connect with server through socket
· Wait for acknowledgement from server
· Send message to the server
· Receive message from server
The following tasks are done at server side:
· Create a socket for communication
· Bind the local port and connection address
· Configure TCP protocol with port number
· Listen for client connection
· Accept connection from client
· Send Acknowledgement
· Receive message from client
· Send message to the client
Here I have written two individual programs, one for sever side and one for client side. We need a computer with Linux environment. But do not worry; you can communicate with the only single system.
Client side program:
//*********************************TCP_client.c********************************//
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <netdb.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <errno.h>
int main()
{
char sendMessage[512],receiveMessage[512];
int sock, result;
struct hostent *host;
struct sockaddr_in serverAdd;
host = gethostbyname(“xxx.xx.xx.xx”);
if ((sock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0)) == -1)
{
perror(“Socket creation failed”);
exit(1);
}
serverAdd.sin_family = AF_INET;
serverAdd.sin_port = htons(5000);
serverAdd.sin_addr = *((struct in_addr *)host->h_addr);
bzero(&(serverAdd.sin_zero),8);
if (connect(sock, (struct sockaddr *)&serverAdd, sizeof(struct sockaddr)) == -1)
{
perror(“Connection failed”);
exit(1);
}
while(1)
{
result = recv(sock,receiveMessage,1024,0);
receiveMessage[result] = ”;
printf(“nRecieved Message: %s ” , receiveMessage);
printf(“nSEND The message: “);
fgets(sendMessage,512,stdin);
send(sock,sendMessage,strlen(sendMessage), 0);
}
return 0;
}
//*********************************TCP_client.c********************************//
Server side program:
//*********************************TCP_server.c*******************************//
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <errno.h>
int main()
{
char sendMessage[1024] ,receiveMessage[1024];
int sock, connected, result;
struct sockaddr_in serverAdd, clientAdd;
int length;
if ((sock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0)) == -1)
{
perror(“Socket creation is failed”);
exit(1);
}
if (setsockopt(sock,SOL_SOCKET,SO_REUSEADDR,&1,sizeof(int)) == -1)
{
perror(“Set socket option”);
exit(1);
}
serverAdd.sin_family = AF_INET;
serverAdd.sin_port = htons(5000);
serverAdd.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY;
bzero(&(serverAdd.sin_zero),8);
if (bind(sock, (struct sockaddr *)&serverAdd, sizeof(struct sockaddr))== -1)
{
perror(“Unable to bind”);
exit(1);
}
if (listen(sock, 3) == -1)
{
perror(“Listen”);
exit(1);
}
printf(“TCPServer Waiting for client connectionn”);
fflush(stdout);
while(1)
{
length = sizeof(struct sockaddr_in);
connected = accept(sock,(struct sockaddr *)&clientAdd,&length);
printf(“Server is connected with IP address %s and port %d n”,inet_ntoa(clientAdd.sin_addr),ntohs(clientAdd.sin_port));
while (1)
{
printf(” SEND the message : “);
fgets(sendMessage,100,stdin);
send(connected, sendMessage,strlen(sendMessage), 0);
result = recv(connected,receiveMessage,512,0);
receiveMessage[result] = ”;
printf(“Received message : %s n” , receiveMessage);
fflush(stdout);
}
}
return 0;
}
//*********************************TCP_server.c*******************************//
Save the file in directory and compile it. After successful compilation, run the executable file from command terminal. You may refer to the tutorial How to make first C program in Linux if you are not aware of compilation and execution process.
Note: Write down your server’s IP address in place of “xxx.xxx.xx.xx.” in client side program.
Run server –client program on the same system
You can run the server-client program on the same machine. First find your client PC’s IP address as I described above. Now, if you want to run it on same PC same IP is entered in the source code of client. Save both the source code of server and client on the same PC.
Open the command terminal and run first server side executable file. Server side code is in running mode. Do not interrupt from code. Open another command terminal and run client side executable file.
Note: If you do not run server-side code and try to run first client side code, connection refused error will come.
See the following image for understanding:
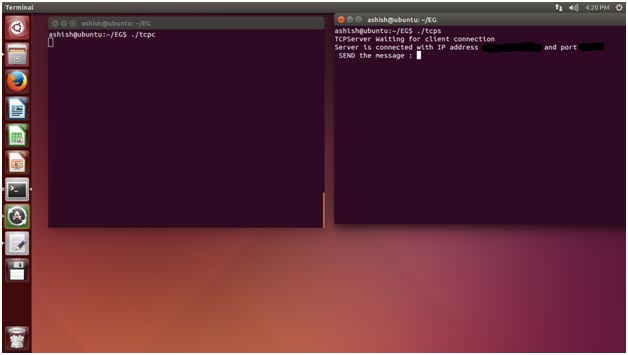
Fig. 2: Screenshot of Terminal Window Engaged in Server-Client Communication
Here black parts in the image indicate connected client IP address and port number. Now, enter the message from server terminal.
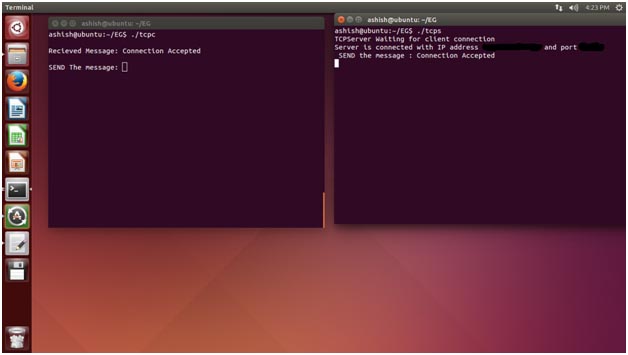
Fig. 3: Screenshot of IP address and port number on Terminal Window
Now you can send data from client to server. Server- client model is communicated using TCP/IP. Enter the data from the client terminal and check it.
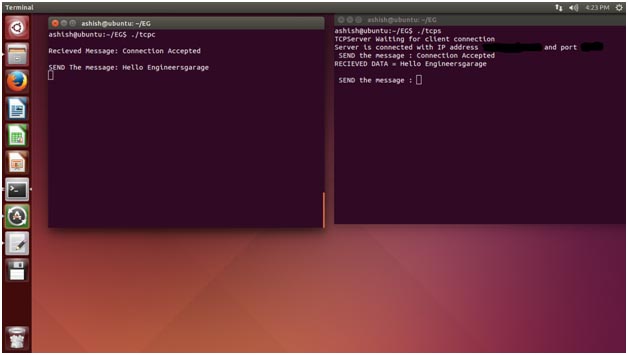
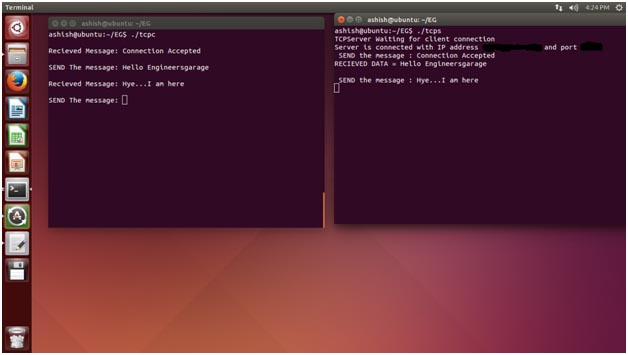
Here I have not terminated connection. So, both can communicate to each other till the connection is not closed. Press ctrl +C from which terminal you want to exit.
Filed Under: Tutorials


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.