Second Generation (2G) technology was launched in the year 1991 in Finland. It is based on the technology known as global system for mobile communication or in short we can say GSM. This technology enabled various networks to provide services like text messages, picture messages and MMS. In this technology all text messages are digitally encrypted due to which only the intended receiver receives message. These digital signals consume less battery power, so it helps in saving the battery of mobiles.
The technologies used in 2G are either TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access) which divides signal into different time slots or CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access) which allocates a special code to each user so as to communicate over a multiplex physical channel.
3G technology generally refers to the standard of accessibility and speed of mobile devices. It was first used in Japan in the year 2001. The standards of the technology were set by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). This technology enables use of various services like GPS (Global Positioning System), mobile television and video conferencing. It not only enables them to be used worldwide, but also provides with better bandwidth and increased speed.
This technology is much more flexible as it can support 5 major radio technologies that operate under CDMA, TDMA and FDMA. CDMA accounts for IMT-DS (direct speed), IMT-MC (multi carrier). TDMA holds for IMT-TC (time code), IMT-SC (single carrier). This technology is also comfortable to work with 2G technologies. The main aim of this technology is to allow much better coverage and growth with minimum investment.
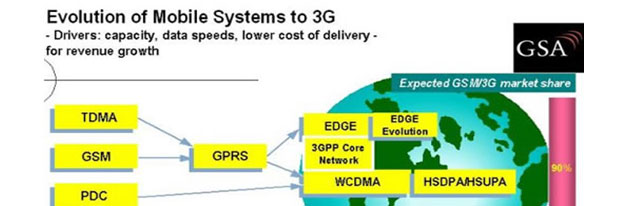
Figure: Evolution of Mobile system from 2G to 3G
Difference between 2G and 3G Technology
· Cost: The license fee to be paid for 3G network is much higher as compared to 2G networks. The network construction and maintenance of 3G is much costlier than 2G networks. Also from the customers point of view the expenditure for 3G network will be excessively high if they make use of the various applications of 3G.
· Data Transmission: The main difference between 2G and 3G networks is seen by the mobile users who download data and browse the Internet on the mobile phones. They find much faster download speeds, faster access to the data and applications in 3G networks as compared to 2G networks. 2G networks are less compatible with the functions of smart phone. The speed of data transmission in 2G network is less than 50,000 bits per sec while in 3G it can be more than 4 million bits per sec.
· Function: The main function of 2G technology is the transmission of information via voice signals while that of 3G technologies is data transfer via video conferencing, MMS etc.
· Features: The features like mobile TV, video transfers and GPS systems are the additional features of 3G technology that are not available with 2G technologies.
· Frequencies: 2G technology uses a broad range of frequencies in both upper and lower bands, under which the transmission depends on conditions such as weather. A drawback of 3G is that it is simply not available in certain regions.
· Implication: 3G technology offers a high level of security as compared to 2G technology because 3G networks permit validation measures when communicating with other devices.
· Making Calls: Calls can be made easily on both 2G and 3G networks with no real noticeable differences except that in 3G network video calls can also be made. The transmission of text messages and photos is available in both the networks but 2G networks have data limit and the speed of the data transmission is also very slow as compared to 3G.
· Speed: The downloading and uploading speeds available in 2G technologies are up to 236 Kbps. While in 3G technology the downloading and uploading speeds are up to 21 Mbps and 5.7 Mbps respectively.
Filed Under: How to


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.