This includes an extra board with IC holder which holds the IC’s that are to be tested. It also includes some push button which tells the system which IC is being tested. For this, you just have to put in the IC and press the relative button to test it.
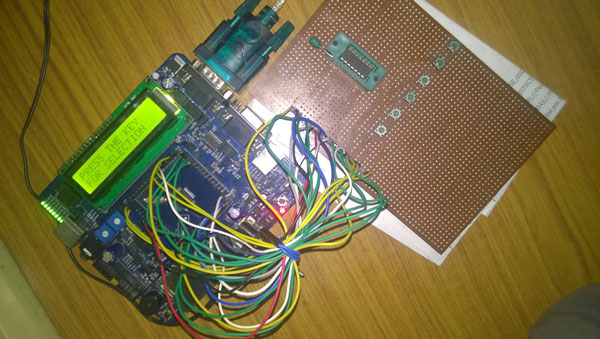
Fig. 1: Prototype of LPC2148 ARM Microcontroller based Digital IC Tester
Application:
The IC is placed in holder and the switch is pressed. Then a set of input is given to its input pin and it observes the output pins.the output pins.

Fig. 2: Image showing soldering on LPC2148 ARM Microcontroller board
BLOCK DIAGRAM:
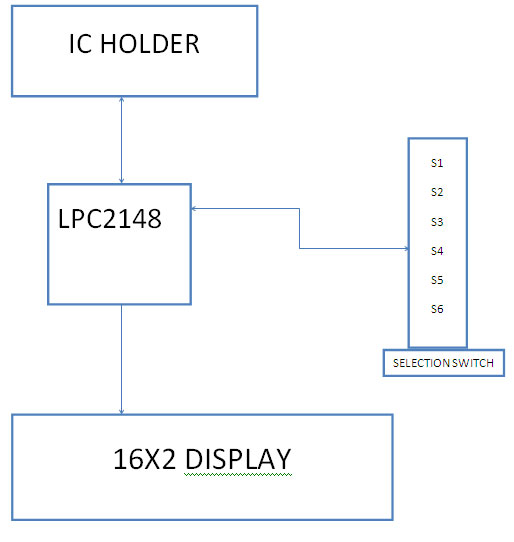
Fig. 3: Overview of LPC2148 ARM Microcontroller based Digital IC Tester
Components & Working
IC HOLDER:
The IC is put onto the holder, locked and then the switch is pressed. Its purpose is to hold the IC in place during testing.
ARM LPC2148:
LCD DISPLAY:
The command register stores the command instructions given to the LCD. A command is an instruction given to LCD to do a predefined task like initializing it, clearing its screen, setting the cursor position, controlling display etc. The data register stores data to be displayed on the LCD. The data is the ASCII value of the character to be displayed on the LCD. Click to learn more about internal structure of an LCD.
WORKING:

Fig. 4: Image showing LPC ARM Microcontroller based Digital IC Tester designed on PCB
MICROCONTROLLER BOARD:
Project Source Code
### #include <LPC214x.H> /* LPC214x definitions */ #include "lcd.h" #define LCD_BACK_LIGHT_TIMEOUT 1000 #define LCD_BACKLIGHT (1 << 21) #define LCD_BACK_LIGHT_DIR IO1DIR #define LCD_BACK_LIGHT_SET IO1SET #define LCD_BACK_LIGHT_CLR IO1CLR #define LCD_DATA_DIR IO0DIR #define LCD_DATA_SET IO0SET #define LCD_DATA_CLR IO0CLR #define LCD_CTRL_DIR IO1DIR #define LCD_CTRL_SET IO1SET #define LCD_CTRL_CLR IO1CLR #define LCDRS (1 << 24) #define LCDRW (1 << 23) #define LCDEN (1 << 22) #define LCD_D4 (1 << 10) #define LCD_D5 (1 << 11) #define LCD_D6 (1 << 12) #define LCD_D7 (1 << 13) #define LCD_DATA_MASK (LCD_D4 | LCD_D5 | LCD_D6 | LCD_D7) #define LCD_BUSY_FLAG LCD_D7 #define LCD_CONTROL_MASK 0x01C00000 /** ************************************************************************** ****1111 Function Name : delay() Description :This function suspends the tasks for specified ticks. Input : ticks:no of ticks in multiple of 1 usec task: task to be suspended Output : void Note : ******************************************************************************* */ void delay(int count) { int j=0,i=0; for(j=0;j<count;j++) { /* At 60Mhz, the below loop introduces delay of 10 us */ for(i=0;i<35;i++); } } /** ******************************************************************************************** Function Name : wait_lcd() Description : Input : Output : Void Note : ******************************************************************************************** */ void wait_lcd( void ) { LCD_CTRL_CLR |= LCDRS; LCD_CTRL_SET |= LCDRW |LCDEN; while(IO1PIN & LCD_BUSY_FLAG); /* wait for busy flag to become low */ LCD_CTRL_CLR |= LCDEN | LCDRW; LCD_DATA_DIR |= LCD_DATA_MASK; delay(100); } /** ******************************************************************************************** Function Name : lcd_command_write() Description : Input : Output : Void Note : ******************************************************************************************** */ void lcd_command_write( unsigned char command ) { unsigned char temp=0; unsigned int temp1=0; temp=command; temp=(temp>>4)&0x0F; temp1=(temp<<10)&LCD_DATA_MASK; LCD_CTRL_CLR = LCDRS; LCD_CTRL_SET = LCDEN; LCD_DATA_CLR = LCD_DATA_MASK; LCD_DATA_SET = temp1; delay(10000); LCD_CTRL_CLR = LCDEN; temp=command; temp&=0x0F; temp1=(temp<<10)&LCD_DATA_MASK; delay(100*2); LCD_CTRL_CLR |= LCDRS; LCD_CTRL_SET |= LCDEN; LCD_DATA_CLR = LCD_DATA_MASK; LCD_DATA_SET = temp1; delay(10000); LCD_CTRL_CLR |= LCDEN; wait_lcd(); } /** ******************************************************************************************** Function Name : set_lcd_port_output() Description : Input : Output : Void Note : ******************************************************************************************** */ void set_lcd_port_output( void ) { LCD_CTRL_DIR |= ( LCDEN | LCDRS | LCDRW ); LCD_CTRL_CLR |= ( LCDEN | LCDRS | LCDRW ); LCD_DATA_DIR |= LCD_DATA_MASK; } /* * ******************************************************************************************** Function Name : lcd_clear() Description : Input : Output : Void Note : ******************************************************************************************** */ void lcd_clear( void) { lcd_command_write( 0x01 ); } /** ******************************************************************************************** Function Name : lcd_gotoxy() Description : Input : Output : Void Note : ******************************************************************************************** */ int lcd_gotoxy( unsigned int x, unsigned int y) { int retval = 0; if( (x > 1) && (y > 15) ) { retval = -1; } else { if( x == 0 ) { lcd_command_write( 0x80 + y ); /* command - position cursor at 0x00 (0x80 + 0x00 ) */ } else if( x==1 ) { lcd_command_write( 0xC0 + y ); /* command - position cursor at 0x40 (0x80 + 0x00 ) */ } } return retval; } /** ******************************************************************************************** Function Name : lcd_data_write() Description : Input : Output : Void Note : ******************************************************************************************** */ void lcd_data_write( unsigned char data ) { unsigned char temp=0; unsigned int temp1=0; temp=data; temp=(temp>>4)&0x0F; temp1=(temp<<10)&LCD_DATA_MASK; LCD_CTRL_SET |= LCDEN|LCDRS; LCD_DATA_CLR = LCD_DATA_MASK; LCD_DATA_SET = temp1; LCD_CTRL_CLR |= LCDEN; temp=data; temp&=0x0F; temp1=(temp<<10)&LCD_DATA_MASK; LCD_CTRL_SET |= LCDEN|LCDRS; LCD_DATA_CLR = LCD_DATA_MASK; LCD_DATA_SET = temp1; LCD_CTRL_CLR |= LCDEN; wait_lcd(); } /** ******************************************************************************************** Function Name : lcd_putchar() Description : Input : Output : Void Note : ******************************************************************************************* */ void lcd_putchar( int c ) { lcd_data_write( c ); } /** ******************************************************************************************** Function Name : lcd_putstring() Description : Input : Output : Void Note : ******************************************************************************************** */ void lcd_putstring( unsigned char line, char *string ) { unsigned char len = MAX_CHAR_IN_ONE_LINE; lcd_gotoxy( line, 0 ); while(*string != '�' && len--) { lcd_putchar( *string ); string++; } } /** ******************************************************************************************** Function Name : lcd_backlight_on() Description : Input : Output : Void Note : ******************************************************************************************** */ void lcd_backlight_on() { LCD_BACK_LIGHT_DIR |= LCD_BACKLIGHT; LCD_BACK_LIGHT_SET |= LCD_BACKLIGHT; } /** ******************************************************************************************** Function Name : turn_off_lcd_back_light() Description : Input : Output : Void Note : ******************************************************************************************** */ void turn_off_lcd_back_light_cb(void) { LCD_BACK_LIGHT_DIR |= LCD_BACKLIGHT; LCD_BACK_LIGHT_CLR |= LCD_BACKLIGHT; } /** ******************************************************************************************** Function Name : init_lcd() Description : Input : Output : Void Note : ******************************************************************************************** */ void init_lcd( void ) { set_lcd_port_output(); delay(100*100); lcd_command_write(0x28); /* 4-bit interface, two line, 5X7 dots. */ lcd_clear() ; /* LCD clear */ lcd_command_write(0x02); /* cursor home */ lcd_command_write(0x06); /* cursor move direction */ lcd_command_write(0x0C) ; /* display on */ lcd_gotoxy(0, 0); lcd_clear(); lcd_putstring(0,"PRESS THE KEY"); lcd_putstring(1,"FOR SELECTION"); } LCD.H #ifndef _LCD_H #define _LCD_H #define MAX_CHAR_IN_ONE_LINE 16 enum ROW_NUMBERS { LINE1, LINE2 }; void init_lcd(void); void lcd_putstring(unsigned char line, char *string); void lcd_clear(void); void lcd_backlight_on(void); int lcd_gotoxy(unsigned int x, unsigned int y); void lcd_putchar(int c); #endif ###
Circuit Diagrams
Filed Under: Electronic Projects



Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.