DTMF (Dual tone multiple frequency) is the most popular and nowadays ubiquitously used telecommunication signalling method. A DTMF decoder detects the DTMF tones and generates the binary sequence corresponding to key pressed in a DTMF keypad. The circuit of this project presented here is a DTMF decoder. DTMF keypads are used in almost all landline and mobile handsets. The DTMF decoders, therefore, are used at the telephone switching centres to detect the number dialled by the caller. The DTMF version used in pushbutton telephones is called touch tone and is a registered trademark of AT&T.
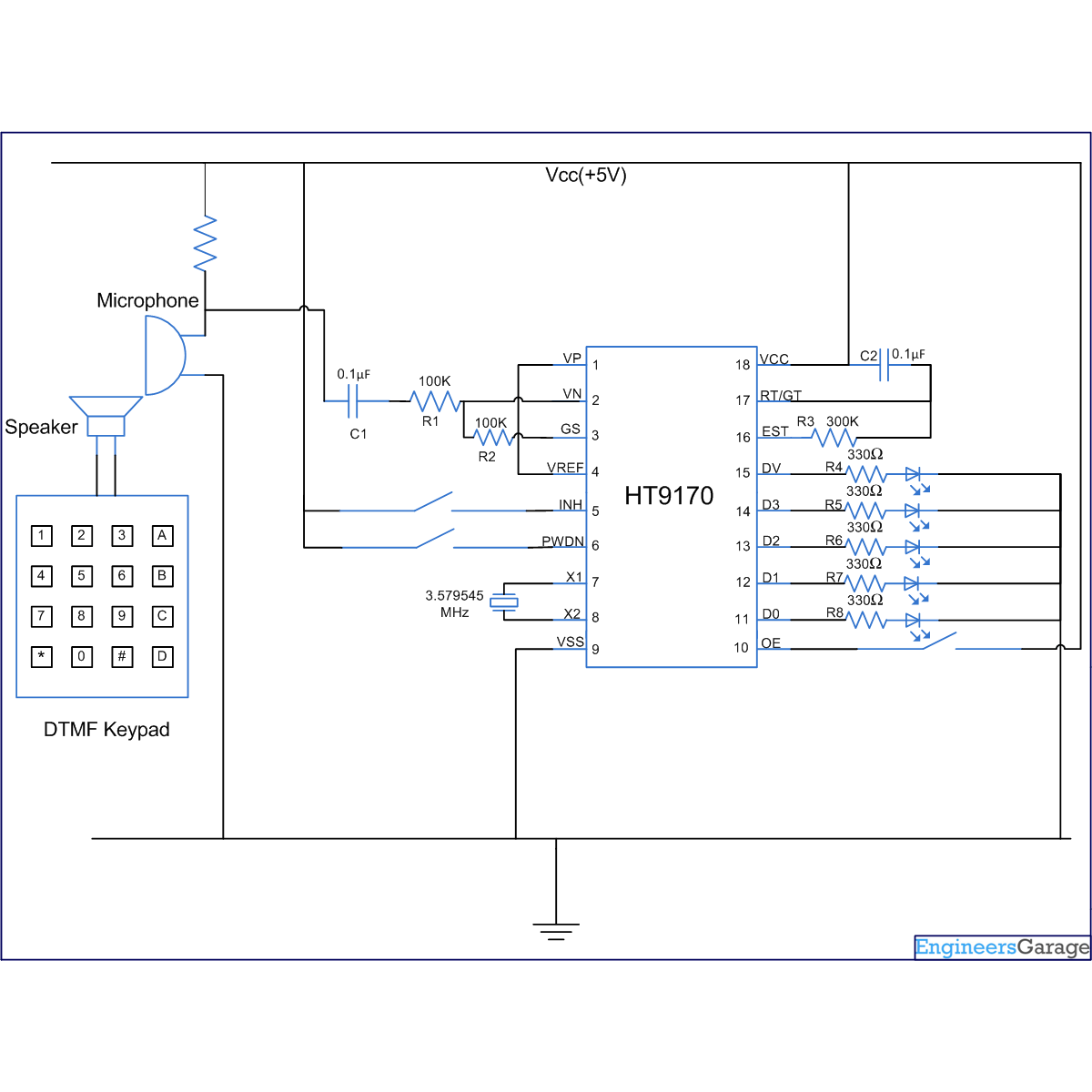
The circuit of this project uses a DTMF decoder IC (HT9170). The DTMF tones are generated by the keypad of a cell phone or by the computer software available on www.polar-electric.com.
The tones generated from the speaker (audio signals) of keypad are given to microphone which converts audio tones into electrical signals. The signals from the microphone are processed by the DTMF decoder IC which generates the equivalent binary sequence as a parallel output.
The electrical signals from microphone (mic) are fed to inverting output (pin2; VN) of Op-amp, present in IC, through a series of resistance and capacitance of value 100 k and 0.1 µF respectively. The non-inverting input pin (pin1; VP) of Op-amp is connected to pin4 (VREF). The voltage at VREF pin is VDD/2. A feedback signal is provided, by connecting the output of Op-amp (pin3; GS) to inverting input pin (pin2; VN) through a resistor R2 (100 k).
The output of Op-amp is passed through a pre filter. The output from this pre filter is then supplied to low group and high group filters. These filters consist of switched capacitors and divide DTMF tones into low and high group signals. High group filters pass the high frequencies while low group filter pass low frequencies. These frequencies are then passed through frequency detector and code detector circuits. Finally the four-digit code is latched on the output pins of HT9170. The output on these pins has been used to drive a set of four LEDs.
The whole process, from frequency detection to latching of the data, is controlled by steering control circuit. So it is very important part of the whole process and is mainly controlled by RT/GT and DV pins of DTMF decoder IC. RT/GT pin is connected to VDD through a capacitor of 0.1 µF. The EST pin is connected to RT/GT pin through a resistor of 300k.
Pin6, PWDN pin (active high) inhibits the working of oscillator thereby stopping the working of circuit; and Pin5, INH pin (active high) inhibits detection of the tones of character A,B,C,D. The pin 10; OE (output enable; active high) enables the latching of the data on the data pins. Pin15; DV (Data valid pin) becomes high on detection of valid DTMF tone otherwise it remains low. An oscillator of frequency 3.579545 MHz is connected between pins 7 and 8.
Circuit Diagrams
Project Components
Filed Under: Electronic Projects


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.