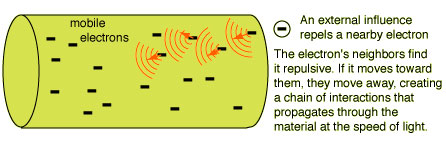
Electricity has very much importance in human life. To run an electric appliance or electronic circuit we need the help of electricity either in the form of AC or DC. Even though electricity is useful to human life, careless handling can cause lethal effects. Electrical safety measures are necessary while dealing with high voltage AC available from the power grid. Ignorance can lead to a fatal shock or fire hazards. Let us see how electricity poses lethal effects on the human body and the safety measures to prevent it. Remember, Electricity travels at the speed of light. Its flow is around 299,460 kilo meters per second so you will not get time to react because you can’t move faster than electricity. So the best way is staying out of its way.
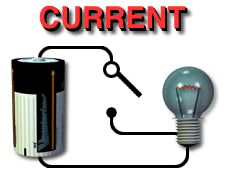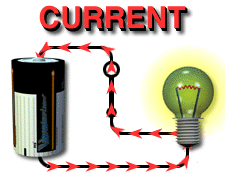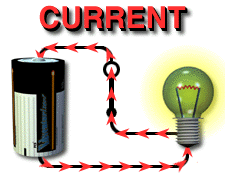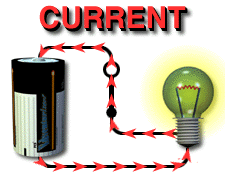
[header = Effect of Current on Human Body]
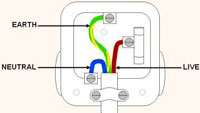
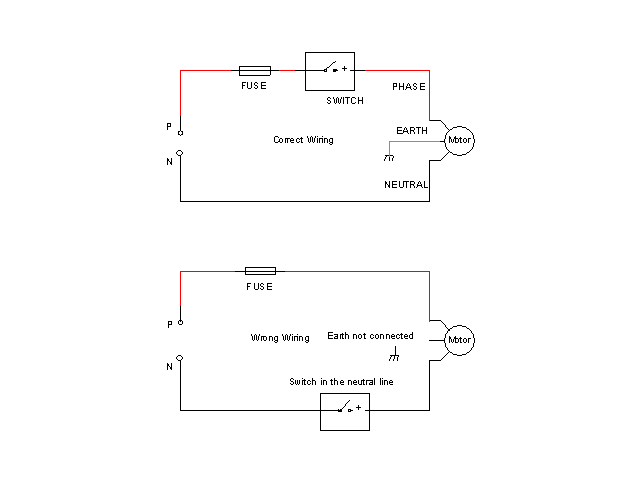
 This not the way to fix sockets
This not the way to fix sockets



Filed Under: Electronic Projects


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.