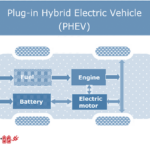
Electric vehicles are the future of the automotive industry. There are already more than 2.5 million BEVs and PHEVs in the United States this year, which is expected to increase. There are more than 2.3 million electric vehicles (EVs) in Europe. In India, the number has surpassed 1.3 million.
Battery aside, one key factor to a successful EV that’s rarely discussed is the embedded software. An embedded system is a blend of hardware and software applications built to perform specific tasks.
 A conventional internal combustion (IC) engine has complex mechanical systems for controlling and managing the vehicle. This engine is made up of more than 2,000 mechanical parts. However, the electric engine of an EV is simpler in that the control and management of the vehicle are entirely assigned to the embedded software.
A conventional internal combustion (IC) engine has complex mechanical systems for controlling and managing the vehicle. This engine is made up of more than 2,000 mechanical parts. However, the electric engine of an EV is simpler in that the control and management of the vehicle are entirely assigned to the embedded software.
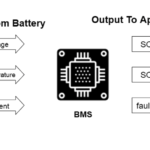
The software is essential for proper EV management. For example, predictive-maintenance software is a critical component for the safe function of the battery and battery-management system.
Let’s review some of the other key roles automotive software performs in an electric vehicle.
Operation
Essentially, the software in an electric vehicle replaces the mechanical system found in IC vehicles, and it’s responsible for multiple aspects of an EC. It controls the battery-management system, the car’s motor, and power electronics. For example, power electronics are responsible for converting the DC voltage from the battery to the AC voltage required by the motor. Embedded software controls this process and ensures that the power is delivered efficiently and reliably.
Additionally, motor-control software controls the motor’s speed and torque, determining how fast the vehicle accelerates and how much power is used. This software also ensures the motor operates within safe temperature limits and protects it from overloading.
Maintenance
Maintenance and repairs for EVs are different than for traditional vehicles, partially because of the significant role of the embedded software. This is where predictive maintenance is important to ensure optimal vehicle performance, prevent breakdowns, and extend the car’s lifespan.
Predictive maintenance software can send real-time alerts to schedule maintenance before a breakdown occurs. This software monitors and collects data from the different components and systems in the EV, notifying the driver of any potential concerns based on the vehicle’s specifications. This helps prevent unexpected downtime and potentially reduces repair costs.
Predictive maintenance software also analyzes data from various sensors installed in the EV, such as those measuring battery voltage, motor temperature, and tire pressure.
Navigation
Since electric vehicles have a limited range based on their battery power, it’s common to pre-plan most routes. No one wants to be delayed or stalled because of a depleted battery.
The EV’s software provides data about the status of the battery and can predict the travel distance between charges. Smart navigation software can also offer the shortest and least busy route to a destination to make the best use of the battery — and locate the closest charging stations.
Safety
Embedded software is critical to the safety of electric vehicles, ensuring they operate properly while protecting against potential hazards. The electronic control systems in an EV are more tightly coupled than in any IC engine. The connectivity among onboard embedded systems in an EV must ensure vehicle safety and performance.
Along with monitoring and helping maintain the vehicle’s performance, some EVs have software that can detect potential collisions, using sensors and cameras that warn the driver or automatically apply the brakes if necessary.
Car performance
In EVs, the software is not only essential for operation but also supports improvements in vehicle design. The diagnostic data is shared with cloud servers that analyze the data for improving safety and performance. This is important because EV manufacturers still have challenges to overcome.
The industry must find viable ways to cut the cost premium while increasing the driving range and reducing the charging time. Battery safety is another area that requires more R&D.
The data collected by EV software is also useful in determining locations and improvements for new charging infrastructure.
Software updates
Software updates in traditional vehicles are typically done through cables. On the other hand, EV software is done mostly wirelessly through over-the-air (OTA) updates. It’s extremely important EV software is updated regularly and upgraded as needed to ensure vehicle safety, security, and functionality. The OTA updates will remain the way to maintain electric car software.
Embedded software includes cybersecurity features, such as encryption and secure communication protocols, to protect against hacking and unauthorized access to vehicle systems.
Autonomous driving
EVs have paved the way for the development of connected and autonomous driving. The reliance on software control for the entire operation of the EV means that they can be automated more easily than IC engine vehicles. With the use of electric motor technology, electric cars can be precisely controlled, even if their movement is managed remotely by a cloud service.
Software for EVs that enables autonomous driving has the potential to improve safety, reduce congestion, and increase efficiency on the road. The software is relying on advanced sensors, machine learning algorithms, and mapping technology .
However, there are still obstacles before autonomous driving becomes mainstream. For example, connected cars require an extensive infrastructure involving the Internet of things that must operate to communicate and navigate safely in real-time without fail. Road safety is also a concern that needs to be addressed before driverless cars can hit the road.
Additionally, while EVs are continuously improving their battery efficiency to achieve the longest possible driving range, autonomous cars require a lot of energy overhead for the sensors, connectivity, and computing. The electric car industry must address the need to achieve higher driving ranges while cutting costs and reducing charging times.
Despite these challenges, electric vehicles are a significant first step towards the development of autonomous and connected cars. As the technology continues to evolve, expect ongoing improvements in electric and autonomous vehicles, bringing us ever-closer to a fully autonomous future.
Conclusion
Embedded software is crucial for EV operation, as it plays a vital role in the vehicle’s operation, maintenance, navigation, safety, and security. This technology has already achieved significant milestones, but there is room for improvements. The primary goals for EV development is to increase their driving range, reduce charging times, and lower costs while ensuring safety standards are met.
Only all-electric vehicles with embedded software can become fully autonomous in the future. The automotive software involved in communicating with sensors, connecting to IoT infrastructure, and computing navigation and movement will play a key role in achieving this.
Overall, the continued development of embedded software for electric vehicles is essential for the growth and success of the industry and the future of autonomous driving.
You may also like:
Filed Under: Electric Vehicles, EVs, Software, Tech Articles, Tutorials



Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.