The plotting of data on a graph is used to observe and subsequently describe the visible patterns that exist within the data. The main aim of this project is to show, how to plot a variable graph using processing environment and Arduino. In this article temperature is plotted on the processing graph. Processing environment is quite similar to Arduino but the difference is that in the former we can plot the graph whereas in the latter we can’t plot any type of graph. Processing Environment is very useful in cases of plotting Analog graphs.Processing Environment is very useful in cases of plotting Analog graphs. For this project reader need to know how to start with arduino.
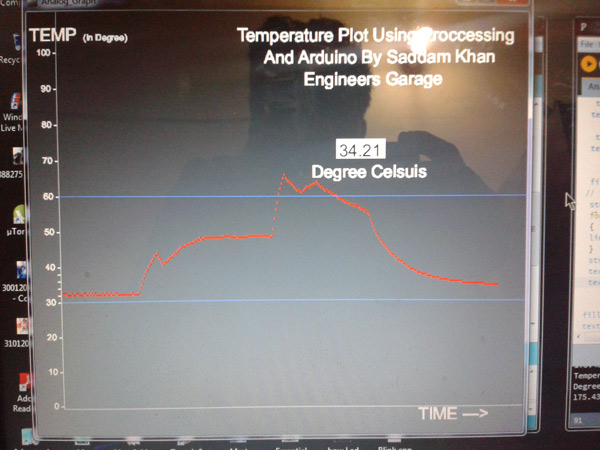
Fig. 1: Graph showing temperature plot on Processing Application
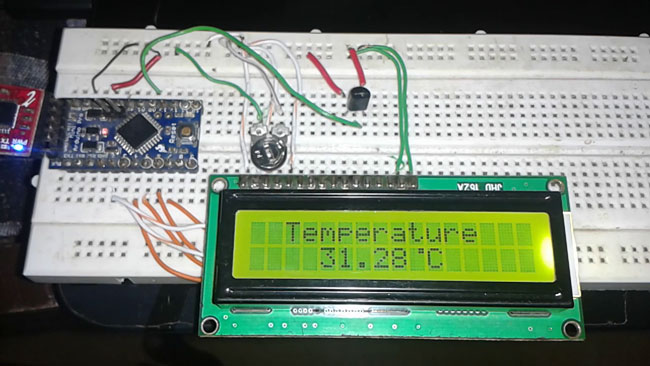
Fig. 2: Prototype of Arduino based Temperature Sensor
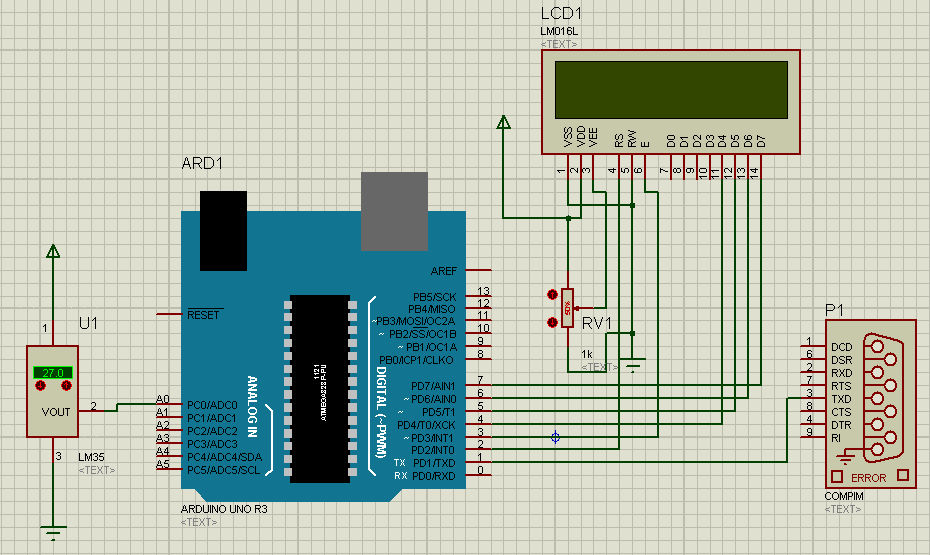
Here we are going to discuss plotting temperature graph on computer or laptop using Processing Environment and Arduino. Circuit of reading temperature is very simple. In this system only one circuit LM35 temperature Detector / Reader is used and directly connected with Analog pin number A0 of Arduino. And a 16×2 lcd interfaced with arduino is connected with this circuit for displaying temperature. See the block diagram given below to understand the working of this project.
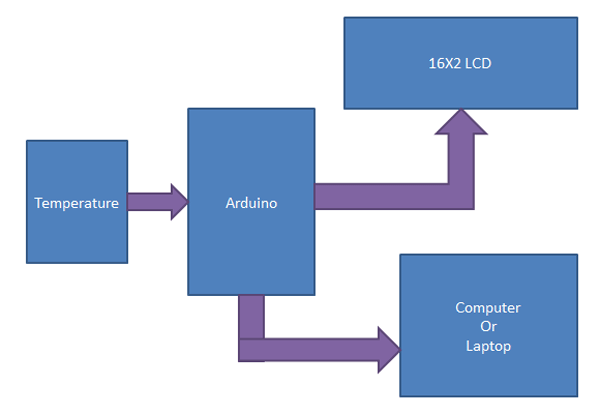
Fig. 3: Block Diagram of Arduino based Temperature Sensor
From Arduino, we just read Analog output of temperature sensor and after some calculations Arduino sends data for Processing by using FTDI basic breakout. But you can use any of TTL logic converters to communicate with Desktop or Laptop with Arduino. But in Arduino UNO, there is no need of any other external converter because Arduino UNO Board is already configured with logic converter. But if you have Arduino UNO at home or lab then you should have a TTL Logic Converter.
Displaying the Graph
The formula for calculation of temperature given below:
Temperature= Analog reading * (5.0/1023.0) * 100;
Processing: Processing is an Environment like Arduino. In Arduino we uses

Fig. 4: Screenshot of Code used to plot a line on Processing Application
Fig. 5: Screenshot of a line plotted on Processing Application
Font and Text

Fig. 6: Screenshot of Code used to display text on Processing Application
Fig. 7: Screenshot of text displayed on Processing Application
Port
Circuit
Components Used
Project Source Code
###
// Arduino Code #include<LiquidCrystal.h> #define sensor A0 float analog_value; LiquidCrystal lcd(2,3,4,5,6,7); byte degree[8] = { 0b00011, 0b00011, 0b00000, 0b00000, 0b00000, 0b00000, 0b00000, 0b00000 }; void setup() { lcd.createChar(1, degree); lcd.begin(16,2); Serial.begin(9600); pinMode(sensor, INPUT); lcd.setCursor(0,0); lcd.print("Temperature Plot"); lcd.setCursor(0,1); lcd.print("Using Proccesing"); delay(2000); lcd.clear(); lcd.setCursor(0,0); lcd.print(" By Saddam Khan "); lcd.setCursor(0,1); lcd.print("ENGINEERS GARAGE"); delay(2000); lcd.clear(); } void loop() { float reading=analogRead(sensor); analog_value=reading*(5.0/1023.0)*100; lcd.setCursor(0,0); lcd.print(" Temperature "); lcd.setCursor(4,1); lcd.print(analog_value); lcd.write(1); lcd.print("C"); Serial.println(analog_value); delay(700); } // ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ // Processing Codeimport processing.serial.*;PFont f;PFont F;Serial myPort; // The serial portint xPos = 40; // horizontal position of the graphvoid setup () {// set the window size: and Font sizef = createFont("Arial",12,true);F = createFont("Arial",24,true);size(700, 600);// List all the available serial portsprintln(Serial.list());myPort = new Serial(this, Serial.list()[0], 9600);myPort.bufferUntil('n');// set inital background:background(70);}void draw (){// everything happens in the serialEvent()}void serialEvent (Serial myPort) {// get the ASCII string:String inString = myPort.readStringUntil('n');if (inString != null) {// trim off any whitespace:print("Temperature: ");print(inString);println("Degree Celcius");inString = trim(inString);// convert to an int and map to the screen height:float inByte = float(inString+(char)9);inByte = map(inByte, 0,117, 0, height);println(inByte);stroke(175); // temperature lineline(40,height-40,40,0);stroke(175); // Time lineline(40,height-40,width,height-40);stroke(100,100,255); // 30 degree lineline(40,height-194,width,height-194);stroke(100,100,255); // 60 degree lineline(40,height-344,width,height-344);textFont(F);fill(255);textAlign(RIGHT);text("Temperature Plot Using Proccessing",680,40);textAlign(RIGHT);text("And Arduino By Saddam Khan",653,70);textAlign(RIGHT);text("Engineers Garage",580,100);textAlign(RIGHT);text("TEMP",70,40);textAlign(RIGHT);text("TIME --->",650,580);textAlign(RIGHT);text(inString,500,200);textAlign(RIGHT);text(" Degree Celsuis",560,230);fill(0);// int j;stroke(255);for(int j=500;j>430;j--){line(j,height-398,j,height-425);}stroke(0,0,0);textAlign(RIGHT);text(inString,495,200);fill(240);textFont(f);textAlign(RIGHT);text("(In Degree)",140,40);textAlign(RIGHT); // 100 degreetext("100 -",40,60);textAlign(RIGHT); // 90 degreetext("90 -",40,110);textAlign(RIGHT); // 80 degreetext("80 -",40,160);textAlign(RIGHT); // 70 degreetext("70 -",40,210);textAlign(RIGHT); // 60 degreetext("60 -",40,260);textAlign(RIGHT); // 50 degreetext("50 -",40,310);textAlign(RIGHT); // 40 degreetext("40 -",40,360);textAlign(RIGHT);text("30 -",40,410);textAlign(RIGHT);text("20 -",40,460);textAlign(RIGHT);text("10 -",40,510);textAlign(RIGHT);text("0 -",40,560);/*---- scale between 30 degree to 40 degree------*/textAlign(RIGHT);text(" -",40,370);textAlign(RIGHT);text(" -",40,380);textAlign(RIGHT);text(" -",40,390);textAlign(RIGHT);text(" -",40,400);// textAlign(RIGHT);// text("0 -",40,360);// draw the line:int shift=40; // set trace originstroke(255,0,0); // trace colourfor(int i=0;i<2;i++){// line(xPos, height-inByte-1, xPos, height - inByte);line(xPos, height-inByte-(shift+2), xPos, height-inByte-shift);xPos++;}if (xPos >= width) // go back to begining{xPos = 40;background(100);}}}###
Circuit Diagrams
Project Video
Filed Under: Electronic Projects
Filed Under: Electronic Projects


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.