In the previous tutorials, the IOT devices designed were connecting with the internet network via Wi-Fi. Wi-Fi is a wireless standard. It is commonly used to provide data communication among mobile devices and the internet network. Another common standard used for networking devices and computers is Ethernet.
Ethernet is most commonly used Local Area Network (LAN) technology. It provides a wired communication to connect the devices to the Internet. It is a physical and link layer protocol in the TCP/IP stack which describes how the networked devices share their data to the computer or other network devices through the physical medium. It is based on IEEE 802.3 standard. Within an IOT system, Ethernet can be used to connect stationary or fixed IOT devices. For example, the Ethernet cables are used for connecting the computers with the routers to provide the Internet connectivity. The Ethernet cable serve as wired medium for connecting the computer and the router. This is a simple example of Ethernet LAN Technology.
The data speed over Ethernet depends on the cable type and can be limited by the network administrator. There may be fiber optic, co-axial or twisted pair cables used for Ethernet networking. The Ethernet has very low latency which makes it suitable for mission critical IOT applications where devices may be co-located or located in a local area network. A standard Ethernet cable is different from other cables. To connect the devices to the router, devices should have the Ethernet port so that the Ethernet cable can be plugged or unplugged on that port to provide Internet connectivity.
The co-axial cables are more commonly used for setting up Ethernet network. There are the following types of co-axial cables standard within Ethernet –
1) 10BASE-T – It is the IEEE standard which defines the requirement of sending information on Ethernet cable, in which 10 refers the transmission speed in Mbps. BASE refers to the baseband signaling which means only Ethernet signals are carried on the medium and T refers to the type of cable i.e. twisted pair. So, basically the transmission speed from this cable supports up to 10 Mbps. To increase the Speed, more standard cables were introduced with modified features.
2) 100BASE-T – It supports transmission speed up to 100 Mbps.
3) 1000BASE-T – It supports transmission speed up to 1000 Mbps. It is sometimes called as Gigabit Ethernet.

Fig. 1: Image of Ethernet Cables
The IEEE has standardized categorization of the Ethernet cables. These cables are categorized as cat 3, cat 5, cat 5e, cat 6, cat 6a and cat 7. The term ‘cat’ refers to category and the succeeding number indicates the category type. The higher is the number, the greater transmission speed and frequency is supported by the cable. The different Ethernet cable categories have the following specifications –
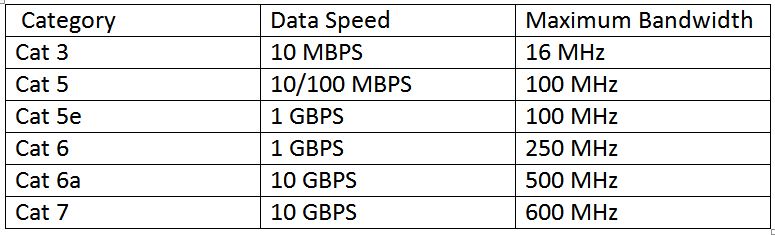
Fig. 2: Table listing categories of Ethernet cables
The Cat 3 and Cat 5 cables are now obsolete. The Cat 5e cables are most commonly used these days. The other cable types are expensive and used for specific applications only. So, for common LAN setup, the Cat 5e cables are generally used.
The Ethernet technology has the following important features –
• Ethernet Network are relatively less expensive to produce high speed local area network.
• Ethernet network is a fast connectivity protocol which has the ability to produce high speed of data.
• The twisted pair cable, thick coaxial cable and fiber optic cables can be used for Ethernet.
• Ethernet also secure the data with detect collision.
The Ethernet technology provides various advantages as follow –
• Reliability: The Ethernet cables are very reliable to transmit the data.
• Speed: 100Mbps for fast Ethernet (100BaseT), 1000Mbps for Gigabit Ethernet. Wired Ethernet are faster than wireless devices.
• Data Security: It uses common firewalls for data security.
• There is less overhead in Ethernet compared to a wireless network. This helps with packet throughput on the wired system.
Though, Ethernet also has some limitations. These are as follow –
• Limited mobility: It is suited for short distance transmission of data.
• Installation cost: There is additional cost included due to installation of hubs, routers, switches.
• Speed: The traditional Ethernet (10BaseT) has data speed of only 10 Mbps.
• Crosstalk occurs in longer data transmission.
• Infrastructure Requirement: There should be necessary wiring and equipment. There is also need of a port on the switch for each wired connection.
The Ethernet is suitable for setting up IOT networks in which the devices are located within a range of 100 Meter. With Cat 5e cables, it provides a networking solution for the IOT devices with low latency and optimum data speed.
In the next tutorial, an Arduino based temperature monitor will be connected to the internet network via Ethernet technology and will be programmed to transmit temperature and humidity data to a remote PC via MQTT broker.
You may also like:
Filed Under: IoT tutorials, Tutorials








Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.