eSIMs are not only going to cater to M2M solutions. They are about to have a significant impact on the consumer segment as well. Apple has already incorporated eSIM is some of its latest models. Other consumer device manufacturers are also moving on to include eSIMs in their smartphones and wearable devices. GSMA has proposed a different architecture of eSIM for consumer devices. Being GSMA-compliant solution, eSIM in consumer devices will be ensuring global internet connectivity and easy portability.
The consumer solution has a different backend infrastructure and different roles assigned to the architectural entities. While the M2M solution is server-driven and based on a push model, the consumer solution is client-driven and based on a pull model. To make the consumer model client-driven, Local Profile Assistant (LPA), either integrated into the eSIM or the consumer device, manages the entire subscription management. Let us have a look at architectural entities and the underlying architecture of consumer solutions. The consumer solution is based on GSMA’s consumer dedicated technical specifications – SGP.21, SGP.22, and SGP.23.
eSIM Architecture for consumer solutions
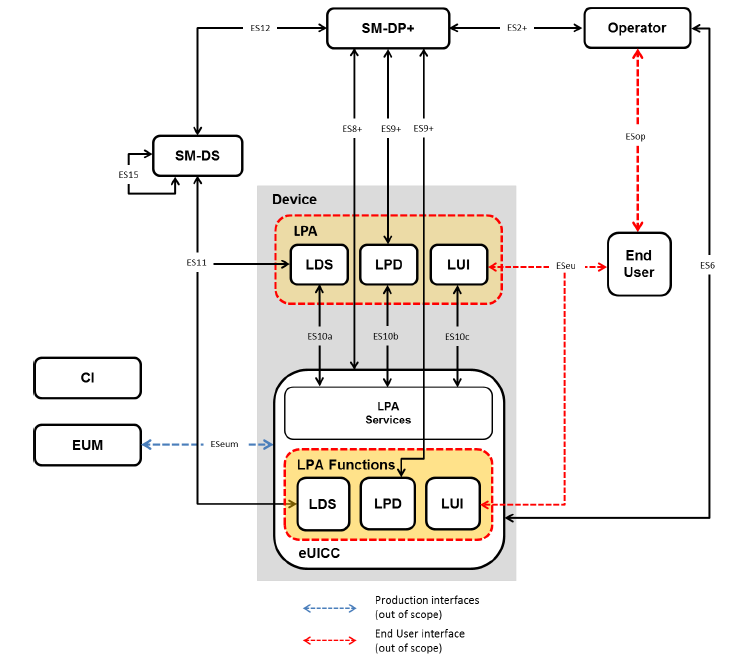
For consumer solutions, GSMA has specified remote SIM provisioning architecture, as illustrated in the diagram below.
Let us discuss different entities and their roles in this architecture.
- eUICC manufacturer – eUICC manufacturer (EUM) provides the eUICCs to the consumer device manufacturers. The eUICC contains the initial cryptographic configuration and security architecture. It may also contain Local Profile Assistant (LPA) integrated into the eSIM or at least interface to connect with LPA integrated into the consumer device. EUM is also responsible for issuing certification for eUICC authentication and certificates for authenticated keyset establishment between eSIM and SM-DP+.
- Consumer Device Manufacturer – The device manufacturer implements the LPA elements on the consumer device as well as applications that must reside on the primary (consumer) device.
- Operator and Communication Service Provider – Communication Service Provider (CSP) has access to SM-DP+. When a customer selects a CSP, the service provider initiates provisioning of a Profile package. The operator (MNO), on behalf of the CSP, specifies Profile characteristics, features, and applications that apply to the target eUICC.
- SM-DP+ – When requested by the operator (MNO), SM-DP+ creates Profiles and is responsible for their security and management. It is responsible for the delivery of a Profile to the client device within a Bound Profile Package. It also requests for the creation of ISD-P in the eUICC into which the Profile has to be installed. It remains responsible for the lifecycle management of ISD-P installed on the eUICC.
- SM-DS – Subscription Manager – Discovery Service (SM-DS) provides mechanisms to inform Local Discovery Service (LDS) within a device that SM-DP+ wants to communicate with it. SM-DP+ sends an Event Registration message to the SM-DS for a target consumer device. A Root SM-DS is configured on the eUICC, which has a unique address. Local Discovery Service (LDS) on the target device polls root SM-DS using the same address. If Root SM-DS has an event ID, it responds with SM-DS+ address; otherwise, it sends back a null response. In the case of cascaded SM-DS+, event registration is done with an alternative SM-DS. Then, this alternative SM-DS cascades event registration to the root SM-DS.
- Certificate Issuer – The certificate issuer is responsible for issuing certificates GSMA-compliant Remote SIM Provisioning entities (EUM, SM-DP+, SM-DS). It acts as a trusted third-party to authenticate different entities of the consumer solution.
- Subscriber and end user – A Subscriber can be a contract partner of the communication service provider (CSP). At the same time, the end-user is a customer, who may be using the consumer device and services related to enabled Profiles.
eSIM hardware and working
The hardware interface and commands remain the same for the eSIM irrespective of it is used in an M2M device or a consumer device. eSIM is a single global SIM, and its hardware and other technical specifications are not dependant on its use-case. eSIM is always based on GlobalPlatform Card Specifications (GPCS) and may be available in standardized ETSI form factors (2FF, 3FF, 4FF, MFF2). It is loaded with the eUICC operating system, on top of which various other security profiles, network applications, and SIM applets run. The SIM exchanges commands with the device controller to manage various subscription and services related functions. The structure of commands and responses is determined by the ETSI specifications (TS 102 221). Check out the eSIM architecture for M2M solutions to learn more about hardware specifications, commands, and responses of eSIM.
eSIM card architecture for consumer solutions
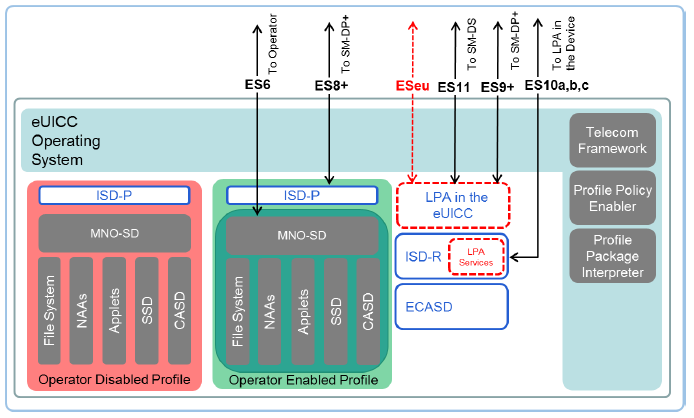
The card architecture of eSIM mainly refers to the software architecture of the eSIM. The following diagram shows the eSIM card architecture for consumer solutions.
As the off-card entities in a consumer solution have different roles, the different on-card representatives also operate differently on eSIM when it is embedded in a consumer device.
The eUICC is loaded with an eUICC operating system (SIM operating system) that supports all features defined in the GlobalPlatform Card Specifications (GPCS). As a SIM operating system, it includes a telecom framework, profile package interpreter, and profile policy enabler. The OS is responsible for managing security domains, and MNO enabled Profiles (Provisioning/Operational Profiles). The telecom framework is an operating system service and is responsible for the implementation of standardized network authentication algorithms to the NAAs (Network Access Applications) hosted in the ISD-P. It is also responsible for the configuration of algorithms with necessary parameters. The Profile Policy Enabler is responsible for the validation and enforcement of Profile Policy Rules. The Profile Package Interpreter is also an operating system service that translates Profile package data into installed Profile using the internal format of the target eUICC.
Embedded UICC Controlling Authority Security Domain (ECASD) is responsible for the storage of necessary credentials for the security domains on the eUICC. There can be only one ECASD on an eUICC. It is installed and personalized by the EUM according to the GlobalPlatform Card Specification. It contains eUICC private keys for creating signatures, Certificates for eUICC authentication, Certificate Issuers’ (CI) root public keys for verifying SM-DP+, and SM-DS Certificates and eUICC Manufacturers’ (EUMs) keyset for key/Certificate renewal. It also provides security functions during key establishment and eUICC authentication.
ISD-R creates new ISD-Ps and is responsible for the lifecycle management of all ISD-Ps. ISD-P is again a security domain that is responsible for hosting of a Profile. ISD-P is used to download and install Profiles and is on-card representative of SM-DP+. MNO-SD is the on-card representative of MNO (Operator). It contains OTA (Over-The-Air) Keys and is responsible for providing a secure OTA channel.
The most important on-card entity in consumer solution is Local Profile Assistant. LPA services provide necessary access to the services and data required by the LPA functions like Root SM-DS address, default SM-DP+ address, Local Profile Management, functions for the LPA to authenticate, and interact with the SM-DS. It enables the reception of Bound Profile Package and provides information about installed Profiles and Profile metadata. It also ensures that access to EID (eUICC ID) is restricted only to LPA.
How eSIM works in consumer devices
In consumer solutions, eUICC operates on a pull-model. When subscribed to a CSP, LPA on the eUICC facilitates the reception of Bound Profile Package. ISD-R then creates an ISD-P, which is responsible for hosting a Profile. The enabled ISD-P downloads and installs the requested Profile. The MNO-SD provides a secure OTA channel through which various network applications and SIM applets access services subscribed by the consumer device user. In a consumer solution, the client device that manages all the subscription-related operations instead of those operations being remotely managed by the SM-DP server.
Filed Under: Tech Articles


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.