Heat sensor senses the heat present around the sensor. When temperature rises above the set value, it will indicate the presence with the help of glowing LED. This heat sensor circuit can be used in kitchen or inside your PC. If your kitchen appliances or PC are over heated, it may be possible that it will damage the expensive components present in it. So to protect them from damage we have described a simple circuit which will give an indication when temperature around the sensor increases above the level set by you. This circuit is very small and can be easily install. In short, this simple project with easy to build electronic circuit is very useful to fight with problems like overheating.
The circuit is based on two IC and few more discrete components namely-
1. LM35 – LM35 is a precision integrated circuit temperature and its output voltage is linearly proportional to centigrade temperature. LM35 detects the surrounding temperature and according to reference value set it which will give you the output. When output voltage is multiplied by 100 it will give you the temperature sensed in degrees. So you can easily set your reference voltage. Pin configuration of LM35 IC is shown below.
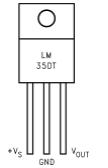
Feature of LM35 IC
• It directly gives output temperature in degree Celsius so there is no need for conversion of temperature.
• Operating temperature range varies from -55 to +150 degrees.
• LM35 is also suitable for remote application.
• Operating voltage range varies from 4 to 30 volts.
• It draws only 60 µA from power supply; therefore it has very low self heating.
• It comes in sealed package (plastic covering) therefore problem of oxidation of IC does not happen.
2. CA3130 – IC CA3130 is operational amplifier which combines the advantage of both CMOS and bipolar transistor on a single chip. Operating voltage range varies from 5V to 16V. CA3130 has advantage that they can be phased compensated with a single external capacitor and have terminals for adjustment of offset voltage. In this you can adjust the reference voltage at inverting and non -inverting pin so that when voltage at inverting pin is more than non-inverting pin. It will make the out pin high and vice versa. Pin configuration of CA3130 IC is shown below.
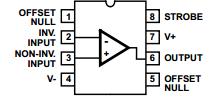
3. LED – LED stands for light emitting diode. It is made up of semiconductor device which emit different light source as its output. LED is a semiconductor diode that emits narrow-spectrum light when electrically biased in the forward direction of the p-n junctions; When LED is switched ON, electronics combines with hole and the device release energy in the form of light. LED are Available in Red, Orange, Amber, Yellow, Green, Blue and White. Now a day’s LED’s are available in visible, ultraviolet and infrared wavelengths and have high brightness.
4. Resistor – Resistor is a two terminal passive component used to control the flow of current into the circuit. A current through resistor is directly proportional to the voltage applied across resistor terminal.
Resistor comes in two varieties –
1. Fixed resistor means they have fixed value of resistance.
2. Variable resistors means there value can be changed like if you have variable resistor of 5K then you can vary the resistance from 0 to 5 K Ohms.
We can calculate the value of resistor with the help of multi-meter or we can do it with help of color code available on resistor.
5. Capacitor – A capacitor is a two terminal passive component which stores electric charge. Capacitor consists of two conductors which are separated by a dielectric medium. It works when potential difference applied across the conductors polarizes the dipole ions to store the charge in the dielectric medium.
Capacitor comes in two varieties-
1. Polarised capacitor- They have polarity means + and – sign. They are basically used to store charge. As they store charge they should be carefully discharge before troubleshooting the circuit.
2. Non polarized capacitor – They do not have polarity and can be mounted any way. They are basically used to remove the fluctuation present in conversion of AC to DC.
Working of circuit
Working of heat sensor circuit
In this circuit we have set the fix voltage at inverting pin that is at pin 2 of IC2 and non inverting pin 3 of IC2 is connected with the output pin 2 of IC1 through a resistor. Initially we have to do some hit and trial method to set the temperature with the help of variable resistor VR1. VR1 provides a reference voltage that can be set anywhere from 0V to approx. 1V. In our circuit we have set a 0.71V approx at pin 2 which means when temperature reaches above 71 degree Celsius it will give you an indicator with the help of LED. Now when temperature at IC1 increases because of heat from kitchen appliances or PC voltage at pin 2, IC1 also increases which increase the voltage at pin 3 of IC2 and when voltage become more than 0.71 V it will make the output pin 6 high and LED connected to it start blinking. When temperature reaches below the set value, LED stop blinking indicating your device is safe.
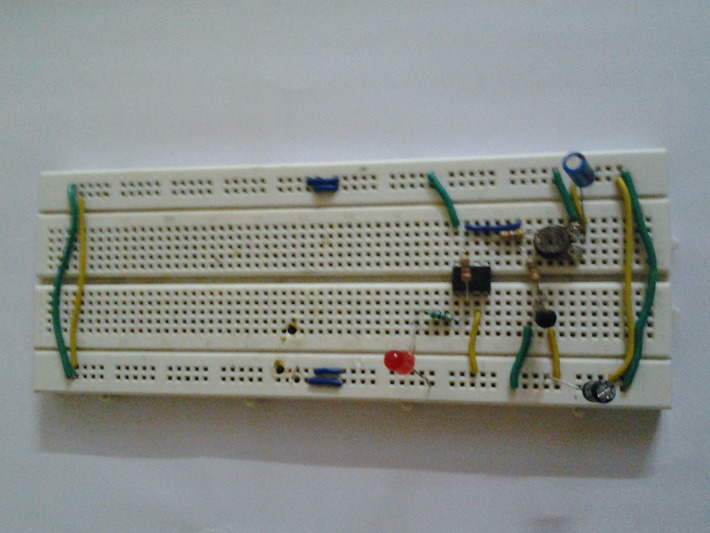
Circuit Diagrams
Project Video
Filed Under: Circuit Design
Filed Under: Circuit Design



Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.