With enhancement in technology, automation has become a need whether it is home, office or some other place. At home we come across many appliances be it fan, AC, TV, lights, etc. What if you could operate all of them with the Android Phone you’re holding in your hand.
Fig. 1: Prototype of Android Mobile controlled Home Automation System
HC-05 module is an easy to use Bluetooth SPP (Serial Port Protocol) module, designed for transparent wireless serial connection setup. It contains 6 pins that are labelled on the back but most modules only have 4 of those populated with pogo pins. KEY & STATE are not required, as KEY is used for flashing the device and STATE simply indicates whether the device is awake or not. So that leaves only GND, VCC, TXD, RXD.
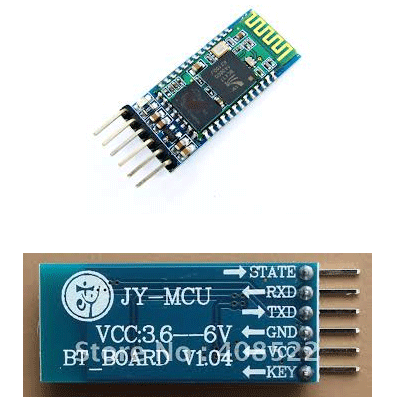
Fig. 2: Typical image of HC-05 Bluetooth Module
For connecting the module with Arduino, we need to use the Serial (Tx and Rx) pins provided on the board.
Connections & Working
Making Connections with HC-05:
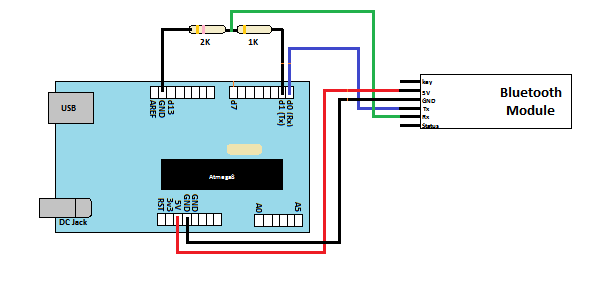
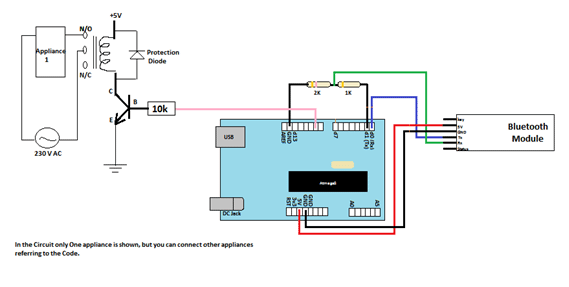
Fig. 3: Image showing circuit connections of Arduino Uno and HC-05 Bluetooth Module
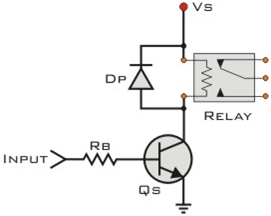
Fig. 4: Circuit Diagram of Transistor based Relay Driver
The ‘Input’ is from Arduino I/O pin. RB is the current limiting resistor at the base of the transistor. Its value is typically 10K Ohm. ‘VS’ is the supply voltage needed to trigger the Relay coil (It depends on the Relay rating). A diode is connected in Reverse in parallel to the relay. This is done to avoid the back e.m.f. generated by coil that can damage the transistor or the Arduino.
A simplified Block diagram of the complete system is shown below:
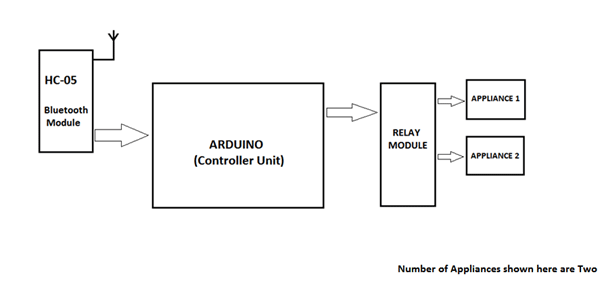
Fig. 5: Block Diagram of Android Mobile controlled Home Automation System
After making above connections, you’ll see blinking led on the module. This just ensures your device is powered properly. After that pick your Android Phone, and get the App- “Arduino Bluetooth Terminal” from the Google Play Store. This app is available for free, and is easy to use.
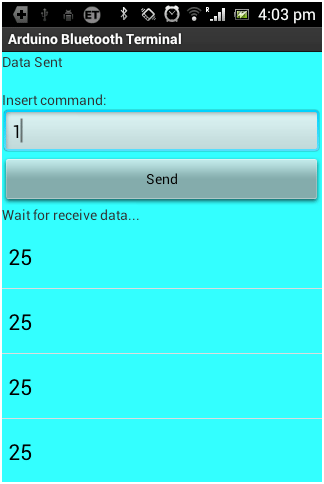
Fig. 6: Screenshot of Android App used to control Home Appliances
After installation, turn ON Bluetooth of phone. Now search for devices until you find HC-05 and then start pairing with it. Enter Password 1234, when asked.
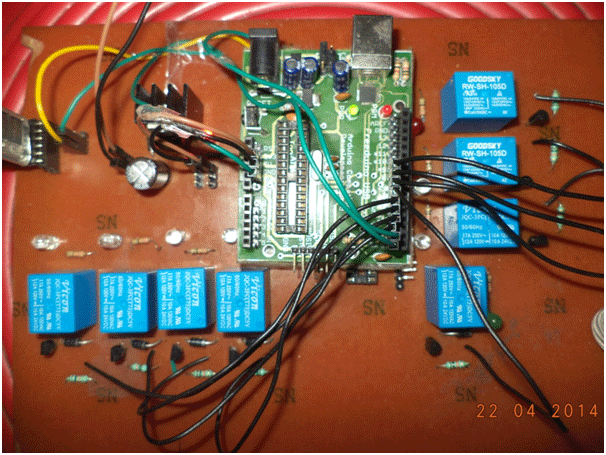
Fig. 7: Image showing complete prototype of Arduino based Android phone controlled Home Automation System
System Operation:
When we send ‘1’ to the Arduino, the Appliance 1 connected to Arduino Turns ON and when ‘2’ is sent, Appliance 2 turns ON. The serial data is read by Arduino, through Serial.read () function and is stored in the integer type variable state declared in the program. After this in the loop(), we just compare state value with 1, 2, 3 and so on till 8 to check the ON condition of 8 Appliances. Then we compare state value with a, b, c and so on till h to check the OFF condition of appliances and perform respective operation.
You may also like:
Project Source Code
### int led1 = 2; int led2 = 3; int led3 = 4; int led4 = 5; int led5 = 6; int led6 = 7; int led7 = 8; int led8 = 9; int state; int flag=0; void setup() { pinMode(led1, OUTPUT); pinMode(led2, OUTPUT); pinMode(led3, OUTPUT); pinMode(led4, OUTPUT); pinMode(led5, OUTPUT); pinMode(led6, OUTPUT); pinMode(led7, OUTPUT); pinMode(led8, OUTPUT); Serial.begin(9600); } void loop() { if(Serial.available() > 0) { state = Serial.read(); flag=0; } if (state == '1') { digitalWrite(led1, HIGH); if(flag == 0){ Serial.println("Appliance 1 is ON"); flag=1; } } else if (state == '2') { digitalWrite(led2, HIGH); if(flag == 0){ Serial.println("Appliance 2 is ON"); flag=1; } } else if (state == '3') { digitalWrite(led3, HIGH); if(flag == 0){ Serial.println("Appliance 3 is ON"); flag=1; } } else if (state == '4') { digitalWrite(led4, HIGH); if(flag == 0){ Serial.println("Appliance 4 is ON"); flag=1; } } else if (state == '5') { digitalWrite(led5, HIGH); if(flag == 0){ Serial.println("Appliance 5 is ON"); flag=1; } } else if (state == '6') { digitalWrite(led6, HIGH); if(flag == 0){ Serial.println("Appliance 6 is ON"); flag=1; } } else if (state == '7') { digitalWrite(led7, HIGH); if(flag == 0){ Serial.println("Appliance 7 is ON"); flag=1; } } else if (state == '8') { digitalWrite(led8, HIGH); if(flag == 0){ Serial.println("Appliance 8 is ON"); flag=1; } } else if (state == 'a') { digitalWrite(led1, LOW); if(flag == 0){ Serial.println("Appliance 1 is OFF"); flag=1; } } else if (state == 'b') { digitalWrite(led2, LOW); if(flag == 0){ Serial.println("Appliance 2 is OFF"); flag=1; } } else if (state == 'c') { digitalWrite(led3, LOW); if(flag == 0){ Serial.println("Appliance 3 is OFF"); flag=1; } } else if (state == 'd') { digitalWrite(led4, LOW); if(flag == 0){ Serial.println("Appliance 4 is OFF"); flag=1; } } else if (state == 'e') { digitalWrite(led5, LOW); if(flag == 0){ Serial.println("Appliance 5 is OFF"); flag=1; } } else if (state == 'f') { digitalWrite(led6, LOW); if(flag == 0){ Serial.println("Appliance 6 is OFF"); flag=1; } } else if (state == 'g') { digitalWrite(led7, LOW); if(flag == 0){ Serial.println("Appliance 7 is OFF"); flag=1; } } else if (state == 'h') { digitalWrite(led8, LOW); if(flag == 0){ Serial.println("Appliance 8 is OFF"); flag=1; } } } ###
Circuit Diagrams
Project Video
Filed Under: Electronic Projects
Filed Under: Electronic Projects




Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.