The Raspberry pi is a single board computer that is designed with an aim of providing help in the computer education to students at school. This is a nice platform to try different programming techniques and learn software tools also. The board is provided with a RCA connector which can be used to connect it directly to a TV screen which is based on PAL and NTSC standard. The board also has a HDMI connector output which can be used to connect the board to a HD TV. One can also use remote login to access the Raspberry pi and view the GUI (Text User Interface) on the PC screen. The Raspberry pi board is also very easy to interface with external devices or circuits through its pin outs. This board is also provided with an audio socket also. All these makes the Raspberry pi a suitable platform for playing and developing interesting games.
The gamepad is a simple circuit built on a breadboard with few buttons, LEDs and a resistor array. There are eight general purpose IO pins on the 13*2 pin connectors of the Raspberrypi board and among them four pins has been selected as input and then remaining four pins as output. The input pins are connected to push button and are pulled down using 1K resistors. The output pins are connected to the LEDs through another set of 1K resistors. For this project the Raspberry pi board is loaded with Ubuntu and is remotely accessed using VNC. To access the pins that coming out of the Broadcom controller the C library “bcm2835” has been downloaded and installed.
mkfifo xyz
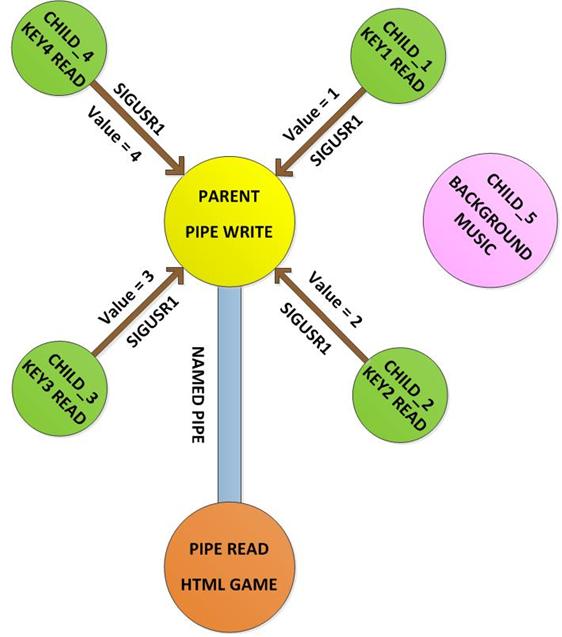
Circuit Diagrams
Project Video
Filed Under: Electronic Projects, Raspberry pi.
Filed Under: Electronic Projects, Raspberry pi.

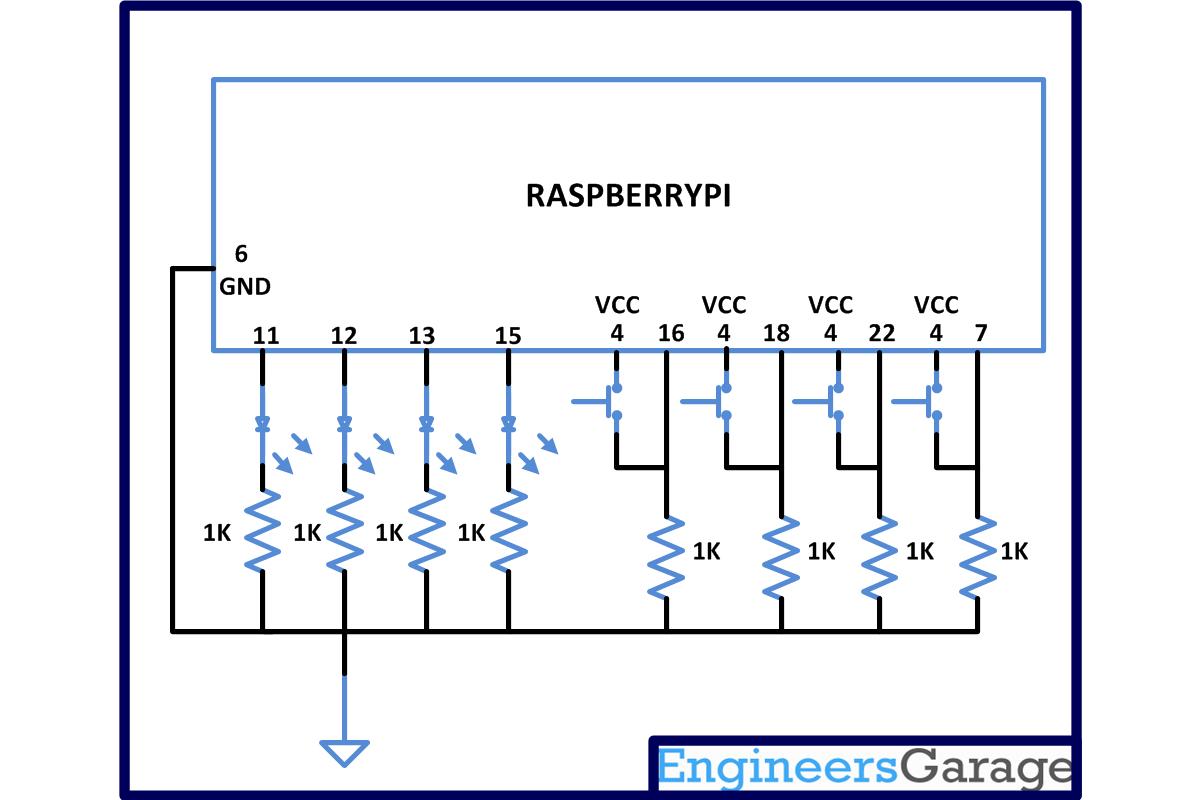

Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.