The Intel and ARM are the two popular processor families widely used in computational device. The Intel processors are mostly used in the Personal Computers whereas the ARM processors are optimized for the embedded system applications. The high end ARM processors can provide embedded system devices with that much computational power as most of the PCs have. The Raspberrypi is a low cost minicomputer board designed to be used as a PC for providing computer education for remote schools, where costly desktops are not available. The embedded system people are interested in it since it is using ARM11 processor based microcontroller and unlike the motherboard of the PC, the Raspberry pi board provides lot of pin outs like GPIO pins, serial communication pins etc. which enable them to be used in embedded system applications.
The Raspberrypi board use Broadcom controller chip which is a SoC (System on Chip). This controller has all the peripherals like timers, interrupt controller, GPIO, USB, PCM / I2S, DMA controller, I2C master, I2C / SPI slave, SPI0, SPI1, SPI2, PWM, UART0 and UART1. This SoC has the powerful ARM11 processor which runs on 700 MHz at its core. The controller also has a graphical processing unit (GPU) which includes VideoCore, MPEG-2 and MPEG-4. It also has a 512 MB SDRAM.
The operating systems like Archlinux ARM, OpenELEC, Pidora, Raspbmc, RISC OS and the Raspbian and also Ubuntu versions are available for the Raspberrypi board. Linux operating systems especially Ubuntu is preferred for all kind of programming and development. This article discusses how to get started with accessing the GPIO pins of the Raspberrypi board using C programming done in Ubuntu.
[[wysiwyg_imageupload:10535:]]
In this project the Raspberrypi board is loaded with Ubuntu and is remotely accessed using VNC. The Raspberrypi board is also connected to the internet. There are 26 connectors which can be taken out from the connector port of the Raspberrypi board. All the connector pins are taken out using 13*2 pin female connectors and at the other end of their wire 26 pin Burg stick male connectors are attached. The Burg stick male connectors allow each pin out from the Raspberrypi board to be plugged into the holes of a breadboard.
To access the pins that coming out of the Broadcom controller of the Raspberrypi board using C language, a C library is available called “bcm2835”. The first step in the process of C coding for accessing the GPIO of the Raspberrypi board is to install the “bcm2835” library. The bcm2835 library is available to download as a zip file which needs to be copied into the /home/pi folder. The zip file appears like bcm2835-1.26.tar.gz in the folder /home/pi.
The zip file should be unzipped first and then start the installation process. All the process here is done using the Linux command line. The command for unzipping the zip folder to is given below:
tar zxvf bcm2835-1.26.tar.gz
This command will unzip the .gz file into a folder named bcm2835-1.26 in which all the source files are present. Now the user should enter that folder to continue the installation process. To enter the folder use the following command;
cd bcm2835-1.26
Now use the following commands one by one to finish the installation process.
./configure
make
sudo make check
sudo make install
Once the installation is completed the library can be included as a header file in any C codes as
#include <bcm2835.h>
The each pin of the Raspberrypi board is declared inside this header file as their pin number or name etc. The functions for accessing those pins are also available in this header file. The pin out details of the raspberrypi board is given below:
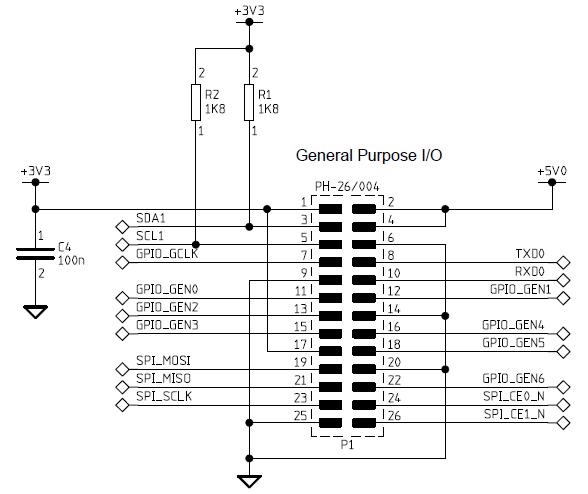
Fig. 2: General Purpose I/O Pins Of Raspberry Pi board
|
PIN NUMBER |
DESCRIPTION |
|
1 |
3.3V |
|
2 |
5V |
|
3 |
SDA |
|
4 |
5V |
|
5 |
SCL
|
|
6 |
GND |
|
7 |
SCK, GPIO_7 |
|
8 |
TX |
|
9 |
GND |
|
10 |
RX |
|
11 |
GPIO_0 |
|
12 |
GPIO_1 |
|
13 |
GPIO_2 |
|
14 |
GND |
|
15 |
GPIO_3 |
|
16 |
GPIO_4 |
|
17 |
3.3V |
|
18 |
GPIO_5 |
|
19 |
MOSI |
|
20 |
GND |
|
21 |
MISO |
|
22 |
GPIO_6 |
|
23 |
SCLK |
|
24 |
CS_1 |
|
25 |
GND |
|
26 |
CS_2 |
Fig. 3: Pin Number And Details Of Raspberrypi Board
The following section discusses how to write a C code for blinking an LED connected to any of the general purpose output pin of the Raspberrypi, say pin number 11 (GPIO_0).
Few functions from the library <bcm2835.h> can be used here and the details of them are given below:
|
No. |
Function |
Description |
Parameters |
Return |
|
1 |
int bcm2835_init(void ) |
initialize the library |
|
1 if successful else 0 |
|
2 |
int bcm2835_close(void ) |
Close the library |
|
1 if successful else 0 |
|
3 |
void bcm2835_gpio_fsel ( uint8_t pin, uint8_t mode ) |
Sets the Function Select register for the given pin, which configures the pin as Input, Output or one of the 6 alternate functions. |
pin: GPIO number mode: Mode to set |
|
|
4 |
void bcm2835_delay ( unsigned int millis ) |
Delays for the specified number of milliseconds |
millis: Delay in milliseconds |
|
Fig. 4: Functions Of Library <bcm2835.h> To Blink LED
The functions are used in the C code for blinking the LED which is given in Code 1 Tab.
The user can use vim editor to write the code and save into a file, say “blink.c”. From command line itself use the following command to compile the code with the new library file to generate the executable file “blink”
cc blink.c -lbcm2835 -o blink
The binary file can be executed using the command:
./blink
As soon as the user enters the command the LED connected to the pin number 11 starts blinking. The execution can be terminated using CTRL + C
Project Source Code
###
//------------------------------------------ led blinking code --------------------------------------------------// #include <bcm2835.h> #define PIN RPI_GPIO_P1_11int main()
{
if (!bcm2835_init()) // initialize the library
return 1;bcm2835_gpio_fsel (PIN, BCM2835_GPIO_FSEL_OUTP); // Set the pin to be an output
while (1)
{
bcm2835_gpio_write(PIN, HIGH); // Turn it on
bcm2835_delay(500); // wait a bit
bcm2835_gpio_write(PIN, LOW); // turn it off
bcm2835_delay(500); // wait a bit
}
bcm2835_close(); // close the libraryreturn 0;
}//------------------------------------------ led blinking code --------------------------------------------------//
###
Project Source Code
###
#include <bcm2835.h>// Blinks on RPi Plug P1 pin 11 (which is GPIO pin 17)
#define PIN RPI_GPIO_P1_11int main()
{
if (!bcm2835_init())
return 1;
// Set the pin to be an output
bcm2835_gpio_fsel(PIN, BCM2835_GPIO_FSEL_OUTP);
// Blink
while (1)
{
// Turn it on
bcm2835_gpio_write(PIN, HIGH);// wait a bit
bcm2835_delay(500);// turn it off
bcm2835_gpio_write(PIN, LOW);// wait a bit
bcm2835_delay(500);
}
bcm2835_close();
return 0;
}
###
Circuit Diagrams
Project Components
Project Video
Filed Under: Electronic Projects, Raspberry pi.
Filed Under: Electronic Projects, Raspberry pi.


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.