The Raspberry pi is a mini computer which is designed in a single board with all the essential components required for running an operating system. The Raspberry pi board runs on a microcontroller from Broadcom with ARM11 processor but is available at extremely cheap price. The board can be powered up from a 5V power adaptor or from the USB port of a PC. The board has two USB2 ports where the keyboard and mouse can be plugged in. The board is provided with a RCA connector which can be used to connect it directly to a TV screen which is based on PAL and NTSC standard. The board also has a HDMI connector output which can be used to connect the board to a HD TV.
There is an Ethernet port which can be used to connect the board to a computer network. Those who don’t want to use a HDTV and separate keyboard and mouse for the Rspberrypi board can plug the board using a LAN cable to the Ethernet port of the PC and do remote access in TUI or GUI mode. The operating systems like Archlinux ARM, OpenELEC, Pidora, Raspbmc, RISC OS and the Raspbian and also Ubuntu versions are available for the Raspberrypi board.
The Raspberrypi board users need to connect the Raspberrypi board with the internet in cases like update the OS, download and install new software to the OS, to use the web browser, to connect the Raspberrypi with other computers etc. This article discusses how to connect the Raspberrypi board with the internet which is plugged directly into the Ethernet port of the PC using a LAN cable.
In this project the Raspberrypi board is booted with the Ubuntu OS and is connected to the Ethernet port of a Windows7 PC. One end of the peer-to-peer LAN cable is connected to the Ethernet port of the Raspberry pi and the other end to the Ethernet port of the PC. It is assumed that the user has Wi-Fi connectivity to the PC where the Raspberrypi board is connected.
In windows the Raspberrypi connected to the Ethernet port of the PC can be provided with the internet access by creating a bridge network adaptor between the Wi-Fi adaptor and the LAN adaptor. The idea is to connect the Raspberrypi board to the Wi-Fi router rather than simply sharing the network connectivity with the board. The advantage is that the Raspberrypi board will be having its own IP and can be connected with all other computers which are connected to that particular Wi-Fi network. Creating the network bridge adaptor is very simple in windows and is discussed below:
In windows machine, go to the Go to the control panel > network and internet > network and sharing center > change adapter settings. The window where all the network adapters are displayed will be opened up. From there select the LAN adapter, right click on it and select the properties.
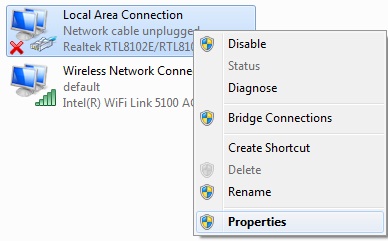
Fig. 2: Changing Network Adapters Setting In Windows
Right click on the ‘Local Area connection’ and select ‘properties’.
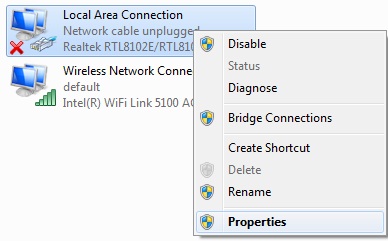
Fig. 3: Select Properties From Local Area Network Option
Select the Internet protocol version 4 (IPV4) and click on the ‘properties’ button.
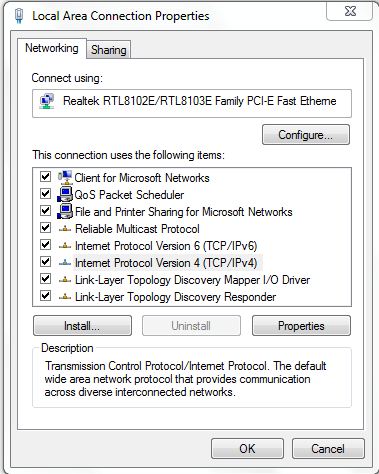
Fig. 4: Select Internet Protocol IPV4 And Click On ‘Properties’
Now click on the button “Obtain IP address automatically” and “Obtain DNS server address automatically” as shown in the following image and click “OK”.
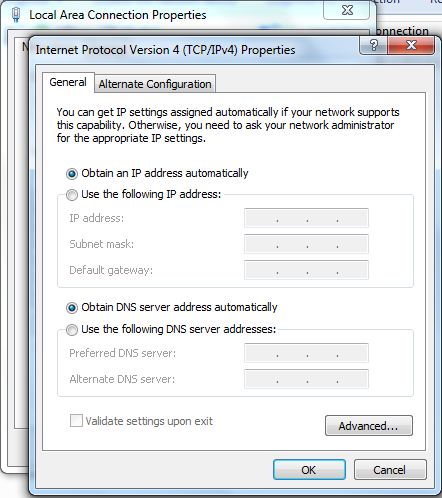
Fig. 5: Obtain IP address and DNS server address for LAN
Now do the same steps with the ‘Wireless Network Adaptor’ also as shown in the following image.
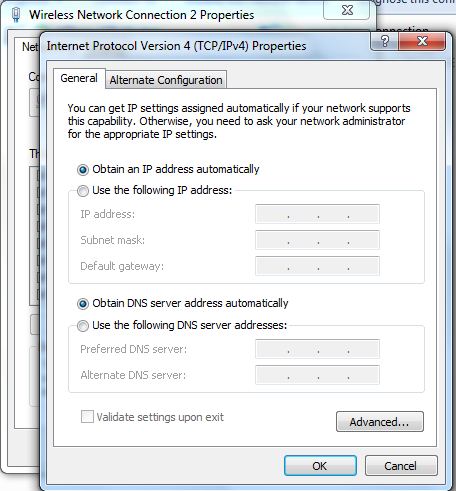
Fig. 6: Obtain IP address and DNS server address using Wireless Network Adaptor
The next step is to create a bridge connection between the two network adaptors ‘Local Area connection’ and the ‘Wireless Network Adaptor’. Hold down the CNTRL key and select the two network adaptors by left click on them. Now right click and select the options “Bridge connections”.
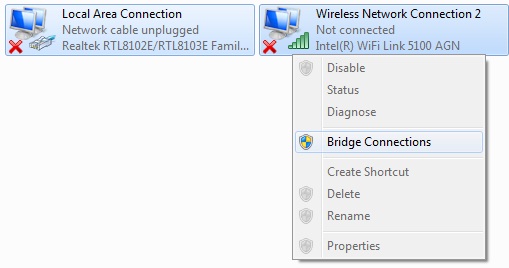
Fig. 7: Bridge Connection Between Network Adaptors
The windows will create a new network adaptor called “Network Bridge” within a couple of seconds after the user clicked on the “Bridge Connections” options. The new network adaptor will appear along with the other adaptors as shown in the following image:
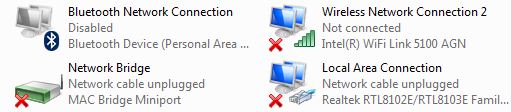
Fig. 8: New network adaptor to connect Raspberry Pi to Wi-Fi
After these steps it is recommended to restart the PC. Once the system boots up again connect the Wi-Fi network and then plug in the Raspberrypi board and power it up. Make sure that the system is getting the net connectivity by pinging it to any website, say Google. Go to All programs > Accessories > Command Prompt and click on it.
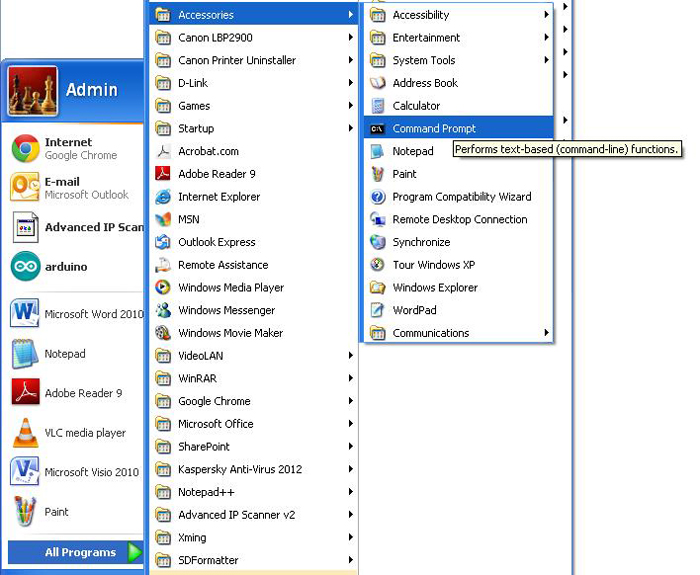
Fig. 9: Click Command Prompt to write text based functions
Type the following commands on the black window which opens up:
ping www.google.com
The above command should return “0% packet loss” within a few seconds and which means the PC is now connected with the internet.
To remote access the Raspberrypi board the user should get the IP provided by the Wi-Fi router to the Raspberrypi board. To get the IP and Hostname of all systems connected with in the network, one can use the following command;
arp -a
Note the IP corresponding to the hostname “raspberrypi” and use the same for remote login with the help of PUTTY. Once logged into the Raspberrypi board, type the same ping command there to confirm that the Raspberrypi is connected with the internet.
ping www.google.com
Note: To get the IP and Hostname of the PC’s connected in the network there are lot of IP scanner software available for download. All the steps discussed in this article are network critical things and errors like ‘IP conflict’ or even temporary blocking of the device by the Wi-Fi router can occur depending upon the network security and other parameters. It is recommended to get expert advice from the network administrator while setting up the connections.
Filed Under: Raspberry pi


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.