This tutorial will explain about how to create socket programming in C language. Socket is virtual end point communication over the network between two hosts or processes. Refer to the tutorial Socket in Linux before learning this tutorial. You always open the Google page in your web browser but do you know how our web browser accesses the Google page form www.google.com? When you type www.google.com in your web browser, it will open the socket and send the request to server (www.google.com). Server always listens to the request from different hosts. When server receives and accepts the request it sends response back to the host (i.e. Local PC). After establishment of connection, server will send the Google page to our web browser.
This tutorial assumes you know about socket in Linux and are aware with C programming language. Linux has standard C library of socket in package named <sys/socket.h> header file. Socket creates file descriptor using the socket ( ) system call.
Socket ( ) system call
The system call socket ( ) creates the end point for communication and returns a descriptor.
Synopsis of function is:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
int socket (int domain, int type, int protocol);
The domain argument specifies a communication domain. This argument selects the protocol family which will be used for communication. These protocols are defined in <sys/socket.h>. The following protocols are included in library:
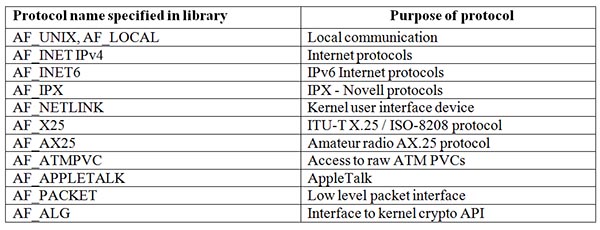
Fig. 1: Table Listing Protocol Names Mentioned in socket.h
The type indicates types of sockets as follows:
SOCK_STREAM – It is a connection oriented bye stream. Data transmission is reliable and flexible.
SOCK_DGRAM – It supports datagram with connection less protocol. Message transmission is unreliable.
SOCK_SEQPACKET – Provides a sequenced, reliable, two-way connection- based data transmission path for datagram of fixed maximum length; a consumer is required to read an entire packet with each input system call.
SOCK_RAW – Provides raw network protocol access.
SOCK_RDM – Provides a reliable datagram layer that does not guarantee ordering.
The default protocol for address family and type will be used if the protocol argument is zero. The specified protocol shall use which is supported by address family if the protocol argument is zero.
The system call socket ( ) returns file descriptor upon success or returns -1 upon error.
Let’s see How to create socket in C programming. We need to call extra library for various purpose of configuration. Here <netinet/in.h> header file defines the internet domain address and <netdb.h > header file defines network database operation.
//*************************************socket.c********************************//
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netdb.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <errno.h>
main()
{
int result;
result = socket (AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (result == -1 )
{
close (result);
exit (EXIT_FAILURE);
}
else
{
printf (“Socket Successfully Created!!!n”);
}
}
//*************************************socket.c********************************//
Save the file in directory and compile it. After successful compilation, run the executable file from command terminal. You may refer to the tutorial How to make first C program in Linux if you are not aware of compilation and execution process.
Here the system call socket ( ) creates the socket file descriptor upon successful execution. AF_INET attribute defines the socket used IPv6 internet protocol and SOCK_STREAM attribute is TCP/IP type of socket with default value indicated by last argument is zero. Upon successful execution of socket ( ), it will return file descriptor and the following line will be printed on the screen:
Socket Successfully Created!!!
If not successfully created, it will return -1 and indicate the error occurred in creation of socket. Specific error type is returned by errno which is located in errno.h file. Program closes the socket file descriptor and exits from execution of program.
Filed Under: Tutorials


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.