This project is an extension to interfacing GPS with 8051. Here the microcontroller interfaced with GPS module is used to obtain latitude, longitude, time, date and speed of the receiver. These received values are displayed on a 16x2 character LCD.
The GPS module continuously transmits serial data (RS232 protocol) in the form of sentences according to NMEA standards. The latitude, longitude, time, date and speed values of the receiver are contained in the GPRMC sentence as given in the following example (also refer NMEA format for other sentences). In this project, these values are extracted from the GPRMC sentence and are displayed on LCD.
Example : $GPRMC,132455.970,A,2651.0145,N,07547.7051,E,0.50,342.76,301010,,,A*64
where:
|
RMC
132455.970
A
2651.0145, N
07547.7051, E
0.50
342.76
301010
Empty field (xxx.x, y)
*64
|
Recommended Minimum sentence C
Fix taken at 13:24:55.970 UTC
Status A=Active or V=Void.
Latitude 26 deg 51.0145′ N
Longitude 075 deg 47.7051′ E
Speed over the ground in knots
Track angle in degrees True
Date : 30th of October 2010
Magnetic Variation
The checksum data, always begins with *
|
The serial data is taken from the GPS module through MAX232 into the SBUF register of 8051 controller (refer serial interfacing with 8051). The serial data from the GPS receiver is taken by using the Serial Interrupt of the controller. This data consists of a sequence of NMEA sentences from which GPRMC sentence is identified and processed.
The extraction of required values is done as follows. The first six bytes of the data received are compared with the pre-stored ($GPRMC) string and if matched then only data is further accounted for; otherwise the process is repeated again. From the comma delimited GPRMC sentence, latitude, longitude, date, time, speed values are extracted by finding the respective comma positions. The values thus extracted are displayed on the LCD interfaced with AT89C51.
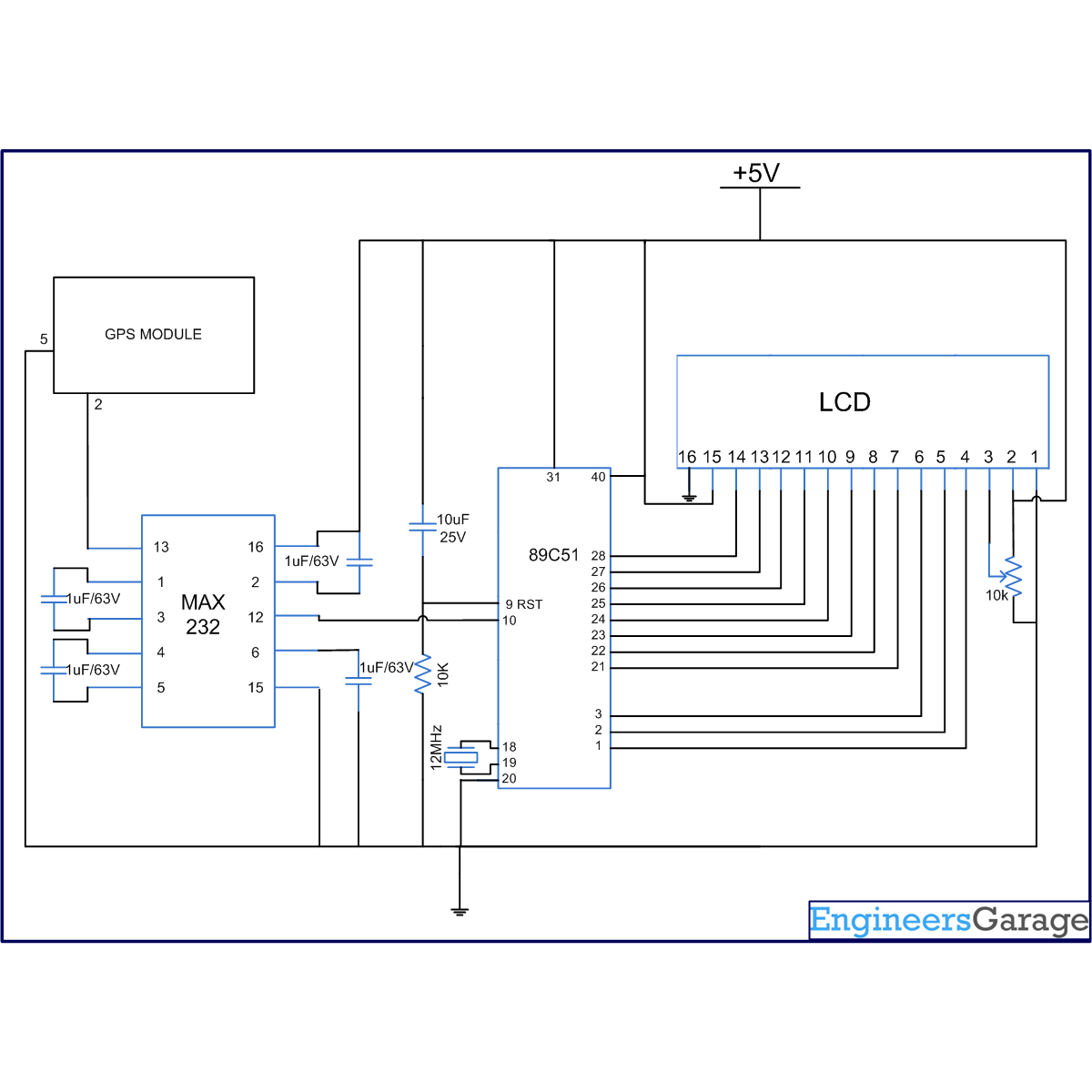
The circuit connections are as follows:
Receiver1 (R1) of MAX232 has been used for the serial communication. The receiver pin of GPS module is connected to R1IN (pin13) of MAX232. R1OUT (pin 12) of MAX232 is connected to RxD (P3.0) of AT89C51.
Pins 1-3 of port P1 (P1.0, P1.1 & P1.2 respectively) of AT89C51 are connected to the control pins (RS, R/W& EN) of LCD. The data pins of LCD are connected to Port P2 of the controller. The latitude and longitude positions are displayed on the LCD.
Project Source Code
###
/* Program to display time date,latitude,longitude,speed on LCD by extracting the GPRMC... ...statement sent by GPS receiver*/ #include<reg51.h> #define port2 P2 sbit rs = P1^0; sbit rw = P1^1; sbit e = P1^2; char info[70]; char test[6]={"$GPRMC"}; char comma_position[13]; unsigned int check=0,i; unsigned char a; void receive_data(); void lcd_time(); void lcd_latitude(); void lcd_longitude(); void lcd_speed(); void lcd_date(); //DELAY FUNCTION void delay(unsigned int msec) { int i,j ; for(i=0;i<msec;i++) for(j=0;j<1275;j++); } // LCD COMMAND SENDING FUNCTION void lcd_cmd(unsigned char item) { port2 = item; rs= 0; rw=0; e=1; delay(1); e=0; return; } // LCD DATA SENDING FUNCTION void lcd_data(unsigned char item) { port2 = item; rs= 1; rw=0; e=1; delay(1); e=0; return; } // LCD STRING SENDING FUNCTION void lcd_string(unsigned char *str) { int i=0; while(str[i]!='�') { lcd_data(str[i]); i++; delay(10); } return; } // SERIAL PORT SETTING void serial() { TMOD=0x20; //MODE=2 TH1=0xfa; // 4800 BAUD SCON=0x50 ; // SERIAL MODE 1 ,8- BIT DATA ,1 STOP BIT ,1 START BIT , RECEIVING ON TR1=1; //TIMER START } void find_comma() { unsigned int i,count=0; for(i=0;i<70;i++) { if(info[i]==',') { comma_position[count++]=i; } } } void compare() { IE=0x00; find_comma(); lcd_time(); lcd_date(); lcd_latitude(); lcd_longitude(); lcd_speed(); check=0; IE=0x90; } void receive_data() interrupt 4 { info[check++]=SBUF; //Read SBUF if(check<7) { if(info[check-1]!=test[check-1]) check=0; } RI=0; } void lcd_time() { unsigned int c1=comma_position[0]; lcd_cmd(0x01); //Clear LCD display lcd_data(comma_position[0]); delay(50); lcd_cmd(0x01); //Clear LCD display lcd_cmd(0x86); //Move cursor to position 6 of line 1 lcd_string("TIME"); //Showing time lcd_cmd(0xC0); //Begining of second line lcd_data(info[c1+1]); //Displaying hours lcd_data(info[c1+2]); lcd_string(":"); lcd_data(info[c1+3]); //Displaying minutes lcd_data(info[c1+4]); lcd_string(":"); lcd_data(info[c1+5]); //Displaying seconds lcd_data(info[c1+6]); lcd_data(info[c1+8]); lcd_data(info[c1+9]); lcd_data(info[c1+10]); delay(250); //Delay, so one can see time } void lcd_shape() //Shape of degree symbol { lcd_cmd(64); lcd_data(10); lcd_data(17); lcd_data(17); lcd_data(10); lcd_data(0); lcd_data(0); lcd_data(0); lcd_data(0); } void lcd_latitude() { unsigned int c3=comma_position[2]; lcd_shape(); lcd_cmd(0x01); //Clear LCD display lcd_cmd(0x84); //Move cursor to position 6 of line 1 lcd_string("LATITUDE"); //Showing latitude lcd_cmd(0xC0); //Begining of second line lcd_data(info[c3+1]); lcd_data(info[c3+2]); lcd_data(0); lcd_data(info[c3+3]); lcd_data(info[c3+4]); lcd_data(info[c3+5]); lcd_data(info[c3+6]); lcd_data(info[c3+7]); lcd_data(info[c3+8]); lcd_data(info[c3+9]); lcd_data(0x27); //ASCII of minute sign(') lcd_data(info[c3+10]); lcd_data(info[c3+11]); delay(250); } void lcd_longitude() { unsigned int c5=comma_position[4]; lcd_cmd(0x01); //Clear LCD display lcd_cmd(0x84); //Move cursor to position 4 of line 1 lcd_string("LONGITUDE"); //Showing longitude lcd_cmd(0xC0); //Begining of second line lcd_data(info[c5+1]); lcd_data(info[c5+2]); lcd_data(info[c5+3]); lcd_data(0); lcd_data(info[c5+4]); lcd_data(info[c5+5]); lcd_data(info[c5+6]); lcd_data(info[c5+7]); lcd_data(info[c5+8]); lcd_data(info[c5+9]); lcd_data(info[c5+10]); lcd_data(0x27); //ASCII of minute sign(') lcd_data(info[c5+11]); lcd_data(info[c5+12]); delay(250); } void lcd_speed() { unsigned int c6=comma_position[6], c7=comma_position[7]; lcd_cmd(0x01); //Clear LCD display lcd_cmd(0x80); //Move cursor to position 5 of line 1 lcd_string("SPEED(inKNOTS)"); //Showing longitude lcd_cmd(0xC0); //Begining of second line for(i=c6+1;i<c7;i++) { lcd_data(info[i]); } lcd_string("KNOTS"); delay(250); } void lcd_date() { unsigned int c9=comma_position[8]; lcd_cmd(0x01); //Clear LCD display lcd_cmd(0x85); //Move cursor to position 5 of line 1 lcd_string("DATE"); lcd_cmd(0xC0); lcd_data(info[c9+1]); lcd_data(info[c9+2]); lcd_data('-'); lcd_data(info[c9+3]); lcd_data(info[c9+4]); lcd_data('-'); lcd_data(info[c9+5]); lcd_data(info[c9+6]); delay(250); } void main() { serial(); lcd_cmd(0x38); //2 LINE, 5X7 MATRIX lcd_cmd(0x0e); //DISPLAY ON, CURSOR BLINKING IE=0x90; while(1) { if(check==69) compare(); } }###
Circuit Diagrams
Project Components
Project Video
Filed Under: 8051 Microcontroller.
Filed Under: 8051 Microcontroller.


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.