The 16x2 character LCD can work in two modes, namely, 8-bit and 4-bit. These modes basically correspond to the number of data pins used in interfacing LCD. 8-bit mode uses all the data lines and has been explained in LCD interfacing with PIC18F4550. In 4-bit mode, only four data pins of LCD are connected to the controller. This mode, thus, saves four pins of the controller unlike 8-bit mode. The configuration and display method of LCD in 4-bit mode has been explained here.
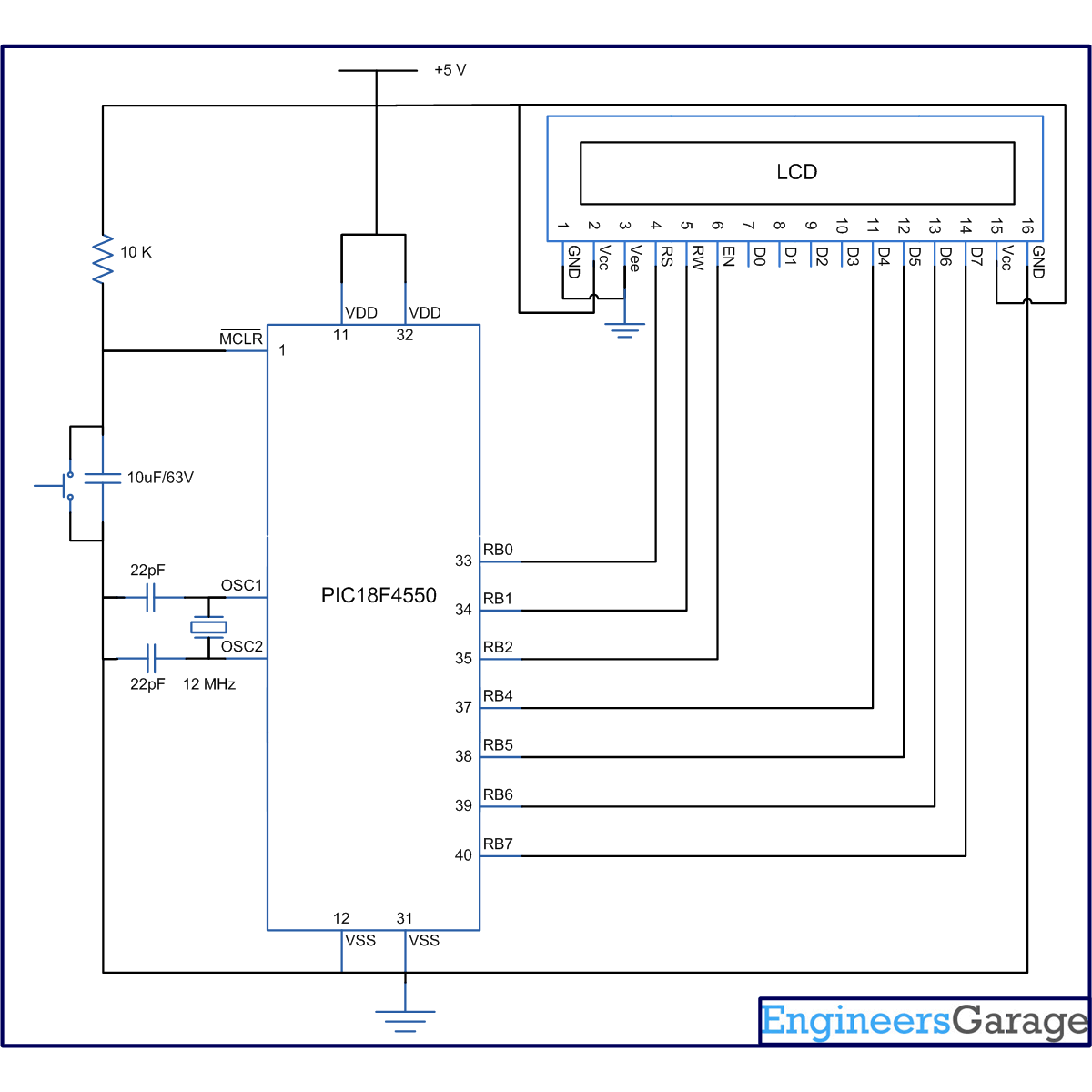
The 8-bit mode of LCD interfacing with PIC has been explained earlier. In the 4-bit mode the (8-bit) data/command is sent in nibble (four bits) format to LCD. The higher nibble is sent first followed by the lower nibble. In 4-bit mode only four data pins (D4-D7) of LCD are connected to the controller. The control pins (RS, RW and EN) are connected the same way as in 8-bit mode. The connections of LCD with PIC18F4550 are shown in the adjoining circuit diagram. Please note that here only PortB is used to connect data lines as well as control lines unlike in 8-bit mode. Refer LCD interfacing with PIC in 8-bit mode.
|
Instruction
|
RS
|
RW
|
D7
|
D6
|
D5
|
D4
|
D3
|
D2
|
D1
|
D0
|
|
Function Set
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
1
|
DL
|
N
|
F
|
–
|
–
|
|
Value
|
DL
|
N
|
F
|
|
1
|
8 bit
|
2 lines
|
5×10 dots
|
|
0
|
4 bit
|
1 line
|
5×7 dots
|
Project Source Code
###
// Program to interface 16x2 LCD with PIC18F4550 Microcontroller using 4-bit mode // Configuration bits /* _CPUDIV_OSC1_PLL2_1L, // Divide clock by 2 _FOSC_HS_1H, // Select High Speed (HS) oscillator _WDT_OFF_2H, // Watchdog Timer off MCLRE_ON_3H // Master Clear on */ //LCD Control pins #define rs LATA.F0 #define rw LATA.F1 #define en LATA.F2 //LCD Data pins #define lcdport LATB void lcd_ini(); void dis_cmd(unsigned char); void dis_data(unsigned char); void lcdcmd(unsigned char); void lcddata(unsigned char); void main(void) { unsigned char data0[]="EngineersGarage"; unsigned int i=0; TRISB=0; // Configure Port B as output port LATB=0; lcd_ini(); // LCD initialization while(data0[i]!='�') { dis_data(data0[i]); Delay_ms(200); i++; } } void lcd_ini() { dis_cmd(0x02); // To initialize LCD in 4-bit mode. dis_cmd(0x28); // To initialize LCD in 2 lines, 5x7 dots and 4bit mode. dis_cmd(0x0C); dis_cmd(0x06); dis_cmd(0x80); } void dis_cmd(unsigned char cmd_value) { unsigned char cmd_value1; cmd_value1 = (cmd_value & 0xF0); // Mask lower nibble because RB4-RB7 pins are being used lcdcmd(cmd_value1); // Send to LCD cmd_value1 = ((cmd_value<<4) & 0xF0); // Shift 4-bit and mask lcdcmd(cmd_value1); // Send to LCD } void dis_data(unsigned char data_value) { unsigned char data_value1; data_value1=(data_value&0xF0); lcddata(data_value1); data_value1=((data_value<<4)&0xF0); lcddata(data_value1); } void lcdcmd(unsigned char cmdout) { lcdport=cmdout; //Send command to lcdport=PORTB rs=0; rw=0; en=1; Delay_ms(10); en=0; } void lcddata(unsigned char dataout) { lcdport=dataout; //Send data to lcdport=PORTB rs=1; rw=0; en=1; Delay_ms(10); en=0; }###
Circuit Diagrams
Project Components
Project Video
Filed Under: PIC Microcontroller.
Filed Under: PIC Microcontroller.


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.