The given article demonstrates how to measure frequency and duty cycle of pulses using arduino. Frequency measurement is required in so many different applications. In communication field frequency measurement is at most essential. Duty cycle is also an important parameter to measure because it gives % of pulse width – means ON time of the pulse. In DC motor speed control and servo motor angle control, it is required to measure the width of the pulse. Also, the pulse width is measured to check the symmetry of pulse in some of the application like a digital signal receiver, repeaters etc. So let us see how we can use arduino to measure frequency and duty cycle of pulses. In given project, the arduino measures frequency, ON time, OFF time and duty cycle of pulses and displays them on 16×4 LCD.
DESCRIPTION
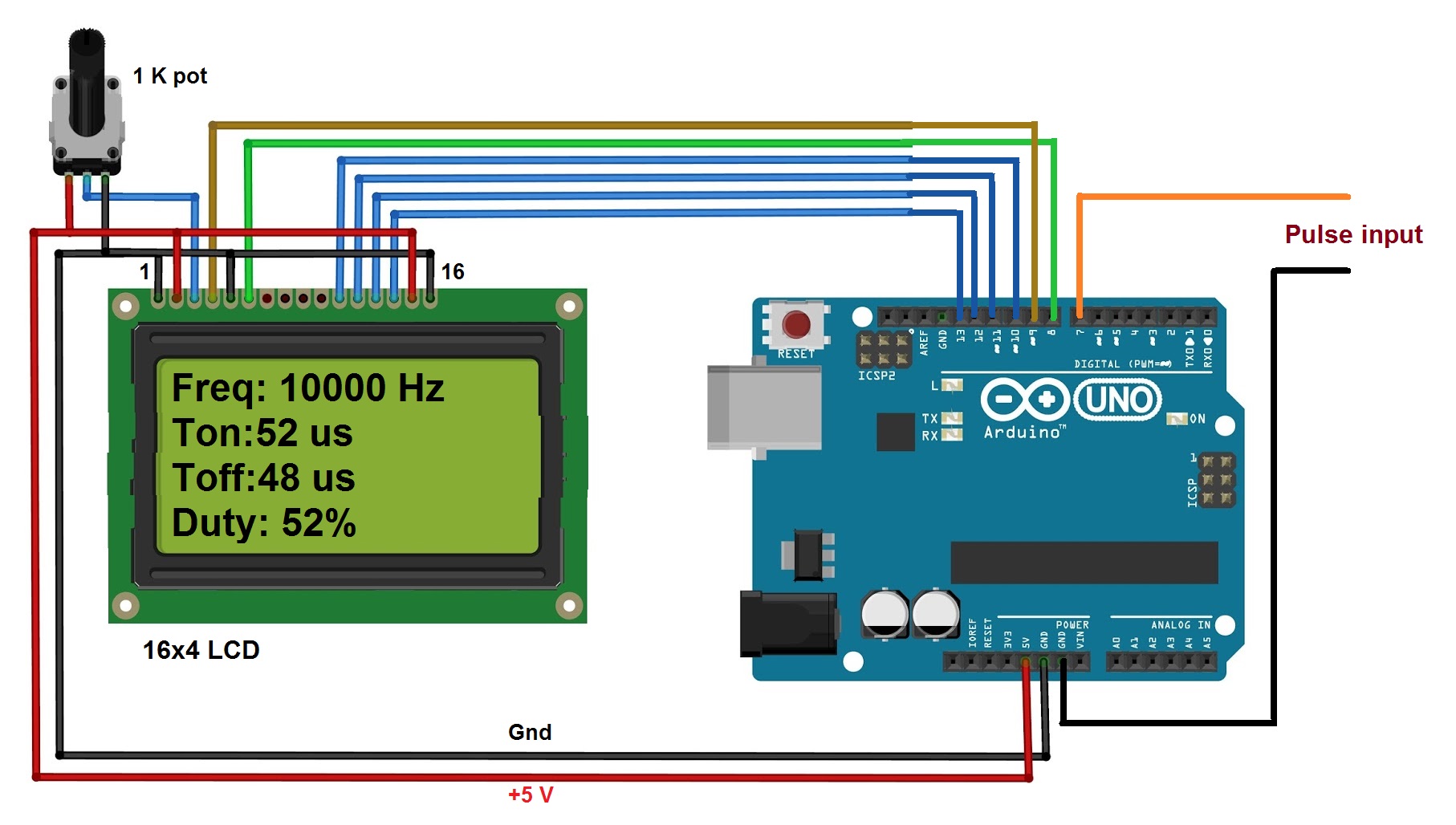
As shown in above figure there is only two major components in the circuit (1) arduino UNO development board and (2) 16×4 LCD display.
• The pulses are directly given as an input to digital pin 7 of arduino.
• The Rs and En pins of LCD are connected to digital pins 9 and 8 respectively of arduino board. Rw pin is connected to ground.
• Last four data pins D4 – D7 are connected to arduino pins 10, 11, 12 and 13.
• The anode pin of backlight LED (pin 15) and Vcc pin (2) of LCD are given 5 V supply through arduino board.
• The cathode of backlight LED (pin 16) and Vss pin (1) are connected to ground.
• One 1 K pot is connected to Vee pin to vary LCD contras.
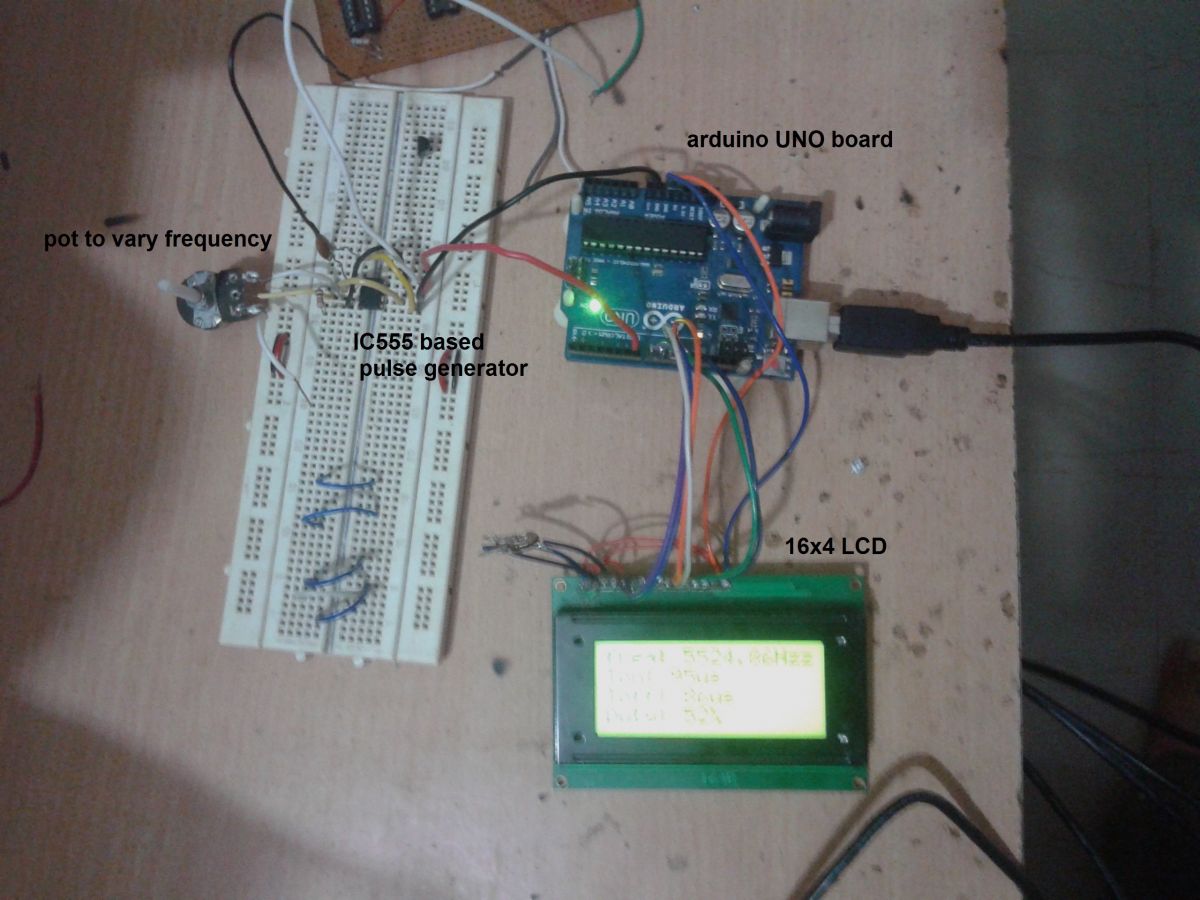
Fig. 1: Prototype of Arduino based Frequency and Duty Cycle Meter
CIRCUIT OPERATION
• When arduino board is given supply through USB, four parameters are displayed on LCD as “freq: Ton: Toff: Duty” on each row as shown.
• Now when pulses are fed to pin 7, the arduino first wait for the pulse to be high. When it becomes high it calculates the time period (in a micro second) for which the pulse remains high. This it Ton time.
• Then it calculated time period (in a micro second) for which pulse remains low. This is Toff time.
• Then it adds these two-time intervals to get total time – means period.
• From the total time the arduino calculates frequency as -:
Frequency = 1 / time
• And from Ton and Toff it calculates duty as -:
Duty = Ton / (Ton + Toff)
• Then it displays all four parameters on LCD.
• Again after 1 second, it repeats the same procedure.
• So it continuously measures the change in frequency and duty cycle of the pulse.
Project Source Code
###
#include <LiquidCrystal.h> LiquidCrystal lcd(8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13); #define pulse_ip 7 int ontime,offtime,duty; float freq,period; void setup() { pinMode(pulse_ip,INPUT); lcd.begin(16, 4); lcd.clear(); lcd.print("Freq:"); lcd.setCursor(0,1); lcd.print("Ton:"); lcd.setCursor(0,2); lcd.print("Toff:"); lcd.setCursor(0,3); lcd.print("Duty:"); } void loop() { ontime = pulseIn(pulse_ip,HIGH); offtime = pulseIn(pulse_ip,LOW); period = ontime+offtime; freq = 1000000.0/period; duty = (ontime/period)*100; lcd.setCursor(4,1); lcd.print(ontime); lcd.print("us"); lcd.setCursor(5,2); lcd.print(offtime); lcd.print("us"); lcd.setCursor(5,0); lcd.print(freq); lcd.print("Hz"); lcd.setCursor(6,3); lcd.print(duty); lcd.print('%'); delay(1000); }###
Circuit Diagrams
Project Video
Filed Under: Electronic Projects
Filed Under: Electronic Projects


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.