AT24C02 is two-wire serially programmable EEPROM. This means that for programming, the data and control signals are provided serially along with clock signals from the other wire. The read-write operations are accomplished by sending a set of control signals including the address and/or data bits from a microcontroller.
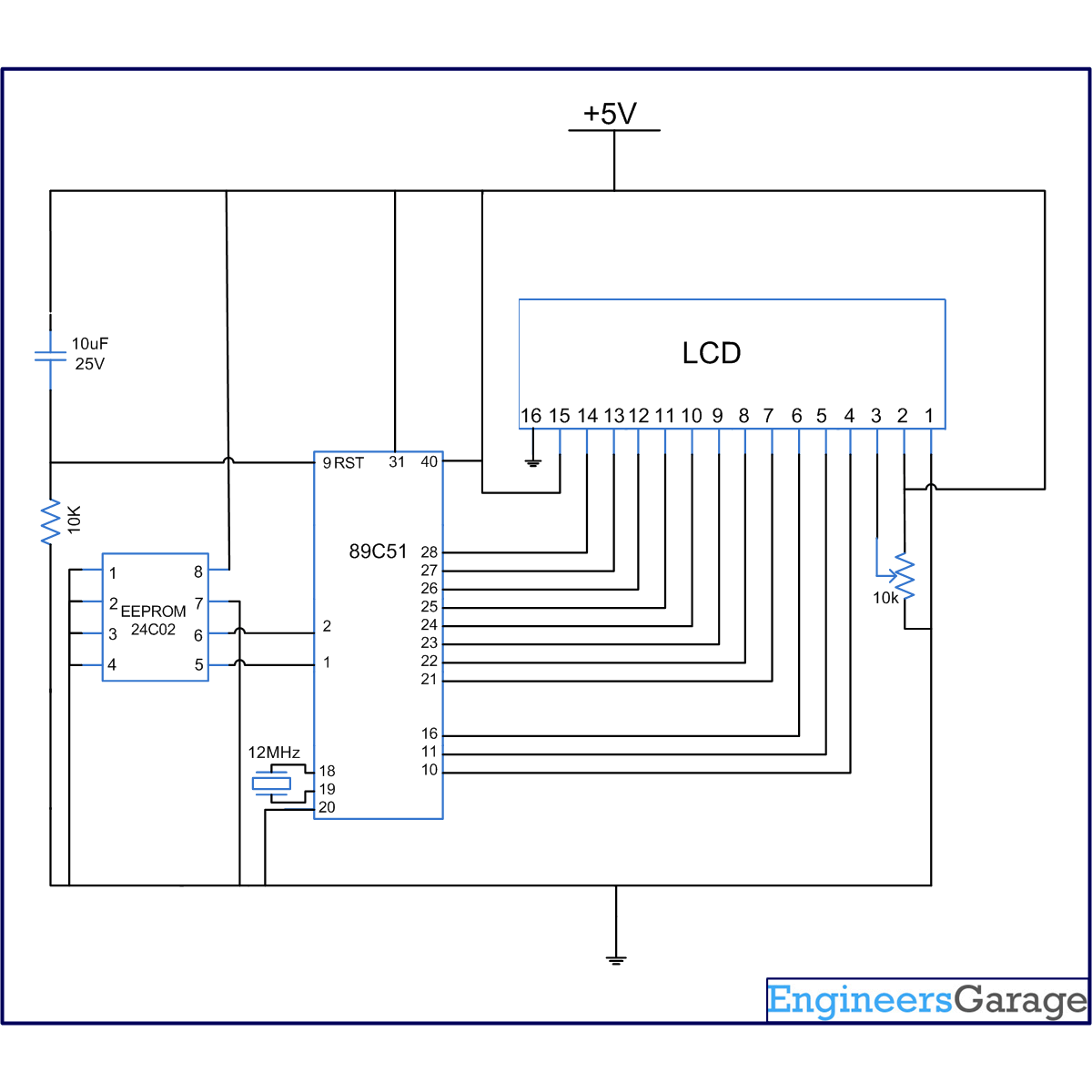
AT24C02 is a two-wire serial EEPROM from Atmel. 24C02 is an 8 pin IC and reads 8 bit data serially. Its memory size is 2KB. Pins 1- 3 are address pins which are connected to ground. Pin 4 is GND; Pin 5 is SDA (serial data); and pin 6 is SCL (serial clock input). Pin 7 is WP (write protect) pin and is connected to GND. Pin 8 is Vcc for providing power supply. For details on its interfacing and operation, refer interfacing 24C02 with 8051.

Project Source Code
###
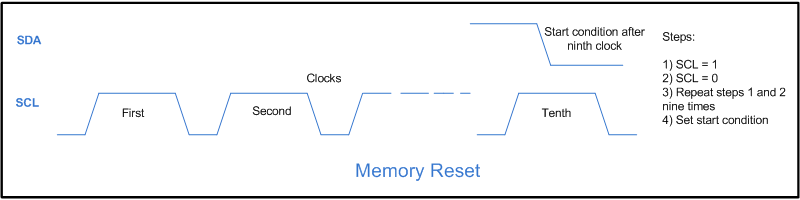
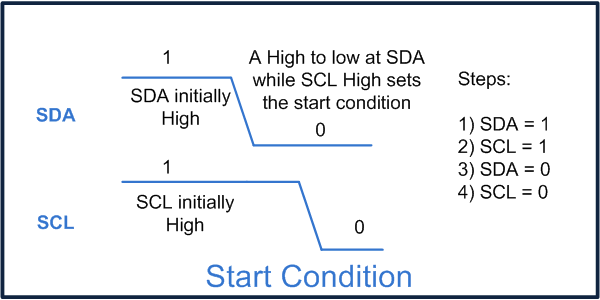
//Program for Memory Reset of Serial EEPROM 24C02 using 8051 microcontroller (AT89C51) #include<reg51.h> #include<intrins.h> //For using [_nop_()] 'No operation' sbit sda=P1^0; sbit scl=P1^1; sbit led=P0^3; bit ack; sbit led1=P0^1; sfr lcd_data_pin=0xA0; //Port P2 sfr output=0x80; //Port P0 sbit rs=P3^0; sbit rw=P3^1; sbit en=P3^6; unsigned char reead,write,write2,i,j; unsigned int temp; void delay(unsigned int count) { int i,j; for(i=0;i<count;i++) for(j=0;j<1275;j++); } void lcd_command(unsigned char comm) { lcd_data_pin=comm; en=1; rs=0; rw=0; delay(1); en=0; } void lcd_data(unsigned char disp) { lcd_data_pin=disp; en=1; rs=1; rw=0; delay(1); en=0; } lcd_dataa(unsigned char *disp) { int x; for(x=0;disp[x]!=0;x++) { lcd_data(disp[x]); } } void lcd_ini() { lcd_command(0x38); // for using 8-bit 2 row LCD delay(5); lcd_command(0x0F); // for display on cursor blinking delay(5); lcd_command(0x80); delay(5); } void aknowledge() { scl=1; _nop_(); _nop_(); scl=0; } void start() //Start condition { sda=1; scl=1; _nop_(); _nop_(); sda=0; scl=0; } void stop() //Stop condition { sda=0; scl=1; _nop_(); _nop_(); sda=1; scl=0; } void send_byte(unsigned char value) { unsigned int i; unsigned char send; send=value; for(i=0;i<8;i++) { sda=send/128; send=send<<1; scl=1; _nop_(); _nop_(); scl=0; } ack=sda; sda=0; } unsigned char read_byte() { unsigned int i; sda=1; reead=0; for(i=0;i<8;i++) { reead=reead<<1; scl=1; _nop_(); _nop_(); if(sda==1) reead++; scl=0; } sda=0; return reead; } void Read() //Read operation { start(); send_byte(0xA0); aknowledge(); send_byte(0x00); aknowledge(); start(); send_byte(0xA1); aknowledge(); i=read_byte(); aknowledge(); j=read_byte(); aknowledge(); stop(); if(i==5) { led=0; delay(100); led=1; delay(100); write=i+48; lcd_command(0xC6); lcd_data(write); } else { led=1; lcd_command(0xC6); lcd_dataa(' '); } if(j==65) { lcd_command(0xC7); lcd_data(j); } else { lcd_command(0xC7); lcd_data(' '); } aknowledge(); i=0; j=0; } void main() { int k,l,m=0; k=0; l=0; lcd_ini(); lcd_dataa("Sent :"); lcd_command(0xC0); lcd_dataa("Read :"); temp=0; start(); while(1) { while(k<9) //9 times cycle { k++; aknowledge(); } if(k==9) { k=0; start(); //Start condition after 9 times clocking } Read(); } }###
Circuit Diagrams
Project Components
Project Video
Filed Under: 8051 Microcontroller.
Filed Under: 8051 Microcontroller.


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.