In Part I and Part II of this series, we learned how to use an analog sensor — including a potentiometer (POT), a light-dependent resistor (LDR), and a soil-moisture sensor — to present values on an organic light-emitting diode (OLED) display.
In Part III, we’ll also present data on an OLED display, but this time using a digital temperature and humidity sensor, the DHT11.
Refer to Part I for a discussion about the basics of an OLED display and how to properly interface it with Arduino.
The DHT11
The DHT11 is a low-cost digital sensor that senses temperature and humidity. Humidity is the measure of water vapor that’s present in the air.
There are two types of humidity sensors, based on their measurement units:
- An absolute humidity sensor – the measure of water vapor in the air, regardless of temperature, expressed as grams of moisture per cubic meter of air.
- A relative humidity sensor – the measure of water vapor in the air relative to the temperature, expressed as the amount of water vapor in the air as a percentage of the total amount that could be held at its current temperature.
The DHT11 measures the relative humidity in the environment. To measure the temperature, this sensor uses a thermistor. It also has an in-built chip (IC) that provides an analog-to-digital conversion and the digital signal output as the temperature and humidity.
Working principle of the DHT11
Along with the thermistor, the DHT11 sensor has a capacitive humidity sensing element. This capacitor has two electrodes with a moisture-holding substrate that serves as a dielectric, which is an electrical insulator, between the two.
A change in the capacitance value occurs when there is a change in humidity levels. The in-built chip measures the change in the capacitor and converts it into a digital value of relative humidity.
To measure the temperature, the DHT11 uses a negative temperature coefficient thermistor, which causes a decrease in the resistance value when there is an increase in temperature. Typically, the sensor is made of semiconductor ceramics or polymers to ensure a greater resistance value when there is even a slight change in temperature.
The in-built chip measures this change in resistance and converts it into a digital value in Celsius.
Specifications
- Voltage ratings: 3 – 5V
- I/O voltage range: 3 – 5 V
- Current ratings: 2.5mA (max current use during conversion – while requesting data)
- Humidity range: 20-80% (5% accuracy)
- Temperature range: 0-50° C ( ±2° C accuracy)
- Sampling rate: 1 Hz max (output readings update after every second)
- Dimension: 15.5 x 12 x 5.5mm
Pin outs and functions
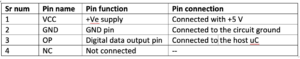
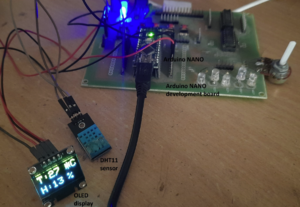
For this project, we use the DHT11 module, which can easily and directly connect with Arduino. This sensor has one 10K pull-up resistor, which connects between the VCC and data-output pins. It only has three pins instead of the typical four. It also has a power ON LED indicator.
Circuit diagram
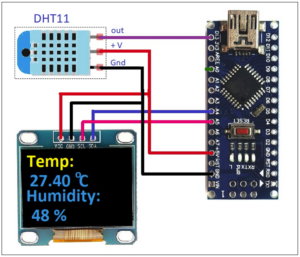
Circuit connections
The circuit is built using only three components:
1. The Arduino NANO board
2. An OLED display
3. The DHT11 module
- The DHT11 module has three pins: the +V, GND, and signal (op) pin. The +V and GND pins are connected with Arduino’s +5 V and GND pins. The signal pin is connected to Arduino’s digital pin 13.
- The OLED has four interfacing pins (as discussed in Part 1): the VCC, GND, SDA, and SCL. The VCC and GND pins are connected with Arduino’s +5 V and GND pins, providing the power supply to the display. The SDA and SCL pins are connected with Arduino’s A4 (SDA) and A5 (SCL) pins for data communication.
- Arduino receives its power supply from a computer’s USB port. The onboard voltage regulator chip provides a 5V supply to the DHT11 module and OLED display.
Circuit operation
- The DHT11 module senses the room temperature and humidity, providing direct values of the temperature in oC and humidity in % RH.
- These values are read by Arduino, which used the DHT.h library to read the temperature and humidity.
- Arduino then displays both the temperature and humidity values on the OLED display
Software program
The Arduino board microcontroller (ATMega328) performs these tasks because of the below program:
1. Reads the temperature and humidity values from the DHT11 sensor.
2. Displays the values of the temperature and humidity on the OLED display.
This program is written in C/C++ language using Arduino IDE’s software. It’s also compiled and uploaded to Arduino’s microcontroller using the same software.
The program…
Video
You may also like:
Filed Under: Electronic Projects, Featured, Sensors