Most of us today do our shopping online and we pay for all the merchandise and services using online or mobile banking, but to complete the transaction one requires OTP (One Time Password) from the bank providing online banking. At the point of convenience we forget that the SMS containing the OTP is been routed through the Service Providers exposing the confidential data to an unauthorised person (The third party at the service provider company).The same thing happens when certain amount is debited or credited to your account and the details of the last transaction with current balance information will be sent to you through SMS via GSM with arduino . It is assumed that the reader has gone through the project how to get started with the Arduino and how to interface lcd with Arduino ..
In the following project of DENcryptor we present and implement a method to send your account credentials from your bank to you using AES and decrypt to get the secured details off of it.
The word DENcryptor is a play on De-cryptor and En-cryptor.

Fig. 1: Prototype of Arduino based DENcryptor Implementation for Secure Messaging
HARDWARE COMPONENTS REQUIRED:
1. Arduino UNO/ Freeduino / Teensy / MSP430 / compatible microcontroller board

Fig. 2: Image of Arduino Board
2. GSM Modem (SIM 900/ SIM 300)
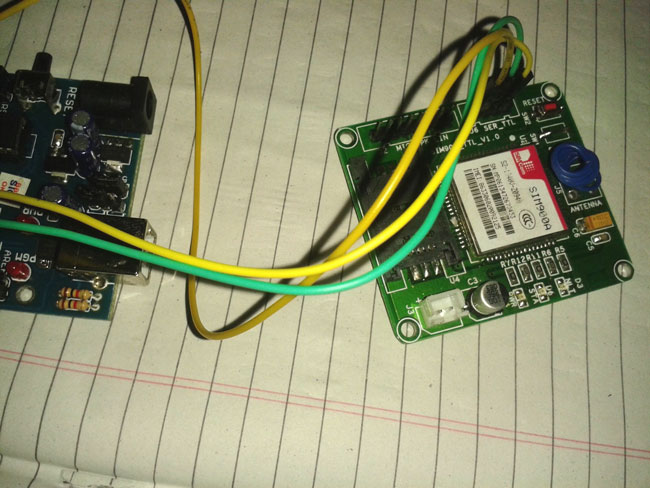
Fig. 3: Image of SIM900 GSM Modem
3. Adapter 5v – 2A (Compatible with GSM modem)

Fig. 4: Image of 16X2 Character LCD from back side
5. USB Cable Type A to Type B, Jumper wires
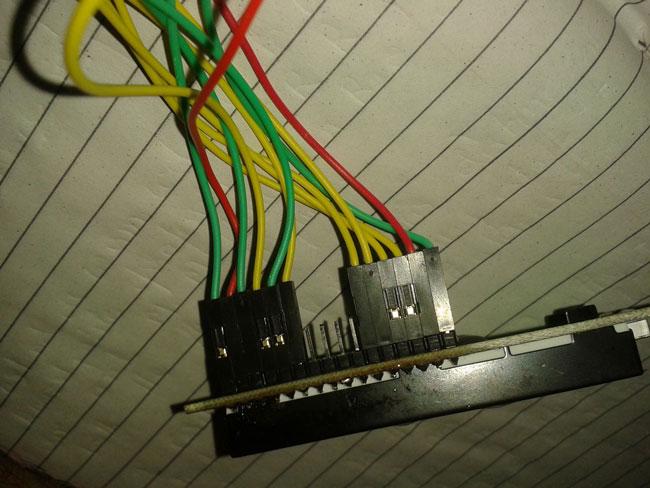
Fig. 5: Image showing jumper wire connections with Character LCD
Encryption
BASIC IDEA OF ENCRYPTION:
Encryption is a technique of masking the information from unauthorised personal, there are plenty of methods of encrypting the information the science of which is called cryptography.
We unknowingly use the encryption in everyday life on internet while accessing mails, viewing bank credentials or even when chatting with someone on Facebook. The act of encryption remains hidden but is very essential to guard your privacy from preying eyes of hackers.
AES is one of the most popular and widely accepted encryption scheme in the digital world. Using this to encrypt the SMS data creates a very high layer of safety and simplicity.
BLOCK DIAGRAM:
TRANSMISSION END (BANK)
As shown in figure it makes use of the customer database for using a cipher key and encrypts the credentials like balance statement or OTPs and send it via GSM Modem

Fig. 6: Block Diagram of Arduino based AES Encryption and AES Decryption Devices
RECEPTION END (CONSUMER)
IMPLEMENTATION BOOT UP:
Before we start up with writing the codes to interface Arduino to GSM or an LCD we need to setup a basic encryption methodology. To obtain the AES cipher text DENcryptor makes use of one of the standard libraries in C available online at (also included as attachment with the mail) although this library is written keeping Texas Instruments MSP430 microcontroller in mind it works really well with the rest of the microcontrollers as well.
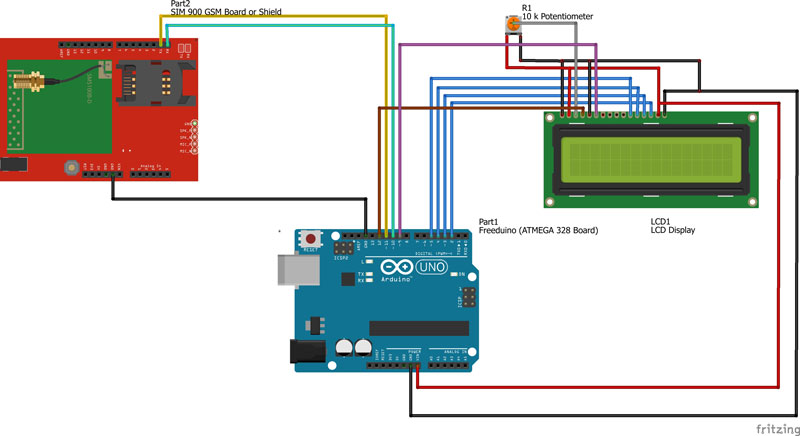
WIRING:
The following circuit uses 4 bit mode of 16×2 LCD Display to efficiently utilize the pins on the Freeduino. The communication with the GSM board is done using the software serial pins which in this case is pin 11 and 10, the detailed wiring is as given below.
ALGORITHM:
The communication between the GSM modem and the Arduino is done using the AT (Attention Telephone) commands the various commands used are as follows,
|
AT Commands |
Parameters / Function |
Response |
|
AT |
– |
OK |
|
AT+IPR=? |
AT+IPR=9600 or AT+IPR=4800 |
Gives / Sets supported baud rates |
|
AT+CMGF=1 |
sets the modem to text mode |
OK |
|
AT+CNMI=2,2,0,0,0 |
Set new message indication modes, Unsolicited, Detailed etc. |
OK |
|
AT+CSMP=17,167,0,0 |
Sets encoding method |
OK |
|
AT+CSCS=”IRA” |
Set character mode to ASCII |
Ok |
|
AT+CSCS=”GSM” |
Set mode to send message back to the modem |
OK |
|
AT+CSCS=”UCS2” |
Sets text encoding to Unicode |
OK |
|
AT+CMGR=1 |
Read the last SMS received or stored |
Displays the SMS |
Note: The communication with the GSM Modem is at a baud rate of 115200 by default, but the Modem baud rate can be brought down to work at 9600 which is sufficient and has a very good Signal to Noise ratio for error free transmission. This is done by sending following AT command.
AT+IPR=9600
If there is no response at the beginning of transmission keep sending the characters ‘A’ this should reset the baud rate for that particular session.
The GSM modem requires the commands to be terminated with a CR,LF or CR+LF to complete the transmission or else results in displaying back the sent text. The termination character is dependent on type of the GSM Modem. The implemented program has been written taking only CR (r) as the terminal character.
LIBRARIES:
TI_AES
The TI_AES Library is a library with two main functions that are called to achieve 128 bit encryption or decryption on the states using a pre-set key.
aes_encrypt(unsigned char *state, unsigned char *key);
aes_decrypt(unsigned char *state, unsigned char *key);
The above two functions change the values store in states corresponding to the function.
LiquidCrystal
This is predefined library in Arduino which implement the interfacing part with a 16×2 LCD display.
The LCD pins for reset, enable and data D0 – D3 are set by pins 12, 9, 5, 4, 3, 2 using the function call
LiquidCrystal lcd(12, 9, 5, 4, 3, 2);
SoftwareSerial
This is one more predefined library which is used to convert GPIO pins on an Arduino to UART.
The problem with the SoftwareSerial library that has been predefined is that it has default buffer size of 64bytes but when an SMS is received by a GSM in unsolicited mode it will send all the data the relates to message such as senders number time and date message length message storage location index and the original message itself which will exceed this buffer size and creates an overflow. To avoid the buffer overflow condition a small change has to made in the SoftwareSerial.h header file as follows,
- Open the Arduino Installed Folder
- Search the folder and all subdirectories with the keyword SoftwareSerial.h (Its almost always will be available at LIBRARY or LIB folder but sometimes this has been moved to avr depending on version and the derivative of the software like Teensyduino)
- Open the file with notepad or Notepad++ while making sure that the text editor which is opening the said file as the administrative rights to make any modifications to it.
- In the 43rd line replace the Rx buffer size 64byte with 256bytes as follows
#define _SS_MAX_RX_BUFF 64 // RX buffer size
Replace With
#define _SS_MAX_RX_BUFF 256 // RX buffer size
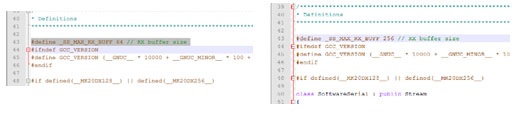
Fig. 7: Screenshot of Arduino Code in Software Serial Library
Note: by using the call SoftwareSerial mySerial(10, 11); we make the pin 10 as RX and 11 as TX
All the communication from moment of initialization are done using mySerial as the object of type SoftwareSerialusing various function calls, such as
· mySerial.print(“Transmits this text”);
· mySerial.read(); reads a byte of data from the modem
· mySerial.available(); evaluates the availability of data in the RX buffer
· mySerial.flush(); flush the buffer
And soon.
AFTER COMPLETION: used ram and rom
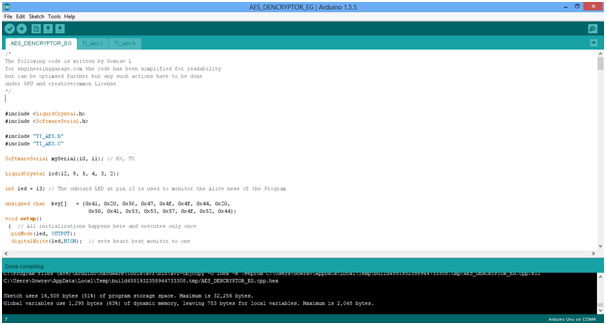
Fig. 8: Screenshot of Arduino Code for AES Decryption
Testing Methodology & Output
TESTING METHODOLOGY:
Make all required connections as said above connect the wires insert simacard to gsm modem burn the program on to Arduino using upload button, Nowits ready to test
Note: Cipher Key is : A VGOOD PASSWORD
Plaintext : 1A2B3C4D5E6F7G8H
CIPHER TEXT :?”*^(&*(M // like this so we are using hex-ascii
In hex
Plain text=4142434445464748494a4b4c4d4e4f50, Key=412056474f4f442050415353574f5244, Cipher text=df4073b52b4b2f41a23120b35ccc16c7
MESSAGE TO DECRYPT
Send sms to the sim on the gsm board as
YOUR OTP IS D<DF4073B52B4B2F41A23120B35CCC16C7>
This will diplay the plain text as 1A2B3C4D5E6F7G8H on LCD
MESSAGE TO ENCRYPT
Send sms to the sim on the gsm board as
YOUR OTP IS E<1A2B3C4D5E6F7G8H>
This will diplay the cipher text as DF4073B52B4B2F41A23120B35CCC16C7on LCD
MESSAGE TO SET KEY
Send sms to the sim on the gsm board as
YOUR OTP IS K<412056474F4F442050415353574F5244> this will set the new cipher key
This will diplay the New Key as 412056474F4F442050415353574F5244ON LCD
Some other combinations (note: Plain text is in Hex conversion required)
PLAIN TEXT=4142434445464748494A4B4C4D4E4F50, KEY=412056474F4F442050415353574F5244, CIPHER TEXT=DF4073B52B4B2F41A23120B35CCC16C7
PLAIN TEXT=41414141414141414141414141414142, KEY=412056474F4F442050415353574F5244, CIPHER TEXT=FA3991AD512BF5E50F15D13787B0EF7A
PLAIN TEXT=41424142414241424142414241424142, KEY=412056474F4F442050415353574F5244, CIPHER TEXT=D1AAA99CA3530FA43C3B9BC56E0747D3
PLAIN TEXT=5A5A5A5A5A5A5A5A5A5A5A5A5A5A5A59, KEY=412056474F4F442050415353574F5244, CIPHER TEXT=0D3E1749F9A96FE0A7BD987100106EA2
PLAIN TEXT=30313233343536373839414243444546, KEY=412056474F4F442050415353574F5244, CIPHER TEXT=5D29C69F5B46F7DA6A9B29027E48899C
PLAIN TEXT=4D59204E414D45204953205157455254, KEY=412056474F4F442050415353574F5244, CIPHER TEXT=791D37FC05F82119AEBEF6BFAA60D05A
PLAIN TEXT=4D59204E414D45204953205157455253, KEY=412056474F4F442050415353574F5244, CIPHER TEXT=17400580C483E1DF5C58B6B45071F0F9
PLAIN TEXT=4D592047415020414C474F524954484D, KEY=412056474F4F442050415353574F5244, CIPHER TEXT=05EA4011B3E9F8E0DEE983E62ADF1ED8
PLAIN TEXT=7E21402324255E262A28295F2B7B7D7C, KEY=412056474F4F442050415353574F5244, CIPHER TEXT=DD3E77FA6B32E310EB2916BC4CBF8612
PLAIN TEXT=564C53492645532053545544454E5453, KEY=412056474F4F442050415353574F5244, CIPHER
TEXT=D7A3B95834D34FF2DCA04AE9034C6C46
RESULTS OUTCOME:
Various wiring circuits and displayed results.

Fig. 9: Image showing initialization of AES Decryption Device
At the beginning of setup

Fig. 10: Image showing setup complete message on AES Decryption Device
At the end of setup

Fig. 11: Image showing decrypted message received on AES Decryption Device
When an encrypted message is sent to be decrypted

Fig. 12: Image showing encrypted message sent from AES Encryption Device

Fig. 13: Image showing body of decrypted message received on AES Decryption Device
When a plain text is sent to be encrypted
Project Source Code
### #include <LiquidCrystal.h> #include <SoftwareSerial.h> #include "TI_AES.h" #include "TI_AES.C" Setup Software Serial Port SoftwareSerial mySerial(10, 11); LCD Pins Initialization LiquidCrystal lcd(12, 9, 5, 4, 3, 2); Global Variables int 13; // Heartbeat of the Device key[] = <16 bytes of values> // A cipher Key /* Setup Function Starts here */ void setup() { // All initializations happens here and executes only once pinMode(led, OUTPUT); digitalWrite(led,HIGH); // sets heart beat monitor to one lcd.begin(16, 2); // set up the LCD's number of columns and rows: lcd.clear(); // Clear all characters on LCD. lcd.print("DENcryptor"); // Lcd test displays DENcryptor delay(1000); Serial.begin(9600); // This is for Debugging Only on a PC using Normal Serial Connection Serial.write("Arduino Bootup..! "); // Serial test message Serial.write("Hi, Programmer"); // Greetings for programmer Serial.println(); // New line only delay(500); lcd.setCursor(0, 0); // Set cursor on LCD to Home position lcd.clear(); // Clear Display lcd.print("Set Up Paramtrs."); // Show the current operation i.e Setup Modem Parameters mySerial.begin(9600); // Software serial Communication with the GSM Modem delay(2000); // give 2 seconds to initialize then start communication mySerial.print("AT+CMGF=1r"); // Set Modem to Text Mode delay(300); // there needs to be at least 300millisecond gap between commands mySerial.print("AT+CNMI=2,2,0,0,0r"); // Set Message Indications to Unsolicited mySerial.print("r"); // new line character to execute previous command delay(300); mySerial.print("AT+CSMP=17,167,0,0r"); // Optional set if Unicode is used delay(300); mySerial.print("AT+CSCS="IRA"r"); // change text encoding to ASCII delay(300); mySerial.print("AT+CSCS="GSM"r"); // change text encoding to ASCII redundant delay(300); lcd.clear(); // clear display on LCD lcd.setCursor(0, 0); // Set cursor to home position lcd.print("Set Up Complete"); // Display setup complete message } /* start of while loop */ void loop (){ { while(mySerial.available() <= 0); // wait for any serial data from modem MyserialEvent(); // if data is available jump to Event loop and start processing data } } /*Since the code was not modularized currently all operation happens inside mySerialEvent() */ voidMyserialEvent() // function name { delay(100); // set initial delay of milliseconds String inputString = ""; // create a string variable to store the incoming message string inputString.reserve(192); // reserve 192bytes in advance max string length is 160bytes/sms booleangotdata = false; // create a flag to signify data arrival // optional unsigned char Decrypted_SMS[16]; // 16bytes to store AES States / Keys / Cipher text String myLCD; // Create string to store and display corresponding data on a LCD myLCD.reserve(10); // reserve 10 characters.. Can be changed when needed to 32 inti,j; // local declaration of variables for loops and indexing purposes if(mySerial.overflow()) // this is inbuilt call to signify buffer overflow Serial.println("OverFlow"); // signify if buffer overflows while(mySerial.available() > 0) // check for available data bytes { delay(5); // wait few milliseconds so that data settles else possibility of corruption inputString += (char)mySerial.read(); // get a byte concatenate to the string delay(5);// wait few milliseconds so that data settles else possibility of corruption } Serial.println(""); // a new line character in Debug window on PC Serial.println("Received DATA"); // Inform Programmer about data arrival if(inputString != "") gotdata = true; // set data arrival flag to true if(gotdata) // if data is available then only enter this section { Serial.println(inputString); // Print the stored data to Debug Window } intlastOpeningBracket= inputString.lastIndexOf('<');// Search for starting position of OTP intlastClosingBracket = inputString.lastIndexOf('>');// Search for ending position of OTP if(lastOpeningBracket != -1 &lastClosingBracket != -1 & (inputString[lastOpeningBracket - 1] == 'D' | inputString[lastOpeningBracket - 1] == 'd')) { // only if both characters are found along with instruction on whether to perform decryption is found enter here else check next section int j = 0; for(i=lastOpeningBracket + 1 ;i <lastClosingBracket;i = i + 2) { // get all characters of OTP starting from index of (<) +1 till index of (<) // the bytes are collected in total of 32 bytes are converted into 16 ie hex values are read and ASCII values are calculated for succeeding characters in pairs. switch(inputString[i]) { case '0' : Decrypted_SMS[j] = 0x00; break; case '1' : Decrypted_SMS[j] = 0x10; break; case '2' : Decrypted_SMS[j] = 0x20; break; case '3' : Decrypted_SMS[j] = 0x30; break; case '4' : Decrypted_SMS[j] = 0x40; break; case '5' : Decrypted_SMS[j] = 0x50; break; case '6' : Decrypted_SMS[j] = 0x60; break; case '7' : Decrypted_SMS[j] = 0x70; break; case '8' : Decrypted_SMS[j] = 0x80; break; case '9' : Decrypted_SMS[j] = 0x90; break; case 'A' : Decrypted_SMS[j] = 0xA0; break; case 'B' : Decrypted_SMS[j] = 0xB0; break; case 'C' : Decrypted_SMS[j] = 0xC0; break; case 'D' : Decrypted_SMS[j] = 0xD0; break; case 'E' : Decrypted_SMS[j] = 0xE0; break; case 'F' : Decrypted_SMS[j] = 0xF0; break; } switch(inputString[i+1]) { case 0x30 : Decrypted_SMS[j] = Decrypted_SMS[j] + 0x00; break; case 0x31 : Decrypted_SMS[j] = Decrypted_SMS[j] + 0x01; break; case 0x32 : Decrypted_SMS[j] = Decrypted_SMS[j] + 0x02; break; case 0x33 : Decrypted_SMS[j] = Decrypted_SMS[j] + 0x03; break; case 0x34 : Decrypted_SMS[j] = Decrypted_SMS[j] + 0x04; break; case 0x35 : Decrypted_SMS[j] = Decrypted_SMS[j] + 0x05; break; case 0x36 : Decrypted_SMS[j] = Decrypted_SMS[j] + 0x06; break; case 0x37 : Decrypted_SMS[j] = Decrypted_SMS[j] + 0x07; break; case 0x38 : Decrypted_SMS[j] = Decrypted_SMS[j] + 0x08; break; case 0x39 : Decrypted_SMS[j] = Decrypted_SMS[j] + 0x09; break; case 0x41 : Decrypted_SMS[j] = Decrypted_SMS[j] + 0x0A; break; case 0x42 : Decrypted_SMS[j] = Decrypted_SMS[j] + 0x0B; break; case 0x43 : Decrypted_SMS[j] = Decrypted_SMS[j] + 0x0C; break; case 0x44 : Decrypted_SMS[j] = Decrypted_SMS[j] + 0x0D; break; case 0x45 : Decrypted_SMS[j] = Decrypted_SMS[j] + 0x0E; break; case 0x46 : Decrypted_SMS[j] = Decrypted_SMS[j] + 0x0F; break; } j=j+1; } Serial.println(""); // send a newline followed by decrypted characters to debug window if(inputString[lastOpeningBracket - 1] == 'd') // perform decryption (redundant comparison) { aes_decrypt(Decrypted_SMS, key); // perform decryption } if(inputString[lastOpeningBracket - 1] == 'D')// perform decryption (redundant comparison) { aes_decrypt(Decrypted_SMS, key); // perform decryption } Serial.print("Deciphered Text: "); for(i=0;i<16;i++) { // send the decrypted copy to debug window Serial.print(char(Decrypted_SMS[i])); } lcd.clear(); // Clear LCD. lcd.setCursor(0, 0); lcd.print("Decrypted Text"); lcd.setCursor(0, 1); // go to second row for(i=0;i<16;i++) { lcd.print(char(Decrypted_SMS[i])); // Disp LCD } } if((lastOpeningBracket != -1) & (lastClosingBracket != -1) & (inputString[lastOpeningBracket - 1] == 'E' | inputString[lastOpeningBracket - 1] == 'e')) { // only if both characters are found along with instruction on whether to perform encryption is found enter here else check next section //Get plain text as ASCII and store data in blocks int j = 0; for(i=lastOpeningBracket + 1 ;i <lastClosingBracket;i++) { // get all characters of OTP starting from index of (<) +1 till index of (<) Decrypted_SMS[j] = inputString.charAt(i); j = j+1; } Serial.print("Cryptic Text: "); for(i=0;i<16;i++) { Serial.print(char(Decrypted_SMS[i])); // show plain text for debugging } Serial.println(""); if(inputString[lastOpeningBracket - 1] == 'e') { aes_encrypt(Decrypted_SMS, key); // perform encryption } if(inputString[lastOpeningBracket - 1] == 'E') { aes_encrypt(Decrypted_SMS, key);// perform encryption } Serial.print("Encrypted Text: "); for(i=0;i<16;i++) { Serial.print(char(Decrypted_SMS[i])); } Serial.println(""); lcd.clear(); // Clear LCD. lcd.setCursor(0, 0); // go to home position lcd.print("Encrypted Text"); unsigned char Decrypted_SMS1; // we need to convert the cipher text to hex-ascii to display iton lcd else some character will be displayed as ‘???’ lcd.clear(); // Clear LCD. lcd.setCursor(0, 0); for(i=0;i<16;i++) { // convert ASCII to hex-ascii to diplay 10110101 as B5 on LCD if(i==8) lcd.setCursor(0, 1); // set up the LCD's number of columns and rows: switch(Decrypted_SMS[i] & 0xF0) { case 0x00 : Decrypted_SMS1 = 0x30; break; case 0x10 : Decrypted_SMS1 = 0x31; break; case 0x20 : Decrypted_SMS1 = 0x32; break; case 0x30 : Decrypted_SMS1 = 0x33; break; case 0x40 : Decrypted_SMS1 = 0x34; break; case 0x50 : Decrypted_SMS1 = 0x35; break; case 0x60 : Decrypted_SMS1 = 0x36; break; case 0x70 : Decrypted_SMS1 = 0x37; break; case 0x80 : Decrypted_SMS1 = 0x38; break; case 0x90 : Decrypted_SMS1 = 0x39; break; case 0xA0 : Decrypted_SMS1 = 0x41; break; case 0xB0 : Decrypted_SMS1 = 0x42; break; case 0xC0 : Decrypted_SMS1 = 0x43; break; case 0xD0 : Decrypted_SMS1 = 0x44; break; case 0xE0 : Decrypted_SMS1 = 0x45; break; case 0xF0 : Decrypted_SMS1 = 0x46; break; } Serial.print(char(Decrypted_SMS1)); lcd.print(char(Decrypted_SMS1)); switch((Decrypted_SMS[i] << 4) & 0xF0) { case 0x00 : Decrypted_SMS1 = 0x30; break; case 0x10 : Decrypted_SMS1 = 0x31; break; case 0x20 : Decrypted_SMS1 = 0x32; break; case 0x30 : Decrypted_SMS1 = 0x33; break; case 0x40 : Decrypted_SMS1 = 0x34; break; case 0x50 : Decrypted_SMS1 = 0x35; break; case 0x60 : Decrypted_SMS1 = 0x36; break; case 0x70 : Decrypted_SMS1 = 0x37; break; case 0x80 : Decrypted_SMS1 = 0x38; break; case 0x90 : Decrypted_SMS1 = 0x39; break; case 0xA0 : Decrypted_SMS1 = 0x41; break; case 0xB0 : Decrypted_SMS1 = 0x42; break; case 0xC0 : Decrypted_SMS1 = 0x43; break; case 0xD0 : Decrypted_SMS1 = 0x44; break; case 0xE0 : Decrypted_SMS1 = 0x45; break; case 0xF0 : Decrypted_SMS1 = 0x46; break; } Serial.print(char(Decrypted_SMS1)); lcd.print(char(Decrypted_SMS1)); } } if((lastOpeningBracket != -1) & (lastClosingBracket != -1) & (inputString[lastOpeningBracket - 1] == 'K' | inputString[lastOpeningBracket - 1] == 'k')) { // only if both characters are found along with instruction to set the new cipher key then execute this section else go back to idle state int j = 0; for(i=lastOpeningBracket + 1 ;i <lastClosingBracket;i = i + 2) { // get all characters of OTP starting from index of (<) +1 till index of (<) switch(inputString[i]) { case '0' : Decrypted_SMS[j] = 0x00; break; case '1' : Decrypted_SMS[j] = 0x10; break; case '2' : Decrypted_SMS[j] = 0x20; break; case '3' : Decrypted_SMS[j] = 0x30; break; case '4' : Decrypted_SMS[j] = 0x40; break; case '5' : Decrypted_SMS[j] = 0x50; break; case '6' : Decrypted_SMS[j] = 0x60; break; case '7' : Decrypted_SMS[j] = 0x70; break; case '8' : Decrypted_SMS[j] = 0x80; break; case '9' : Decrypted_SMS[j] = 0x90; break; case 'A' : Decrypted_SMS[j] = 0xA0; break; case 'B' : Decrypted_SMS[j] = 0xB0; break; case 'C' : Decrypted_SMS[j] = 0xC0; break; case 'D' : Decrypted_SMS[j] = 0xD0; break; case 'E' : Decrypted_SMS[j] = 0xE0; break; case 'F' : Decrypted_SMS[j] = 0xF0; break; } switch(inputString[i+1]) { case 0x30 : Decrypted_SMS[j] = Decrypted_SMS[j] + 0x00; break; case 0x31 : Decrypted_SMS[j] = Decrypted_SMS[j] + 0x01; break; case 0x32 : Decrypted_SMS[j] = Decrypted_SMS[j] + 0x02; break; case 0x33 : Decrypted_SMS[j] = Decrypted_SMS[j] + 0x03; break; case 0x34 : Decrypted_SMS[j] = Decrypted_SMS[j] + 0x04; break; case 0x35 : Decrypted_SMS[j] = Decrypted_SMS[j] + 0x05; break; case 0x36 : Decrypted_SMS[j] = Decrypted_SMS[j] + 0x06; break; case 0x37 : Decrypted_SMS[j] = Decrypted_SMS[j] + 0x07; break; case 0x38 : Decrypted_SMS[j] = Decrypted_SMS[j] + 0x08; break; case 0x39 : Decrypted_SMS[j] = Decrypted_SMS[j] + 0x09; break; case 0x41 : Decrypted_SMS[j] = Decrypted_SMS[j] + 0x0A; break; case 0x42 : Decrypted_SMS[j] = Decrypted_SMS[j] + 0x0B; break; case 0x43 : Decrypted_SMS[j] = Decrypted_SMS[j] + 0x0C; break; case 0x44 : Decrypted_SMS[j] = Decrypted_SMS[j] + 0x0D; break; case 0x45 : Decrypted_SMS[j] = Decrypted_SMS[j] + 0x0E; break; case 0x46 : Decrypted_SMS[j] = Decrypted_SMS[j] + 0x0F; break; } // Store cipher key in the key variable. key[j] = Decrypted_SMS[j]; j=j+1; } Serial.println(""); Serial.print("Cipher Key: "); for(i=0;i<16;i++) { Serial.print(char(key[i])); } lcd.clear(); // Clear LCD. lcd.setCursor(0, 0); lcd.print("Cipher Key: "); lcd.setCursor(0, 1); for(i=0;i<16;i++) { lcd.print(char(key[i])); // Disp LCD } } } ###
Circuit Diagrams
Filed Under: Electronic Projects


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.