DPDT stands for Double Pole Double Throw switch. By using this we can change the polarity of the applied voltage. It is used in situations where we need different outputs. It has 3 states ON, OFF, ON. The difference between the two ON states is that the polarity of both the states is opposite with respect to each other. That’s the reason why it can drive a DC motor in both the directions. It can also switch an AC motor but it can’t change the direction of the motor. Since, AC motor will run in the same direction irrespective of the polarity therefore, it can only be used for switching ON and OFF an AC motor but not for changing its direction.
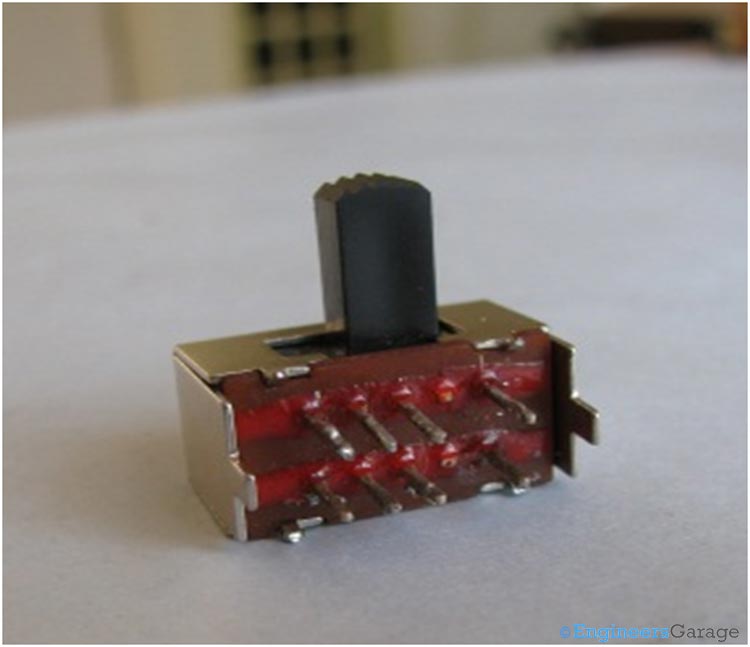
Fig. 1: Image of Double Pole Double Throw Switch

Fig. 2: Diagram of DPDT Switch
Above image shows a diagrammatic representation of DPDT switch.
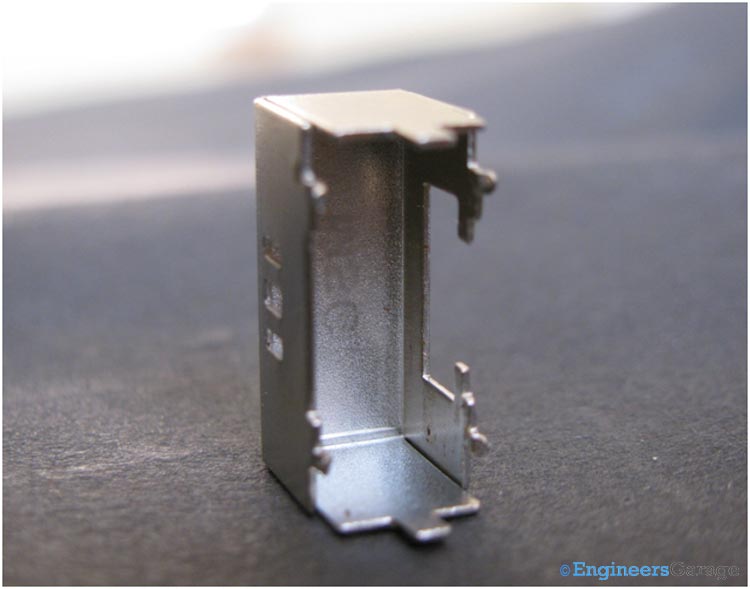
Fig. 3: DPDT Switch
Metallic Case
Let’s take a closer look into the DPDT switch. The switch as a whole is enclosed in a metallic case as shown below.

Fig. 4: Metallic Case that Holds the DPDT Switch
Plastic Casing
There are 3 holes in the metallic case. These holes are used to hold the switch in a particular state. This is done by using a ball bearing and spring which is explained later. The state of the switch is changed by a slider whose image is shown below.
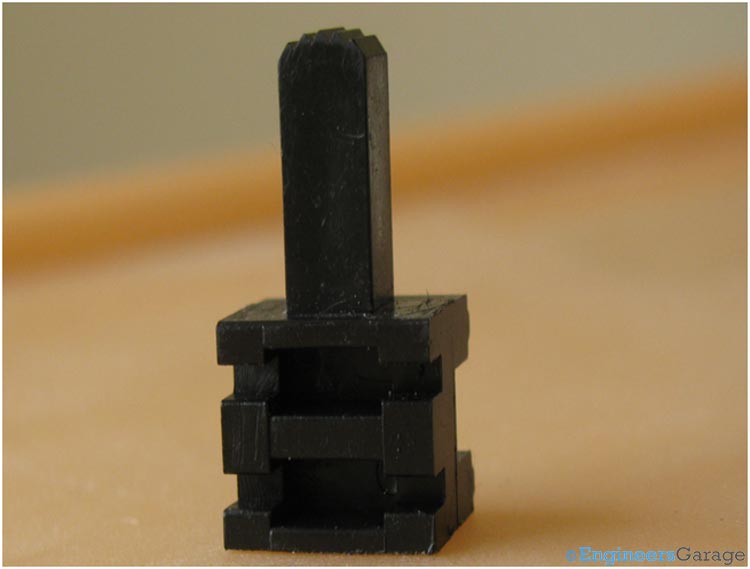
Fig. 5: DPDT switch Slider
Slider Mechanism
There is ball bearing coming out of the slider. This ball bearing along with the spring, which pushes it outwards fits itself into the holes of the metallic case. So, by using them the switch attains different states. Hence, the ball remains in three different holes corresponding to three different states.
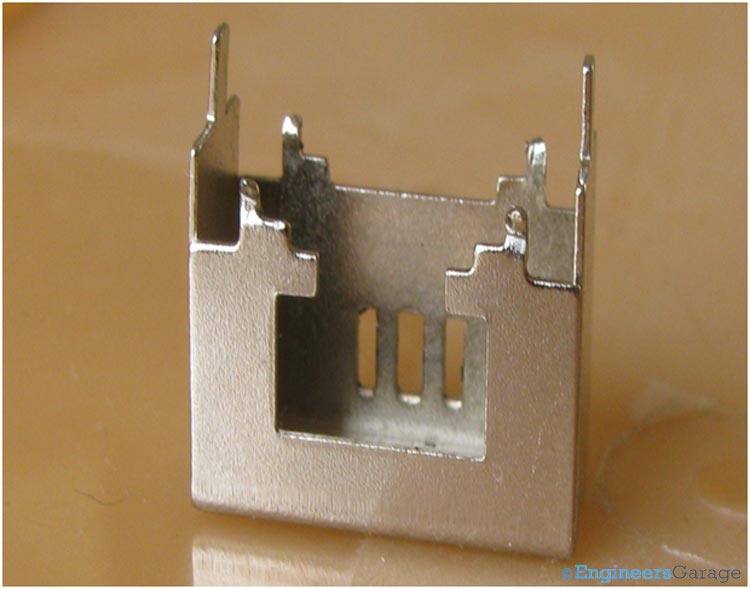
Fig. 6: Image Showing the Holes in Metallic Case
Pins
There are 8 pins provided in this DPDT switch. These 8 pins are engraved in a board like structure. These pins are connected inside to metallic plate like structure. These plates connection in different configurations results in change in the polarity. These 8 pins are engraved in the board which is shown below.

Fig. 7: Image Showing 8 DPDT Switch Pins Engraved in Board
Metallic Plates
Inside this board these pins are connected to a thin metallic plate like structure. These plate like structures when connected to each other in different configuration changes the polarity. The image of these plates is shown below.

Fig. 8: Eight Metallic Plates for each of 8 Pins of DPDT Switch
Clips
er = When the slider is moved from outside different connections of these plates are formed. The connections are formed by connecting these plates . For making different connections sliding clips are used which are shown below.
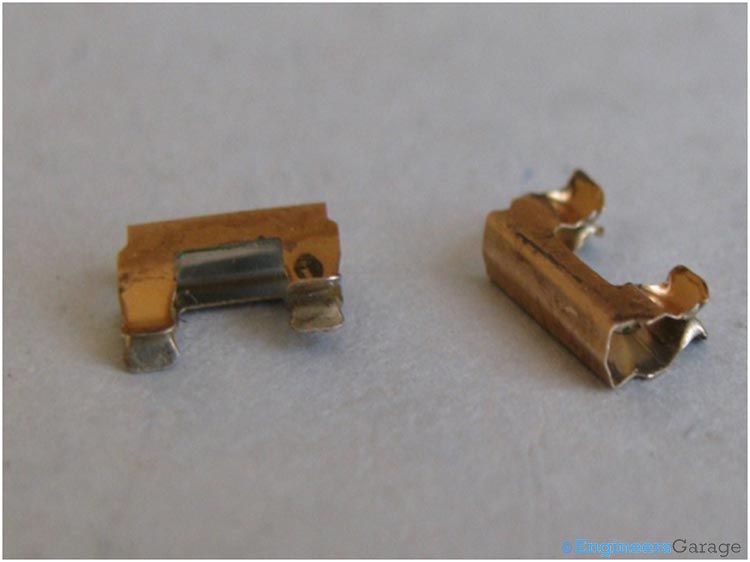

Fig. 9: Sliding Clips used to Enable Movement of Slider
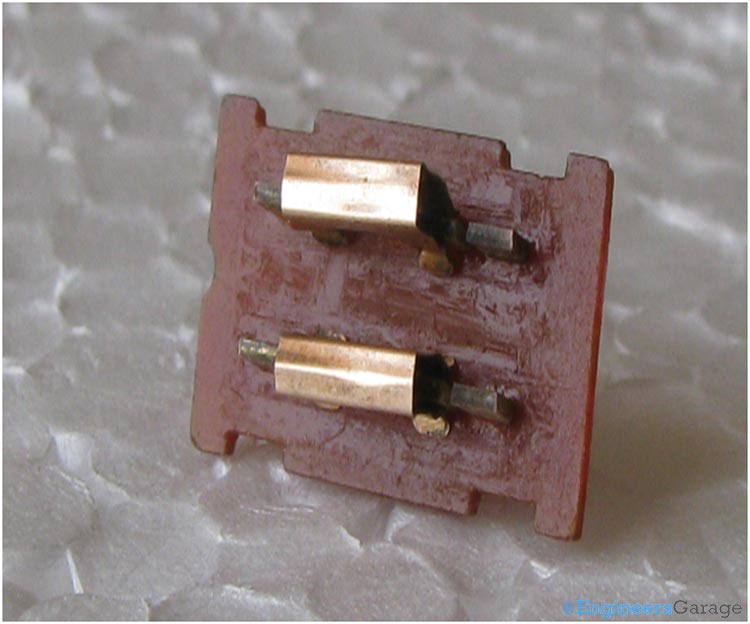
Fig. 10: Image Showing How Clips are used to Make Contacts Between Plates
Image indicating how clips are used to make contacts between plates.
These clips are fitted into the space provided in the slider. These clips, when slide over the metallic plates, result in different configurations. These different configurations give different polarity.
Filed Under: Insight


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.