The replacement of conventional ball mouse by the technically superior optical mouse is not hidden to anybody. An optical mouse works by having a low resolution camera inside it which takes around 1500 to 6000 pictures per second of the surface beneath it, and by analyzing these images, it calculate the position, speed and movement of the mouse.
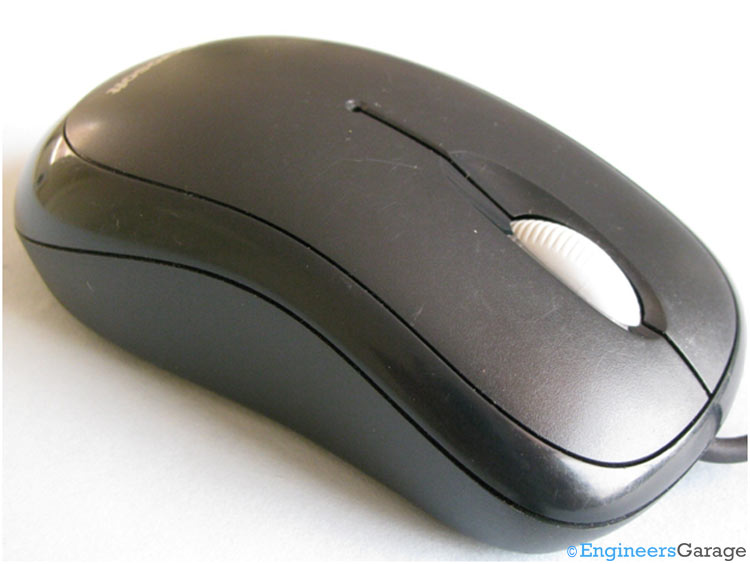

Fig. 1: Computer Optical Mouse

Fig. 2: Rear View of Optical Mouse
The above images are showing different views of an optical mouse.
Electronic Components

Fig. 3: Image Showing Various Electronic Components of Optical Mouse
On removing the outer cover, you can have a glimpse of majority of the components used in mouse.

Fig. 4: Light Reflector at Bottom of Mouse
The plastic covering shown is used to reflect and concentrate all the light rays at bottom of the camera.
Light Scatterer & LED

Fig. 5: Lens Used to Reflect LED Light to Surface
This special shaped lens is designed to reflect the LED light to surface.

Fig. 6: Side View of Lens
The LED shown in the image below is used to flash lights on the surface that bounce back to the camera in order to take clear picture of the surface.
Optical Mouse Sensor

Fig. 7: IC Sensor of Optical Mouse
The IC shown in above image is an optical mouse sensor. It works on Optical navigation technology which measures changes in position by optically acquiring surface images and then determining the direction and distance of movement.
The above IC contains an Image Acquisition System (IAS), a Digital Signal Processor (DSP) and a two wire serial port. IAS takes images of the surface via an in house lens. These images are processed by DSP and the resultant coordinates are continuously stored which can be extracted using the serial interface format.
Communication IC

Fig. 8: IC A2611D and its Various Functions
You can see another IC (A2611D) in the image above which does the following function:
1. It takes input from the Optical Mouse Sensor through I2C protocol.
2. Generate clock for synchronization.
3. Takes inputs from left, right and middle buttons of the mouse and accordingly sends data to the PC.
4. Works as voltage regulator.
5. The IC works as USB Transceiver i.e. at a time it can transmit & receives data from USB.
Scroll Mechanism
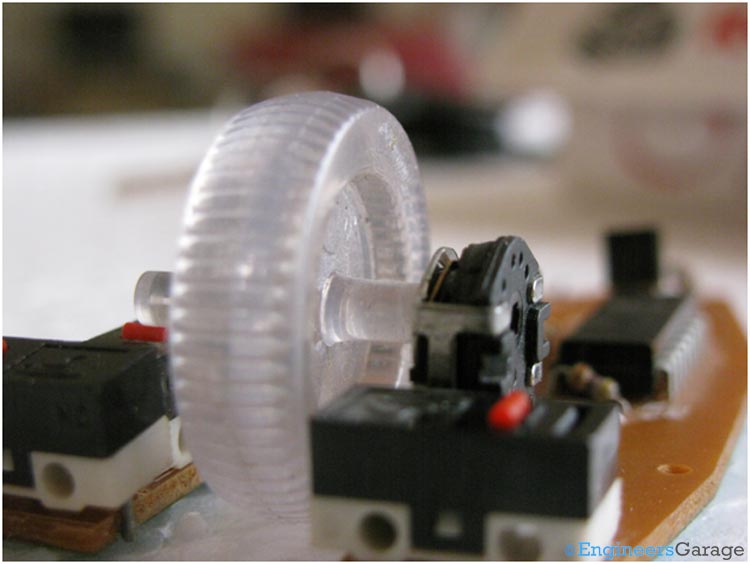
Fig. 9: Scroll Mechanism of Optical Mouse
When we rotate the wheel of a mouse, the potentiometer attached with the wheel as shown in the picture above also rotates, thereby producing different output voltages. The potentiometer works as a sensor and the output signal which is a variable voltage after processing is given to the PC.
Potentiometer

Fig. 10: Optical Mouse Potentiometer—Side View

Fig. 11: Optical Mouse Potentiometer—Second View
The above image shows the internal structure of the potentiometer attached with the mouse wheel.
Click Mechanism
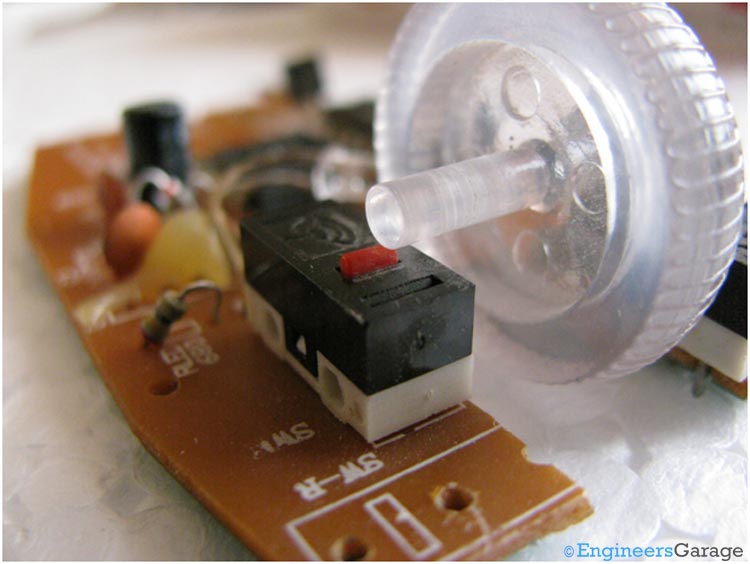
Fig. 12: Image Showing Click Mechanism of Optical Mouse
The red button shown in the above image is the center click of the mouse.

Fig. 13: Internal Architecture of Mouse Click Switches
The internal architecture and working of the switches used for mouse click is shown in the images below.
Switch Structure

Fig. 14: Flexible Metal Plate Inside the Mouse Click Switch
When a button is clicked, a flexible metal plate is pressed which shorts the two points of the circuit that detects the mouse click.
Working: When a mouse is connected with the computer, a red LED starts glowing. This light is focused on the surface beneath the mouse by a special type of lens (HDNS-2100). The reflected light falls back to the camera integrated in Optical Mouse Sensor. The camera takes images of the surface with a frequency in the range of 1500 to 6000 images per second to calculate the position of mouse. These images are processed by Digital Signal Processor and resultant co-ordinates are sent to IC A2611D via serial data transmission. Another IC (A2611D) takes the serial input from and image sensor and the buttons of the mouse, converts it to USB protocols and sends it to the PC. The driver of the mouse installed in the computer receives the co-ordinates and makes the cursor move accordingly.
Filed Under: Insight


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.