A quartz crystal resonator plays a vital role in electronics oscillator circuitry. Sometimes mispronounced as crystal oscillator, it is rather a very important part of the feedback network of the oscillator circuitry. Electronics oscillators are used in frequency control application finding their usage in almost every industry ranging from small chips to aerospace.
A quartz crystal is the heart of such type of resonators. Their characteristics like high quality factor (Q), stability, small size and low cost make them superior over other resonators like LC circuit, turning forks, ceramic resonator etc.
The basic phenomenon behind working of a quartz crystal oscillator is the inverse piezo electric effect i.e., when electric field is applied across certain materials they start producing mechanical deformation. These mechanical deformation/movements are dependent on the elementary structure of the quartz crystal. Quartz is one of the naturally occurring materials which show the phenomena of piezo electricity, however for the purpose of resonator it is artificially developed since processing the naturally occurring quartz is difficult and costly process.
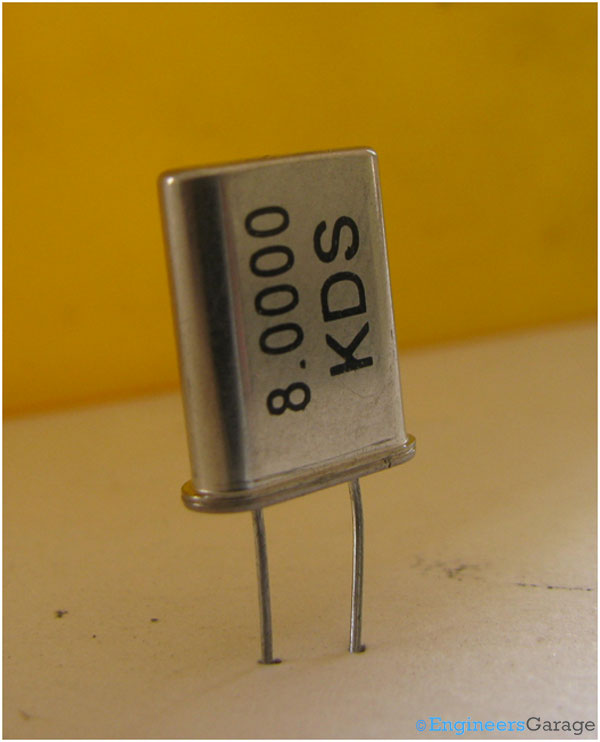
Fig. 1: Image of Quartz Crystal Resonator
The image above shows a commonly used quartz crystal resonator. It is widely used in electronic oscillators circuitry used in digital circuits and microcontroller/processors.
Metal Casing
Fig. 2: Assembly of Resonator Parts
The entire assembly is covered in a metal covering as shown in the image above. On removing the metal covering, a thin blanket with net like structure is present to protect the quartz crystal from mechanical damages.
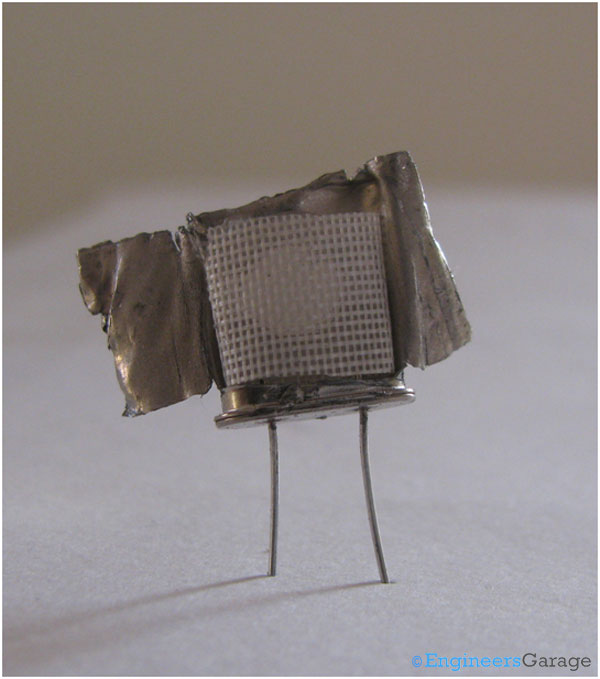
Fig. 3: Protective Net Cover Inside Outer Metal Cover
The above image shows a clear view of protective covering inside the top metal covering.
Crystal Plate
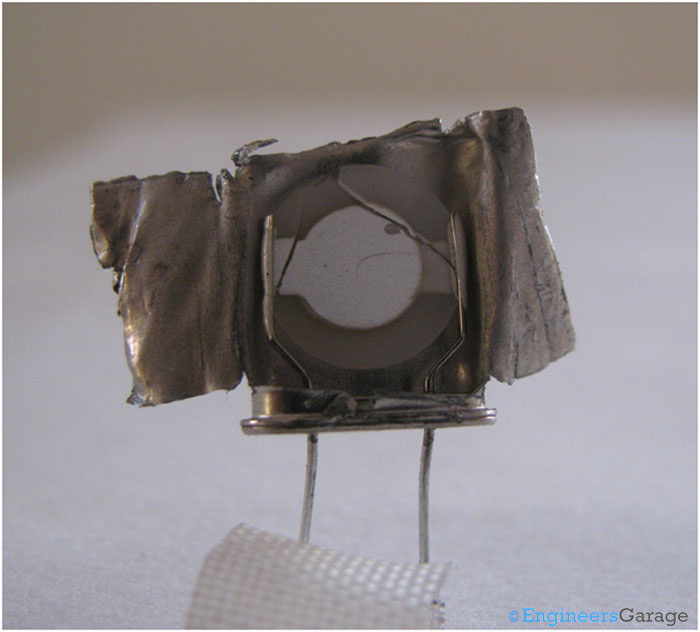
Fig. 4: Internal Mechanism of Quartz Crystal Resonator
Removing the covering, you can see the quartz crystal plate and how it is connected to the two electrodes.
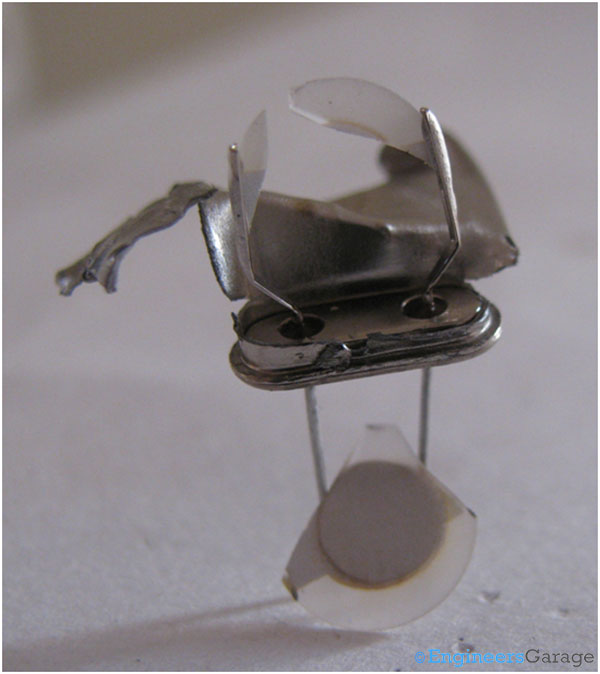

Fig. 5: Electrodes of Resonator
Filed Under: Insight


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.