Floppy disk, another interesting invention of the computer age is a storage device used to store and carry data. Although obsolete now a days, it has been replaced by technologically superior storage media like CD, DVD, Pen drive, portable hard disc etc. Historically this technology was dominant in the markets for more than two decades.
Floppy disks are commonly identified by their sizes. The 3.5 inch disk with a maximum capacity of 1.44MB was the most commonly used floppy. The data inside a floppy is magnetically stored on a thin plastic sheet which is coated with iron oxide. It is commonly called as magnetic disk.
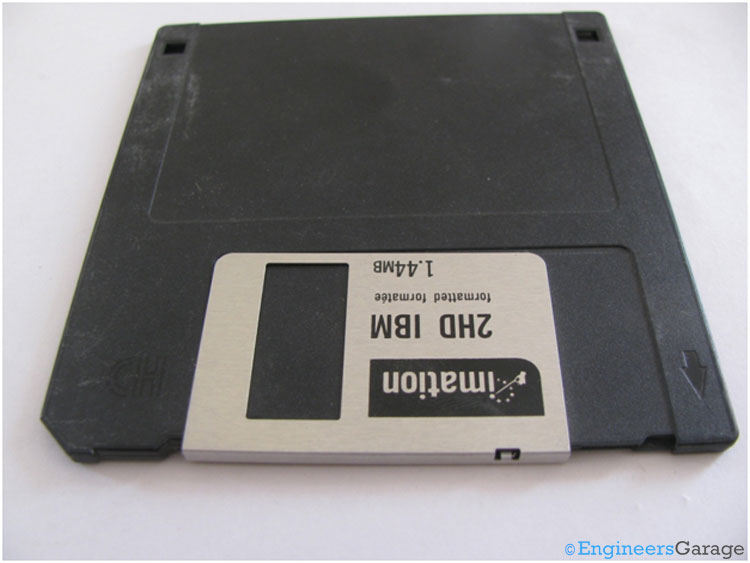

Fig. 1: Front View of 1.44 MB Capacity 3.5 inch Floppy Drive
The above image shows the front view of a 3.5 inch floppy drive with a capacity of 1.44MB.
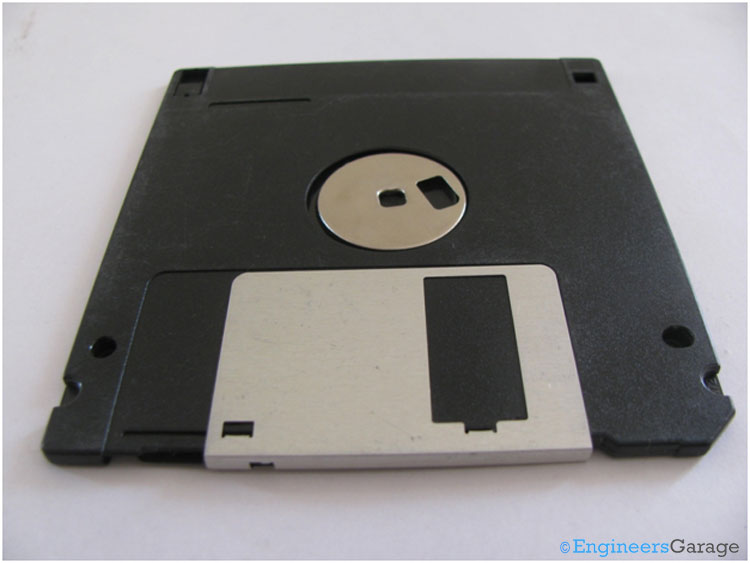

Fig. 2: Backside view of Floppy Disk
The back side of the floppy disk is shown in the image above. A plastic casing covers the magnetic disc on both sides as shown in the above images.
Shutter

Fig. 3: Image Indicating Shutter of Plastic Casing
On the top of the plastic casing is a metallic shutter. It protects the magnetic disk from coming in direct contact with the environment thereby preventing the data and/or the information stored on it from dust and other external factors. In its normal state it covers the magnetic disc. It is connected to the plastic housing by means of a spring. This allows the motion of the shutter over the disc. When the floppy is inserted inside the drive the shutter pulls back horizontally to allow read and write operation by the floppy drive.
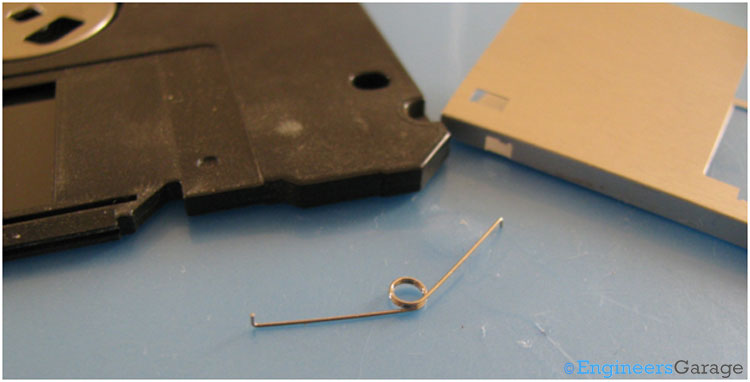
Fig. 4: Image Showing the Spring that Lever with Plastic Casing
The spring is shown in the above image which connects the lever with the outer plastic casing. This spring is responsible for the movement of the shutter and auto closing of the shutter whenever the floppy is taken out of the drive. This spring is placed inside the outermost plastic housing.
Internal Structure
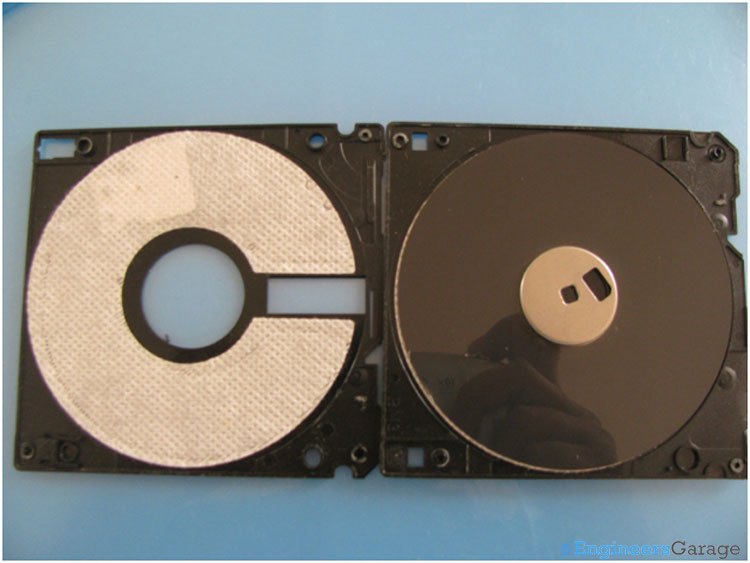

Fig. 5: Internal Structure of Floppy Disc
Opening the outside covering shows the internal structure of the floppy disc. The magnetic disc and the plastic casing from inside are shown in the image below.
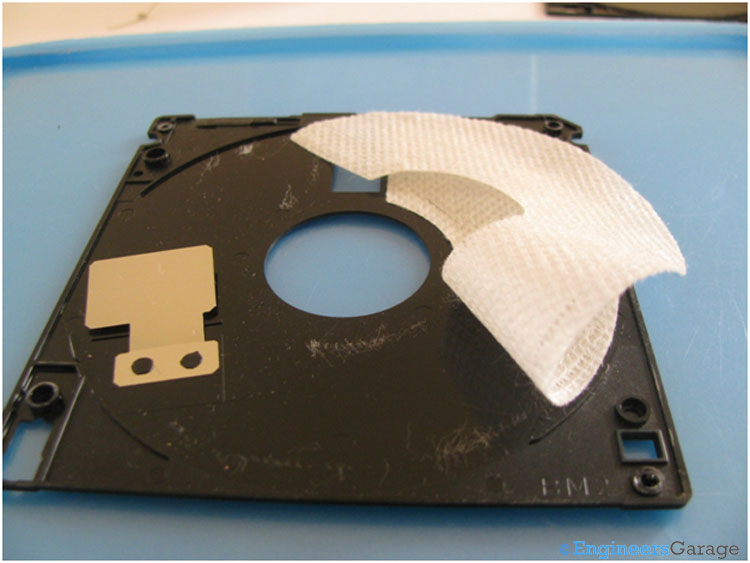
Fig. 6: Image Indicating the Paper Film that Covers Plastic Casings
Both the plastic casings are covered with a thin film of paper covering from inside. This helps in smooth and frictionless motion of magnetic disk. Also it prevents the disk from dust particles. The bottom plastic casing also has a thin metal sheet attached to it, which works like a spring to push the paper covering against the magnetic disk. As a result, in case if any dust particle gets deposited over the magnetic disk, it can be removed by the paper when the disk is rotating.
Magnetic Disc
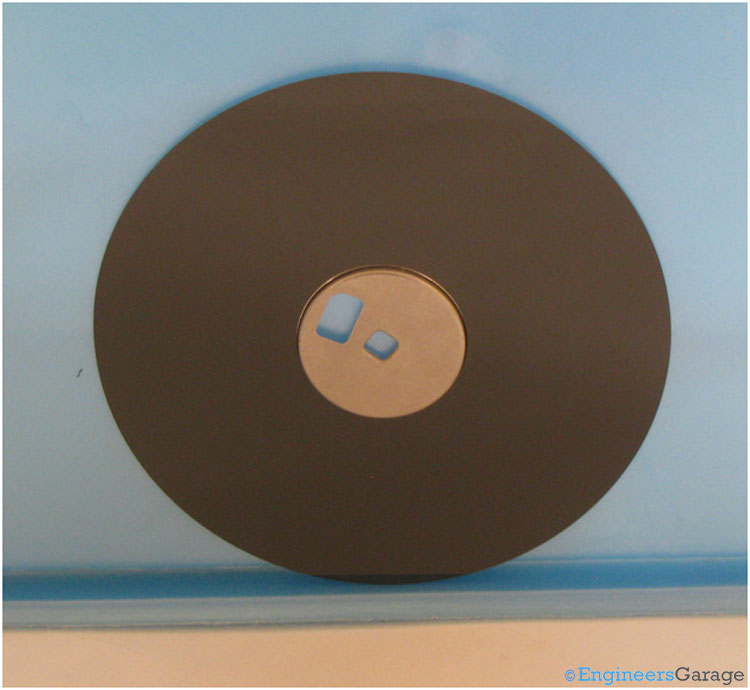

Fig. 7: Image Showing Magnetic Disc that Stores Data
The magnetic disk which is the heart of the floppy, stores the data over it. It is a plastic disk with a coating of iron oxide. Iron oxide is ferromagnetic in nature i.e., when exposed to magnetic field it will get permanently magnetized. The data is stored magnetically over the disk. A center metallic disk also called the hub is glued to the plastic disk. This hub has holes so that it can attach itself tightly with the motor of the floppy drive and rotate the magnetic disk. Technically the disk is divided into tracks and sectors, however they are not visible to the eyes.
As mentioned about the size in the beginning of this article, the size refers to the diameter of the magnetic disk. In this case the diameter of the magnetic disk is 3.5 inches.
Filed Under: Insight


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.