Ultrasonic sensors are devices that use electrical–mechanical energy transformation to measure distance from the sensor to the target object. Ultrasonic waves are longitudinal mechanical waves which travel as a sequence of compressions and rarefactions along the direction of wave propagation through the medium. Apart from distance measurement, they are also used in ultrasonic material testing (to detect cracks, air bubbles, and other flaws in the products), Object detection, position detection, ultrasonic mouse, etc.
These sensors are categorized in two types according to their working phenomenon – piezoelectric sensors and electrostatic sensors. Here we are discussing the ultrasonic sensor using the piezoelectric principle. Piezoelectric ultrasonic sensors use a piezoelectric material to generate the ultrasonic waves.
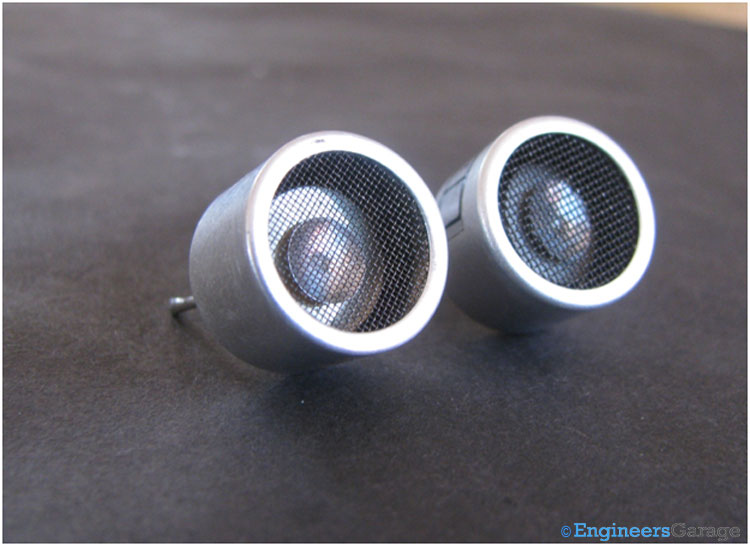

Fig. 1: Image of Ultrasonic Transmitter and Receiver
An ultrasonic sensor consists of a transmitter and receiver which are available as separate units or embedded together as single unit. The above image shows the ultrasonic transmitter and receiver.
Bottom View
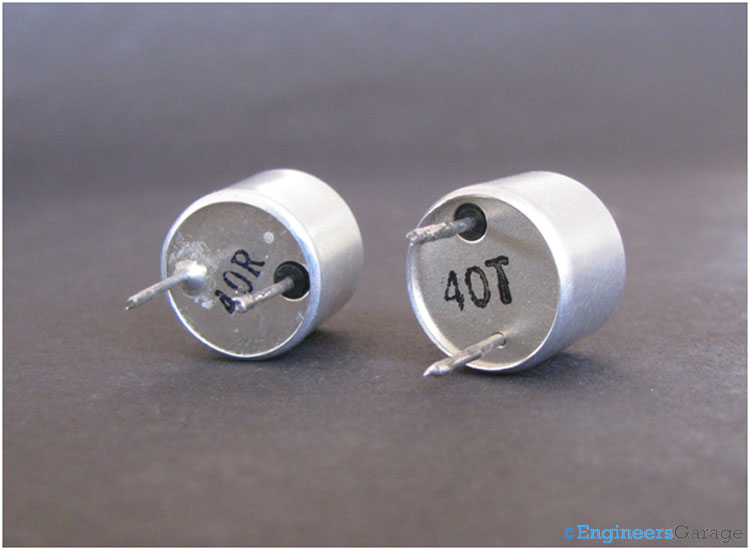

Fig. 2: Backside View of Ultrasonic Transmitter and Receiver
Above image shows the backside view of the ultrasonic sensors – receiver and transmitter. The construction of both is almost same, having two leads to give and take electrical signals to and from the sensor.
Internal Structure
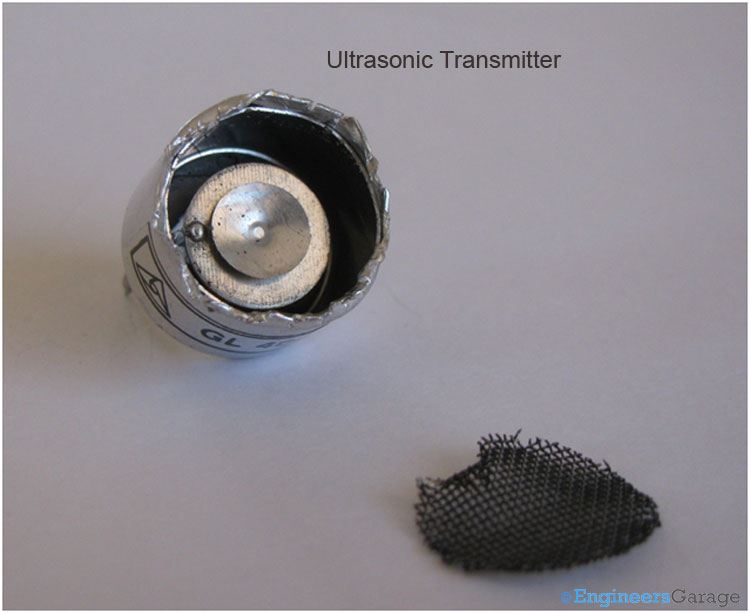

Fig. 3: Ultrasonic Transmitter Internals
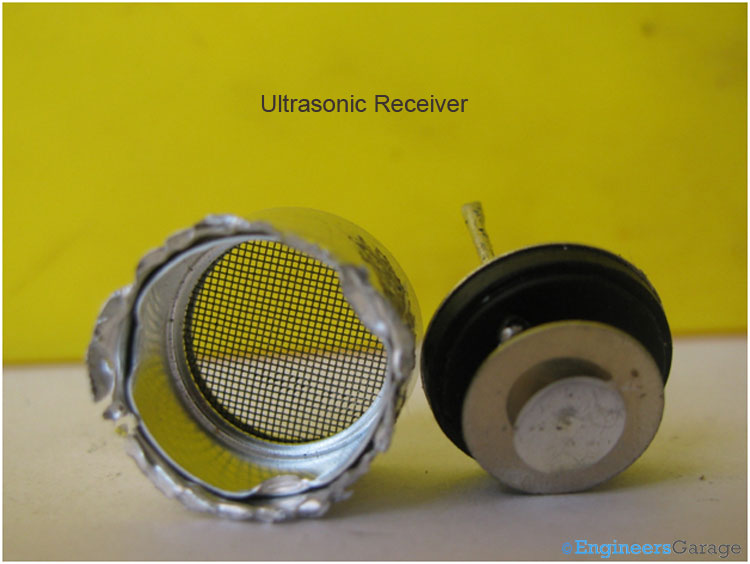

Fig. 4: Ultrasonic Receiver Internals
The ultrasonic sensors are covered with a metal case to protect it from rain, dew and dust.
Metallic Net
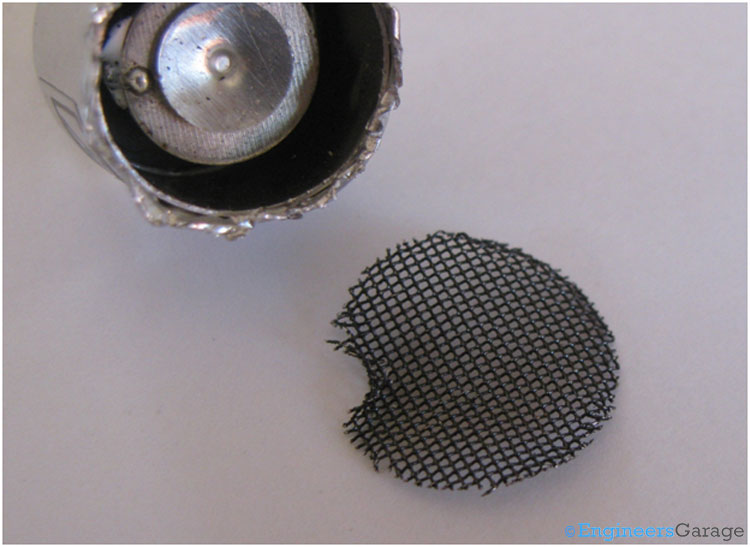
Fig. 5: Net and Metal Case Covering Ultrasonic Transmitter
A metallic net is fixed on the top of the metal case. On removing the net we can see a conical metal sheet placed on another sheet.
Outer Casing
[[wysiwyg_imageupload::]]
On removing the outer case the entire assembly of the ultrasonic transmitter is shown in the above image.
Resonator & Vibrator
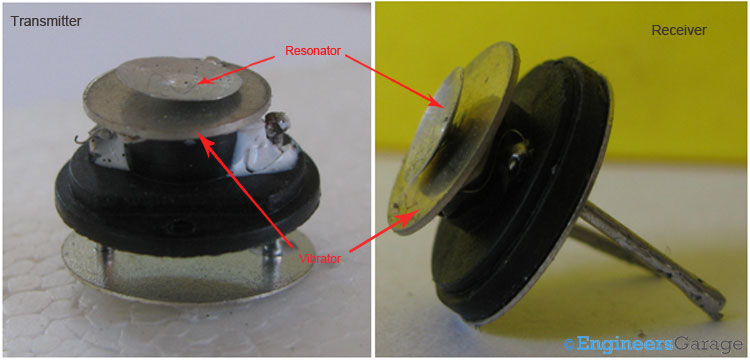
Fig. 6: Resonator and Vibrator of Sensors
As shown in the above images, a unimorgh disc and the metal cone which is the heart of the ultrasonic sensor is glued to the base. The top most metallic conical cup also known as the resonator is used to efficiently radiate the ultrasonic wave generated (also concentrate the waves in case of ultrasonic receiver). The round shaped sheet is a unimorgh disc and also called vibrator generates the ultrasonic waves. The resonator is soldered on the vibrator.
Wiring

Fig. 7: Wiring Pattern of Transmitter and Receiver
The unimorgh disc is electrically connected with the external leads through two wires. It is backed by a block of damping material that suppresses the piezoceramic material after it generates the ultrasonic waves. As shown in the above image, there is a small difference in construction of ultrasonic transmitter and receiver respectively.
Unimorgh Disc
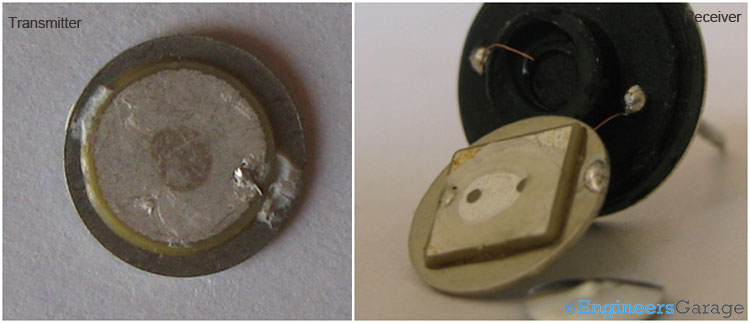
Fig. 8: (a) Rounded Peizoceramic Disk of Transmitter. (b) Squared Peizoceramic Disk of Receiver
The unimorgh disc consists of a disc made up of piezoceramic material fixed to a metal disc. Piezoceramic materials convert the electrical signals to the ultrasonic waves and vice versa. When voltage is applied to the piezoceramics, mechanical distortion is generated in accordance with the voltage and frequency. The peizoceramic disc is shaped round in transmitter and squared in receiver in order to produce vibrations efficiently.
Working of Ultrasonic Sensors
Ultrasonic transmitter uses a piezoceramic crystal attached with a conical metal sheet. When an electrical voltage is applied to the piezoceramic, it vibrates with continuous expansion and contraction. Resultantly, as per the property of piezoelectric material, ultrasonic waves are generated which propagates straight because of the conical shape of the resonator.
Ultrasonic receiver works on the just reverse concept. When ultrasonic waves strike with the resonator, the attached vibrator (metal plate) vibrates. With the vibration of the piezoceramic disc pasted on the vibrator, an electric current is produced as per the property of piezoceramic material. This electric current is further taken out from the two external leads.
Distance Calculation
The ultrasonic sound travels in the atmosphere and by striking with the target object, a fraction is reverting back. Once the ultrasonic waves are transmitted through the transmitter and echo is sensed by the receiver the distance can be calculated using this equation:
Distance = elapsed time x speed of sound/2
You may also like:
Filed Under: Insight






Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.