Ever wondered how are wires connected to a connector. How different number of wires are connected to segments of the connector? A connector aka jack for the earphone, headphone, microphone, like any other gadgets has an equally interesting chapter in the book s of engineering. It is among the cheapest part but not the technically inferior. It deserves its attention from the engineers for its design and quality. The connector plays an important part of tranferring signals from the device like mobile, laptops, music players etc to the earphone and the microphone and vice versa. Even a small problem may lead to an unplesant experience with the device.
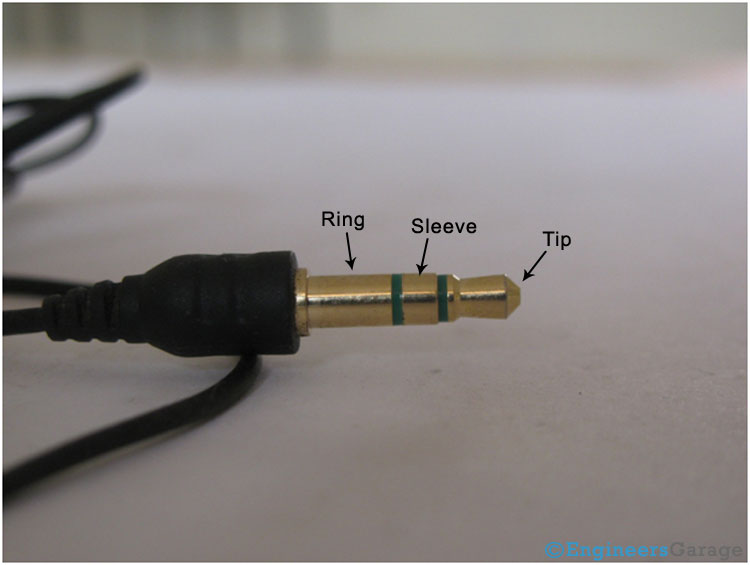
Fig.1 : Image Showing Various Parts of A Typical Head Phone Jack
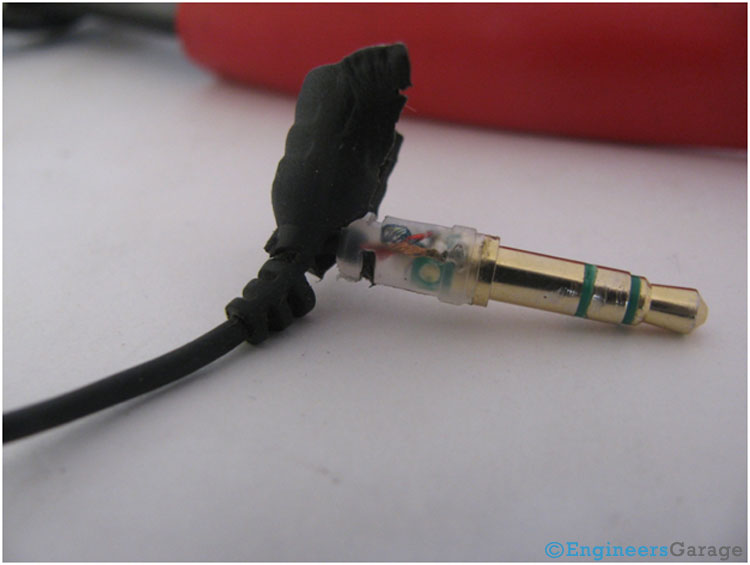

Fig. 2: TRS Connector Inner View After Removal of Rubber Casing

Fig. 3:Picture Showing Various WIres Present In TRS Connector
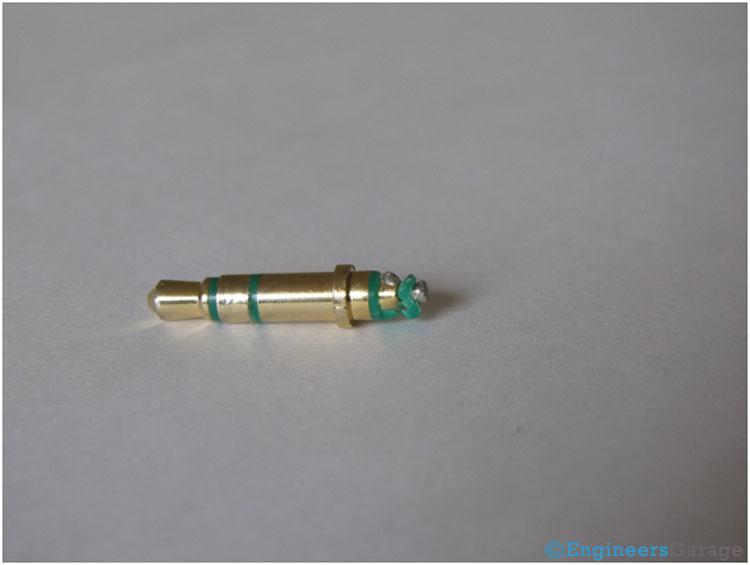
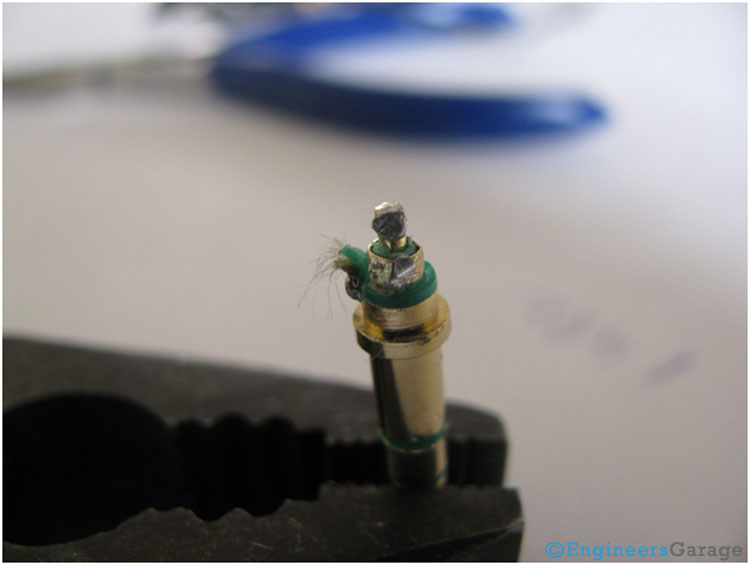


Fig. 5: Image Showing Arrangement of Metallic Contacts in A TRS Connector
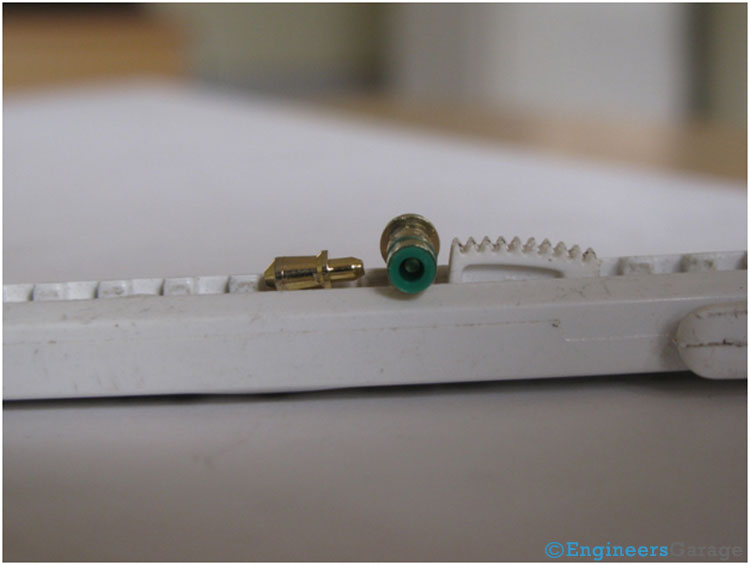

Fig. 6: Bottom Part of TRS Connector
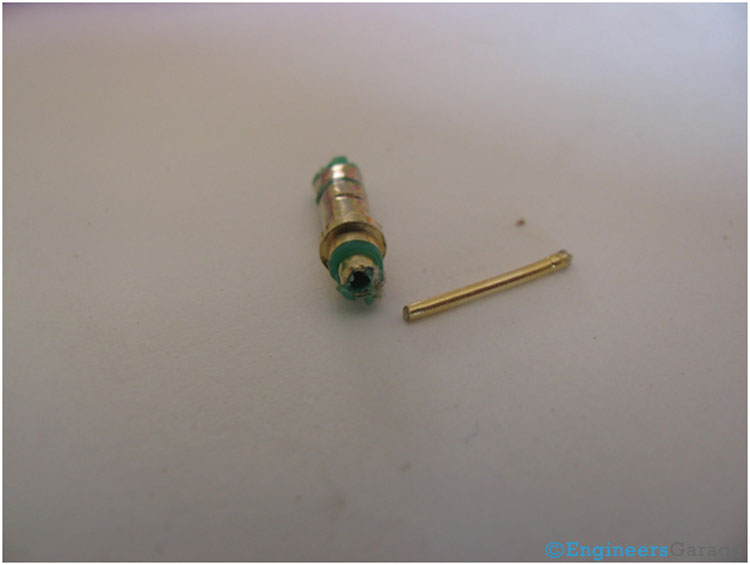

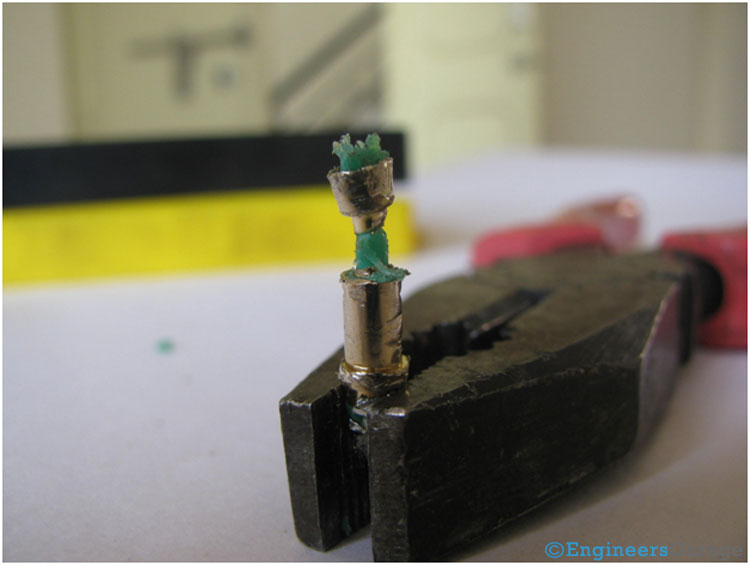
Fig. 8: Image Showing Shape of Middle Metallic Contact In A TRS Connector

Fig. 9: Image Showing Shape of Metallic Contact In TRS Connector
Filed Under: Insight, More Editor's Picks


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.