CD4026 is a Johnson counter IC commonly used in digital display. It has a 5 stage Johnson decade counter with a decoder which converts the Johnson code to a 7 segment decoded output. To put it simply, it will convert the input into numeric display and can be seen on 7 segment display or with LED. It can be used for displaying analogue value such as temperature with pic microcontroller or for counting objects. There is various other applications like in 7 segment decimal display circuit, in clocks, timer etc. Advantages of 4026 counter are: It contains counters and 7 segment decoded in one package, It can be easily interfaced with 7 segment types, Ideal for low power display, Operated at wide range of temperature from 5V to 20V and the biggest advantage of the 4026B counter IC is that it can drive a 7-segment display without needing a decoder driver IC.
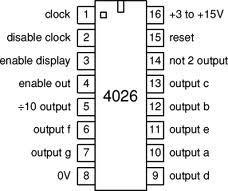
Fig. 2: Pin Diagram Of 4026 IC
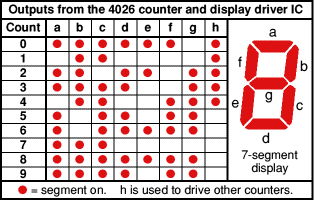
Fig. 3: Image Of Output From 4026 Counter
Circuit Diagrams
| Circuit-Diagram-Interfacing-4026-7-segment-display | 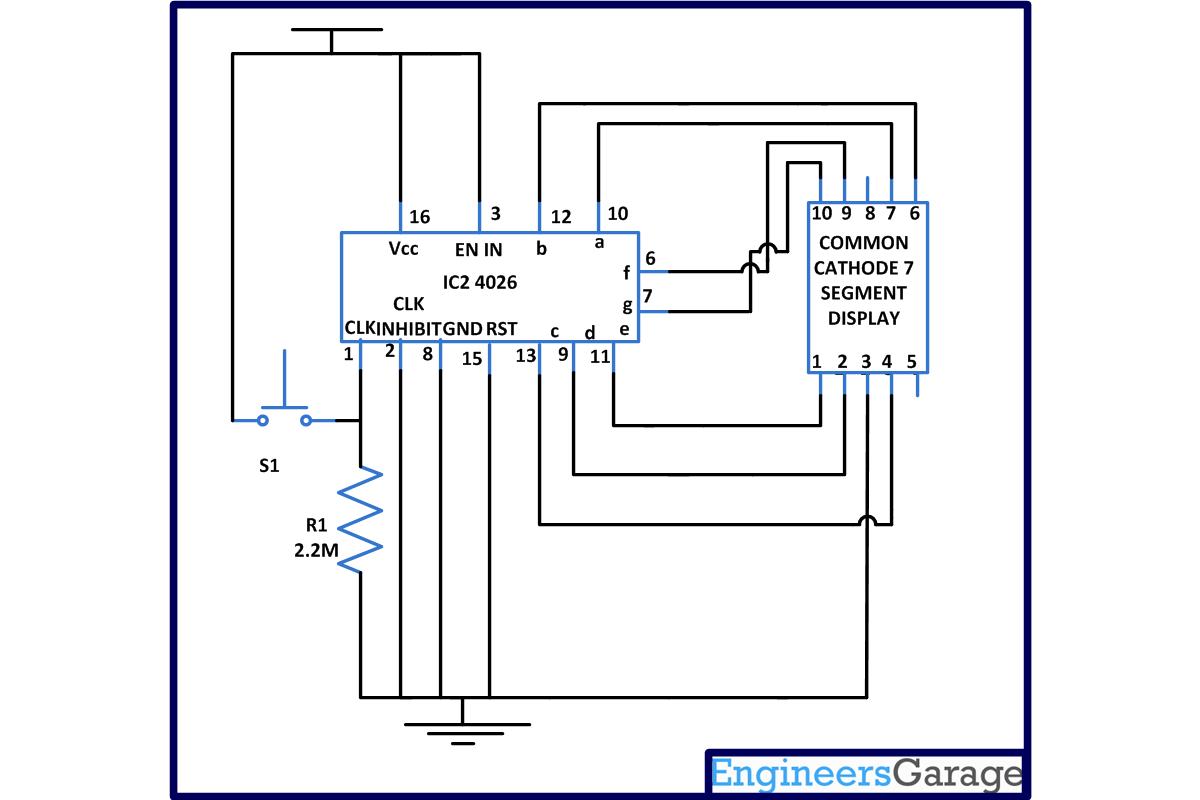 |
| Circuit-Diagram-Interfacing-4026-7-segment-display_0 | 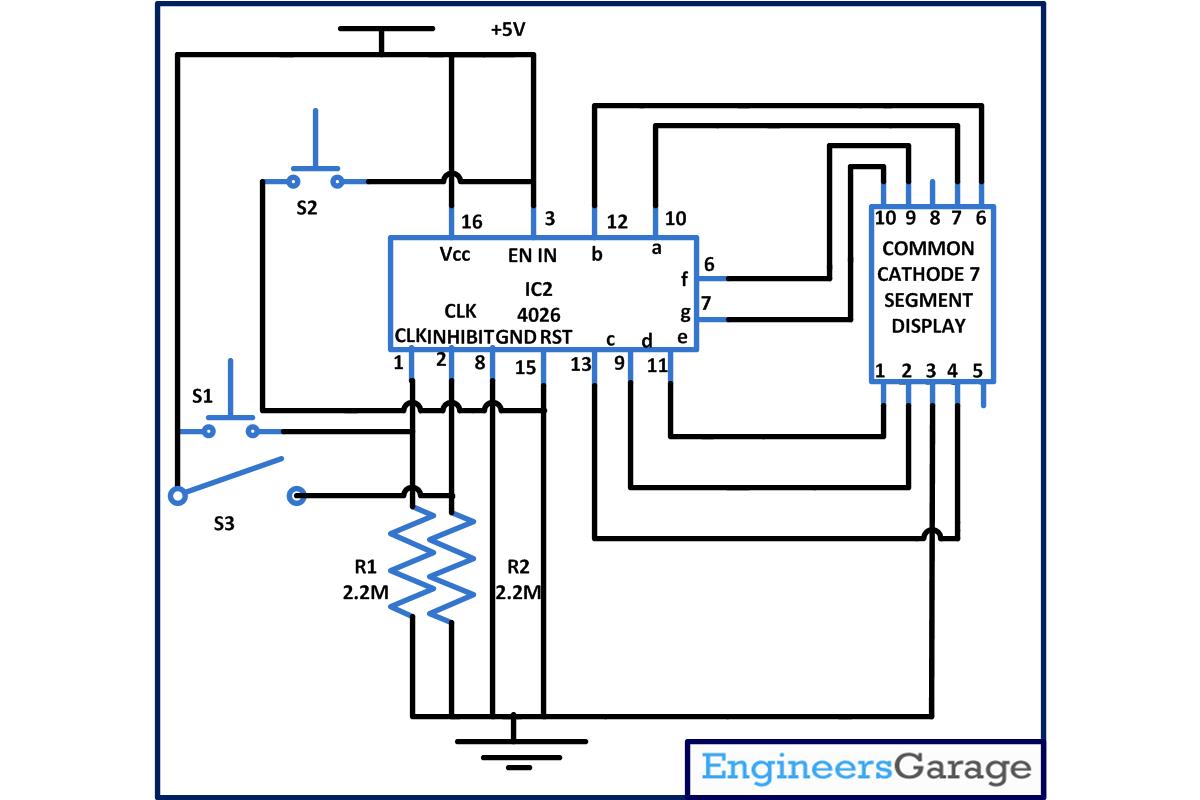 |
Project Components
Project Video
Filed Under: Electronic Projects
Filed Under: Electronic Projects


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.