This project presents a way to interface GSM module with microcontroller AT89C51 without making use of computer to send AT commands to the module. This is an improvement over the previous projects (see MC074 & MC075). Instead of using HyperTerminal or any other PC interface, the controller itself sends a fixed AT command to the GSM/GPRS module. The information response and result codes are received and displayed on a 16x2 LCD.
Instead of sending commands from the HyperTerminal, AT commands are sent to the GSM/GPRS module by the microcontroller itself. In this case, the receive (Rx) and transmit (Tx) pin of the GSM module’s RS232 port are connected to the transmit (Tx) and receive (Rx) pin of AT89C51’s serial port, respectively. This eliminated the role of computer and just the controller’s circuit provides a complete user interface for the module.
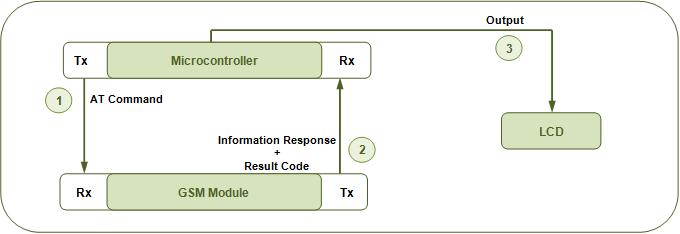
Fig. 2: Block Diagram Of GSM Module with 8051 Microcontroller
The controller is programmed to send a fixed command ‘AT’ to the module. The command AT is used to check the communication with module. It returns a result code OK if the module and the controller are connected properly. If either of the module or SIM are not working, it returns a result code ERROR.
The program complexities for display of information responses and result codes on LCD mentioned in MC075 remain same here as well.
Project Source Code
###
// Program to Interface GSM Module with 8051 microcontroller (AT89C51) without using PC #include<reg51.h> #define port P1 #define dataport P2 // Data port for LCD sbit rs = port^2; sbit rw = port^3; sbit en = port^4; int count,i; unsigned char check,str[15]; bit check_space; void init_serial() // Initialize serial port { TMOD=0x20; // Mode2 TH1=0xfd; // 9600 baud SCON=0x50; // Serial mode=1 ,8-Bit data,1 Stop bit ,1 Start bit, Receiving on TR1=1; // Start timer } void delay(unsigned int msec) // Function for delay { int i,j; for(i=0;i<msec;i++) for(j=0; j<1275; j++); } void lcd_cmd(unsigned char item) // Function to send command on LCD { dataport = item; rs= 0; rw=0; en=1; delay(1); en=0; return; } void lcd_data(unsigned char item) // Function to display character on LCD { dataport = item; rs= 1; rw=0; en=1; delay(1); en=0; return; } void lcd_data_string(unsigned char *str) // Function to display string on LCD { int i=0; while(str[i]!='�') { lcd_data(str[i]); i++; delay(10); } return; } void lcd() { lcd_cmd(0x38); // For using 8-bit 2 row LCD delay(5); lcd_cmd(0x0F); // For display on cursor blinking delay(5); lcd_cmd(0x80); // Set the cursor on first position of LCD delay(5); } void transmit_data(unsigned char str) // Function to transmit data through serial port { SBUF=str; //Store data in SBUF while(TI==0); //Wait till data transmits TI=0; } void receive_data() interrupt 4 // Function to recieve data serialy from RS232 into microcontroller { RI=0; str[++count]=SBUF; //Read SBUF } unsigned char byte_check() // Function to check carraige return and new line character { switch(str[0]) { case 0x0a: { // Return 0x00 for new line return 0x00; break ; } case 0x0d: { // Return 0x01 for carriage return return 0x01; break ; } default :return 0x02 ; // Return 0x02 for characters except new line and carriage return } } void main() { lcd(); // Initialize LCD init_serial(); // Initialize serial port count=(-1); delay(500); lcd_data_string("Ready"); delay(10); lcd_cmd(0x01); IE=0x94; transmit_data('A'); // Transmit 'A' to serial port delay(1); transmit_data('T'); // Transmit 'T' to serial port delay(1); transmit_data(0x0d); // Transmit carriage return to serial port delay(50); while(1) { if(count>=0) { check=byte_check(); // Check the character if(check!=0x00) { if(check==0x01) { if(check_space==1) // Check previous character { lcd_data(0x20); check_space=0; } } else { lcd_data(str[0]); check_space=1; } } count--; for(i=0;i<count;i++) // Shift the whole array to one left { str[i]=str[i+1]; } } } }###
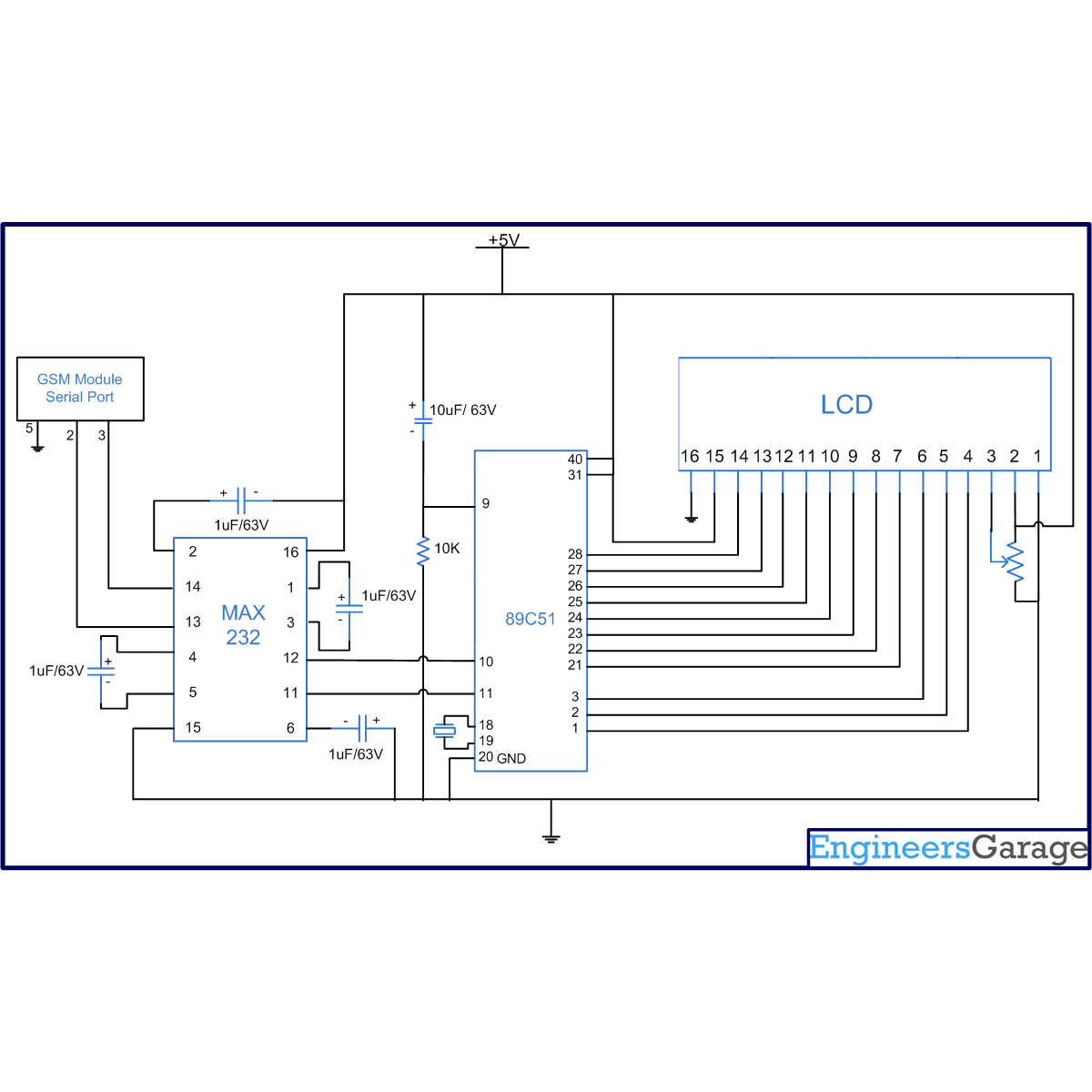
Circuit Diagrams
Project Components
Filed Under: 8051 Microcontroller.


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.