This topic covers the interfacing of RFID system with microcontroller through serial interrupt. An RFID system consists of a reader device and a transponder. A transponder or tag has a unique serial number which is identified by the reader. RFID tag is applied to products, individuals or animals to identify and track them through this number.
This topic covers the interfacing of RFID system with microcontroller through serial interrupt. An RFID system consists of a reader device and a  transponder. A transponder or tag has a unique serial number which is identified by the reader. RFID tag is applied to products, individuals or animals to identify and track them through this number.
transponder. A transponder or tag has a unique serial number which is identified by the reader. RFID tag is applied to products, individuals or animals to identify and track them through this number.
The interfacing has been done through AT89C51. The identification code of the tag is also displayed on a 16×2 LCD. The free source code for the program is available in C.
The RFID system interfaced with AT89C51 requires the controller to continuously scan the input from the RFID reader. In this topic, the program has been made more efficient by incorporating a serial interrupt.
Different RFID tags work on different frequencies. Here low frequency, 125 kHz, RFID tags have been used. These tags work within a range of 10 cm. When an RFID tag comes in this range, the reader detects it and sends a unique code of the tag serially. This serial code, consisting of 12 bytes, is received by the microcontroller.
In the program, Timer1 is configured for serial communication. (Refer Timer programming in 8051) The baud rate is set to 9600bps for data transmission. The LCD is initialized to display the code. When a card/tag comes in the proximity of RFID reader, the microcontroller reads the code and sends it to the LCD module.
The RFID system interfaced with AT89C51 requires the controller to continuously scan the input from the RFID reader. In this topic, the program has been made more efficient by incorporating a serial interrupt.
Different RFID tags work on different frequencies. Here low frequency, 125 kHz, RFID tags have been used. These tags work within a range of 10 cm. When an RFID tag comes in this range, the reader detects it and sends a unique code of the tag serially. This serial code, consisting of 12 bytes, is received by the microcontroller.
In the program, Timer1 is configured for serial communication. (Refer Timer programming in 8051) The baud rate is set to 9600bps for data transmission. The LCD is initialized to display the code. When a card/tag comes in the proximity of RFID reader, the microcontroller reads the code and sends it to the LCD module.
The serial interrupt is triggered on every reception of one byte of data. Since the identification code of transponder consists of 12 bytes, the flag is also generated 12 times to indicate the byte wise transfer of data. Whenever the serial code is generated by the reader, the interrupt is activated and the data is sent to the receiver pin of microcontroller.
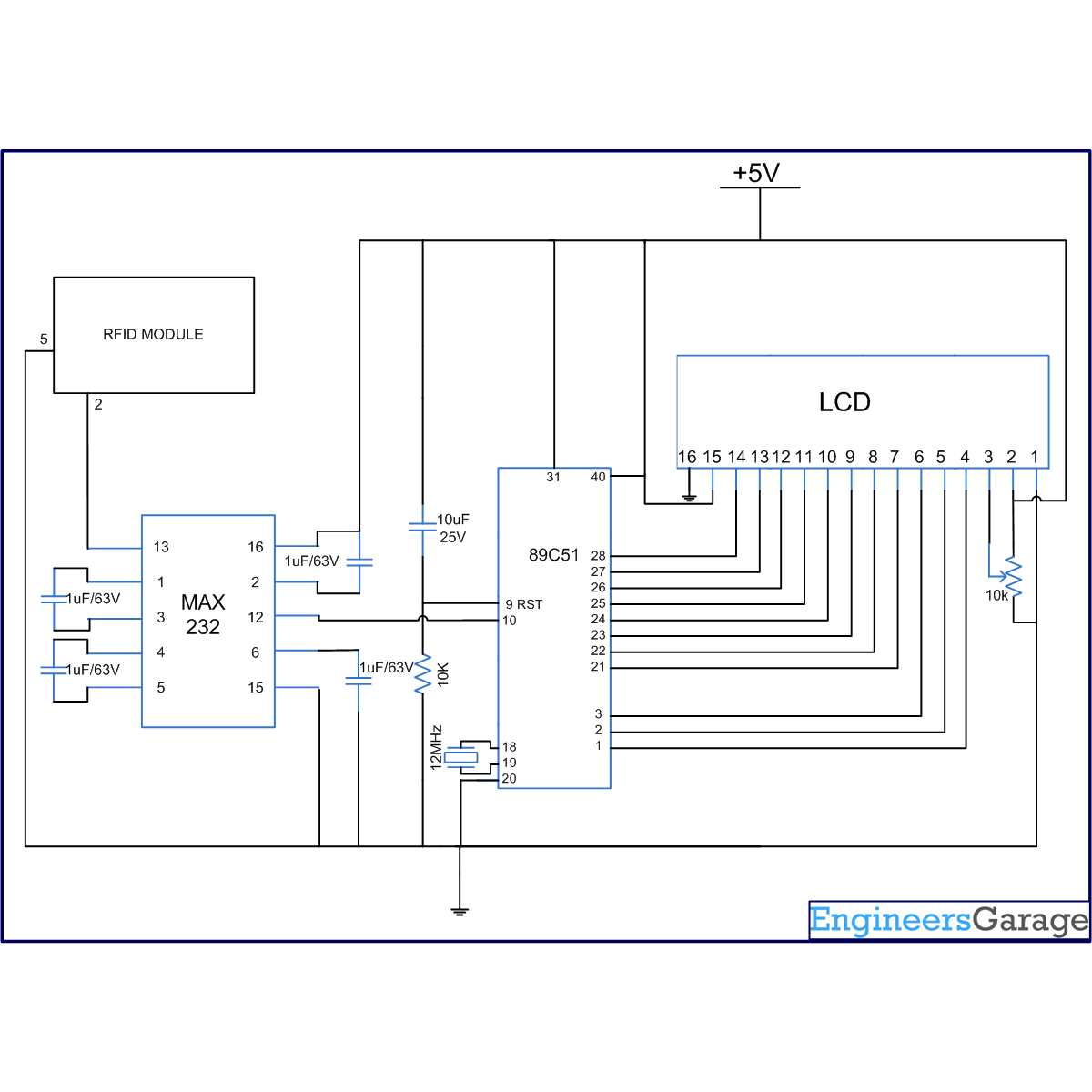
A serial level converter is required for AT89C51 to receive these serial signals. IC MAX232 has been used for this purpose to interface the RFID reader with microcontroller. The circuit connections are as follows:
Receiver1 (R1) of MAX232 has been used for the serial communication. The receiver pin of RFID reader is connected to R1IN (pin13) of MAX232. R1OUT (pin 12) of MAX232 is connected to RxD (P3.0) of microcontroller.
|
RFID Reader
|
MAX232
|
AT89C51
|
|
|
Rx
|
R1 IN
|
R1 OUT
|
Rx
|
Project Source Code
###
//Program to interface RFID with 8051 microcontroller (AT89C51) using serial interrupt #include<reg51.h> unsigned int data_out,command=0x80,temp; sfr lcd_data_pin=0xA0;//p2 port sbit rs=P1^0; // Register select pin sbit rw=P1^1; // Read Write pin sbit en=P1^2; // Enable pin unsigned char card_id[12]; unsigned char current_byte = 0; void delay(unsigned int count) //Function to provide delay { int i,j; for(i=0;i<count;i++) for(j=0;j<1275;j++); } void lcd_command(unsigned char comm) //Lcd command funtion { lcd_data_pin=comm; en=1; rs=0; rw=0; delay(1); en=0; } void lcd_data(unsigned char disp) //Lcd data function { lcd_data_pin=disp; en=1; rs=1; rw=0; delay(1); en=0; } lcd_string(unsigned char *disp) //Lcd string function { int x; for(x=0;disp[x]!=0;x++) { lcd_data(disp[x]); } } void lcd_ini() //Function to inisialize the LCD { lcd_command(0x38); delay(5); lcd_command(0x0F); delay(5); lcd_command(0x80); delay(5); } void display() // Function to display the unique id { unsigned char count; lcd_command(0xC1); //Place cursor to second position of second line for(count=0;count<12;count++) { lcd_data(card_id[count]); } current_byte=0; } void recieve() interrupt 4 Function to recieve data serialy from RS232 { card_id[current_byte]=SBUF; RI=0; // Reset the serial interrupt after recieving the byte current_byte++; } void main() { TMOD=0x20; //Enable Timer 1 TH1=0XFD; SCON=0x50; TR1=1; EA=1; ES=1; // Trigger Timer 1 lcd_ini(); lcd_command(0x81); //Place cursor to second position of first line lcd_string("UNIQUE CARD ID:"); delay(200); while(1) { while(current_byte!=12); display(); } }###
Circuit Diagrams
Project Components
Project Video
Filed Under: 8051 Microcontroller.
Filed Under: 8051 Microcontroller.


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.