How to create pipe in Linux
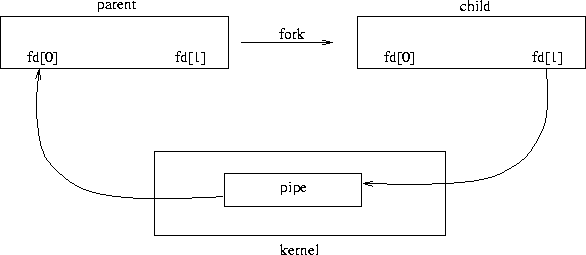
Fig. 1: Overview of Pipes in Linux
Pipe is one way communication of data between one process to another process. It is a form of communication called Interprocess Communication (IPC). Refer to the tutorial Pipe in Linux before learning this one.
Process creates a new pipe using pipe ( ) system call. It creates a pair of file descriptor: one for read channel and one for write channel. These file descriptors may pass through fork ( ) system call. Fork ( ) creates a new process which shares the pipe with them. It takes no argument and returns the process ID. You can learn more about Fork ( ) system call in Process in Linux tutorial.
It can read from pipe by read ( ) system call with first file descriptor and can write to pipe by write ( ) system call with second file descriptor. It is half duplex pipe so each process must be closed before using another.
Pipe ( ) System Call
Pipe ( ) system call creates a pair of file descriptors for communication between two processes. First file descriptor is associated with read operation and second file descriptor is associated with write operator.
SYNOPSIS of pipe ( ) system call:
int pipe ( int file_descriptor [2]);
Array file_descriptor is used to store return pair of file descriptor. file_descriptor [0] refers to the read end of pipe and file_descriptor [1] refers to the write end of pipe.
It returns Zero on success or returns -1 on error and sets the appropriately errno.
Errors may occur as following on return -1:
EFAULT – file_descriptor is not valid.
EMFILE – The per-process limit on the number of open file descriptors has been reached.
ENFILE – The system-wide limit on the total number of open files has been reached.
Create simple demo pipe
This is the basic demo tutorial of how to work with pipe. It is an example of only transferring the data from one write file descriptor to read file descriptor without creating process. Before making the program, refer to the tutorial How to create first C program in Linux.
//*****************************Pipe_demo.c*********************************//
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
int no_of_byte;
char message[1025];
char *write_msg = “Hello this is demo tutorial of working of pipe….”;
int file_d[2]; // array of file descriptor which stores pair of file descriptors
pipe(file_d); // create pipe;
write(file_d[1] , write_msg , strlen(write_msg)); // write the message to pipe using write file descriptor;
no_of_byte = read(file_d[0] , message , 1024 ); // read the message from pipe using read file deascriptor;
if(no_of_byte >= 0) // check the number of byte greater than zero;
{
message[no_of_byte] = 0; // store last byte of message NULL;
printf(“Read %d byte from pipe : %sn ” , no_of_byte , message); // print the message which is read from pipe and store it in message [] array;
}
else
{
perror(“read”);
}
exit(0); // exit from program and close the pipe;
}
//*****************************Pipe_demo.c*********************************//
Write or copy same code in your Linux text editor and save it as Pipe_demo.c. You can save file with any name that you wish.
Compiling the source code
After writing and checking it for error, the next step is to get ready for compiler.
Compile Pipe_demo.c with GCC by following line:
gcc Pipe_demo.c
After compilation, GCC will generate executable (runnable) file. Here we haven’t given the name of executable file so compiler automatically gives the a.out name to file. a.out is executable file of Pipe_demo.c and locates it in the same directory where source file is saved.
But a good programmer always gives name of executable file using the following lines instead of upper method:
gcc -o pipedemo Pipe_demo.c
Now GCC will generate executable file named pipedemo instead of a.out. Before running the executable file, make sure that the executable file is generated within the same directory where the source file is located.
Running the Executable File
Type the file name followed by dot and a forward slash and press the ENTER key as following:
./pipedemo
Following result will print on the monitor screen:
Read 50 byte from pipe : Hello this is demo tutorial of working of pipe….
Filed Under: Tutorials


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.