I’m just conveying my emotions about robots to you. So people what is robotics?? You might be getting confused about the question itself.. Funny.. But in actual Robotics it is a wide field. Robotics is term denoted with respect to robots. WHAT is a ROBOT??
Roughly we can say, ROBOT is a machine with brain and memory. Some bookish language may be elaborating it like “A reprogrammable, multifunctional manipulator designed to move material, parts, tools, or specialized devices through various programmed motions for the performance of a variety of tasks”. This definition is pretty expressive.
So what are the things that go into making a ROBOT ..?? There are some qualities that should be followed by a machine fellow,
1 It should have a BRAIN. (Memory or Controller Unit)
2 It should have an ARM. (Obviously to hold the things)
3 It should have a DRIVE mechanism for movement. (Like degree of freedom, motion and other)
4 It should have an End Effector. (Fingers like structure for sensing, holding and dragging)
5 It should have Sensors. Without Sensors, it is impossible for a ROBOT to understand the environments around it.
The list is showing basic needs for a machine to be called as ROBOT. What are the things mentioned actually?? We will understand them one by one.
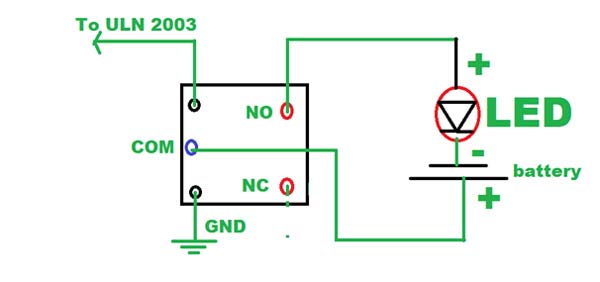
Fig. 1: Representation Image of Microcontroller
BRAIN
As you can understand it by its name, it will guide the machine for the task. Like how to hold the thing, understand the sensors, react on some data and motion. These are basically micro controllers or microprocessors depending on application.

Fig. 2: Representation Image of Robotic Arm
ARM
Robot arm comes in all shapes and sizes. The arm is the part of the robot that positions the End Effectors and Sensors to do their programming business.Many (but not all) resembles human arms, and have shoulders, elbows, wrists, even fingers. This gives the robot a lot of ways to position itself in its environment. Each joint is said to give the robot 1 degree of freedom.

Fig. 3: Representational Image of Battery as Driver for a Robot
DRIVE
The drive is the “engine” that drives the links (the sections between the joints) into their desired position. Without a drive, a robot would just sit there, which is not often desirable. Most of the drives are powered by air,fuel, pressure, or electricity.

Fig. 4: Representational Image of an End-Effectors
END Effectors
The End Effector is the “hand” connected to the robot’s arm. It is often different from a human hand – it could be a tool such as a gripper, a vacuum pump, tweezers, scalpel or a blow torch – just about anything that helps to do its job.

Fig. 5: Representational Image of Sensor
SENSOR
Most robots of today are nearly deaf and blind. Sensors can provide some limited feedback to the robot so it can do its job. Compared to the senses and abilities of even the simplest living things, robots have a very long way to go. The sensor sends information, in the form of electronic signals back to the controller. Sensors also give the robot controller information about it.
Classification of Robots
Classification
As the word indicates “Classification”, which throws light on how many types of ROBOT are present around us. There are some robots which are completely dependent on us i.e. we give them commands manually. Some are quite intelligent as they sense the environment and work without human intervention. The following shall give you an insight to the types of Robots:-
Autonomous Robots
These robots are pre-programmed. Actions which are taken by ROBOTs are predefined for every possible situation. Like we have sensors (eyes, nose, and ears) and we take decisions based on the information we received as per our learning. In the same way, these robots learn from our programming and take decisions according to the sensors mounted on them.
Controlled Robots
These Robots require human intervention. Seriously?? Yes.. Without human control they can’t perform tasks. That is why these are more effective ROBOTs. Controlling can be done by “Wires” or “Wireless”. In case of wireless control, we can send ROBOTs in remote locations where we can’t reach. Yes, your guess is as good as mine, these robots are mostly used for Military, Space Exploration and Deep Sea Exploration. Data collected by the robots is sent back to base station for the study of the subject matter.
Semi-Autonomous Robots
Robots work autonomously in normal conditions but we can control them manually for specific tasks. These are Semi-Autonomous Robots. These are intelligent art of ROBOTICS.
Except this widely accepted classification, ROBOTs can be classified by their motion style and working environments; like Wheeled Robots, Legged Robots, Tracked Robots, Aquatic Robots, and Flying Robots etc.
Application
The application areas depend on the needs of the people at large. For example we made Espresso Coffee Machines because we needed Espresso Coffee instantly. In the same way there are specific areas where there is need for the applications of Robots. The following are some of many examples.
1. Domestic Purpose
· Cleaning Robots
· Nursing Robots
2. Industrial Purpose
· Welding
· Assembling
· Painting
· Inspection robot
· Packaging robots
· Cargo lifters
3. Automated Guided Vehicles
4. Defense purpose
· Bomb Diffusion
· Surveillance

Fig. 6: Image showing different types of Robots
You may also like:
Filed Under: ARM., Electronic Projects, Tech Articles







Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.