Logic high and low indicator is used to measure the voltages (high and low). For measuring the logic state high or low just put the probe on that point and you get the display on 7 segment display. This circuit will display “H” if voltage is high and it will display “L” when voltage is low.
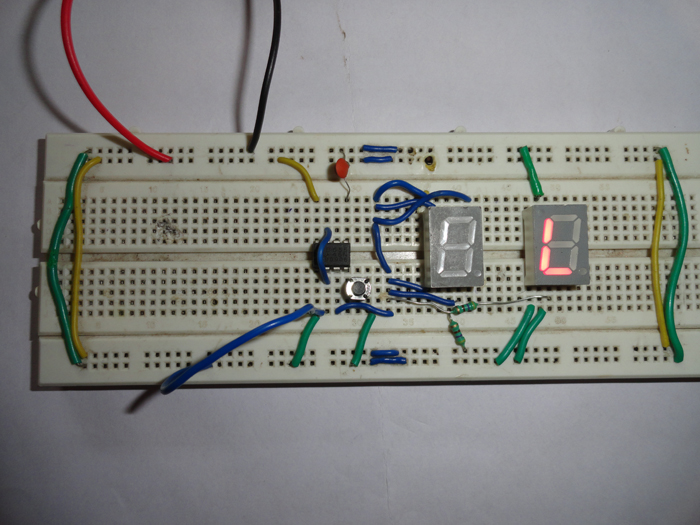
This simple circuit is based on 555 timer which act as a bi-stable multi-vibrator and two common anode seven segment display used as indicator to display logic state and few more discrete components.
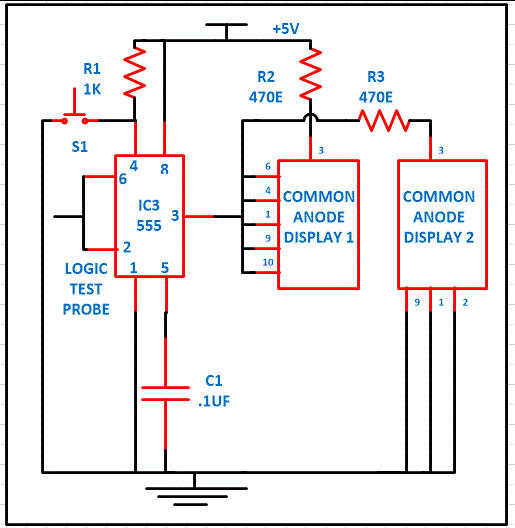
In bi-stable mode 555 timer act as a basic flip flop. We have club the pin 2 and 6 that is trigger and threshold pin and the voltage which is to be measure must be applied on this pin. When this pin 2 is low, circuit is in set position and changes the output state to high. And when pin 2 is high output pin 3 is low. It will hold the state either high or low indefinitely that is why it is called bi-stable multi-vibrator. We have connected the pin 4 with the switch which is used to reset the circuit. Pulling the reset input to ground acts as a ‘reset’ and transitions the output pin to ground (low state).
Seven segment displays are commonly used now days in place of dot matrix display. This can be used in many places like in microwave or fancy toaster oven or you can find the same on washing machine. On 7 segment display you can display numbers from 0 to 9 and some alphabets. It cannot display alphabet which uses diagonal lines (like R, Q etc) and you cannot distinguish between numeric zero and alphabet O.
7 segment display are labeled a to g and decimal point is usually known as DP. DP is the common point. In common cathode display pin 3 and 8 are connected to ground and rest pin are connected to supply. Similarly in common anode pin 3 and 8 are connected to supply and rests are connected to ground.
Advantage of 7 segment display-
1. It uses low power for its operation less than 2.5V.
2. Comes in industry standard size.
3. Comes with a industry standard pin out which can be directly referred from datasheet.
4. Seven segment display comes different size, user can use according to their requirement like 7.6mm, 10mm, 14.2mm etc.
5. You can also choose color of your display. Commonly used- Red, Yellow, and Green.
Following figure shows the pin configuration of 7 segment display-

Fig1.
Here letter “a” represents pin 7.
Similarly
letter “b” represents pin 6.
letter “c” represents pin 4
letter “d” represents pin 2
letter “e” represents pin 1
letter “f” represents pin 9
letter “g” represents pin 10
Working of circuit
To operate the logic high and low indicator circuit, first momentarily press the reset switch S1 connected at pin 4 of IC1 to reset the whole circuit. When logic probe is connected to zero volts or ground, trigger pin 2 of 555 timer goes below 1.7V to make the output pin 3 high. And this pin 3 is connected with 7 segment display. At this time we will get the “L” displayed on 7 segment display 2 which means logic zero. Bi-stable multi-vibrator will hold this state until reset pin is pressed or we have change the logic level.
On the other hand when logic probe is connected to high logic, trigger pin 2 goes high more than 3.3V and output pin 3 become low and “H” is displayed on 7 segment display 1 while second display remain off.
Video of the Circuit
Circuit Diagrams
Filed Under: Electronic Projects


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.