 In July 2019, a new world record was set when 24 LoRaWAN gateways simultaneously received a message transmitted by a node and one of the gateways was residing at a distance of 766 kilometers from the node. The previous record was 702 kilometers. The new record is set by a team from the University of Zaragoza.
In July 2019, a new world record was set when 24 LoRaWAN gateways simultaneously received a message transmitted by a node and one of the gateways was residing at a distance of 766 kilometers from the node. The previous record was 702 kilometers. The new record is set by a team from the University of Zaragoza.
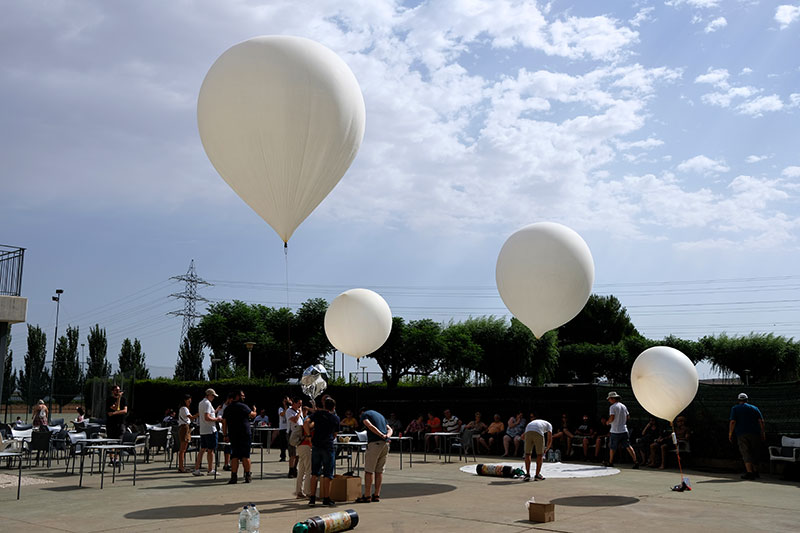
ibercivis held the event in July to explore the upper atmosphere using hot air balloons. Professors, students, and volunteers were invited to take part in the event. Each balloon was equipped with multiple sensors to take measurements of different parameters in the stratosphere. The event was not intended to break or make any record.
For communication (between balloon and base station) purposes LoRaWAN technology was utilized. Low power consumption and wide-area/network coverage is what makes the technology attractive to researchers and organizers.
In total, 7 balloons were released from the base station at Alfamen in Spain. One of the balloons, named “Diana I” by computer engineering research group from the University of Zaragoza transmitted a message while flying at an altitude of 24.8 kilometers. The message was successfully received and decoded by the gateway installed at an altitude of 2.253 kilometers and located at a distance of 766 kilometers from “Diana I”.
The “Diana I” node was comprised of a BME280 temperature, humidity, and barometric pressure sensor along with a GPS tracker module. Diana-I node transmitted the message at just 25mW. Theoretically according to the SEMTECH (the LoRaWAN developers academy) the maximum distance achievable in Europe from LoRaWAN at the cost of 25mW is 800 kilometers under ideal (line of sight, temperature) conditions.
What paved the way?
The gateway which successfully received and decoded the message was installed on a snow mountain resort at an altitude of 2.253 km. The node/balloon was flying at an altitude of 24.8 km. The height difference between node and gateway was 22.5 km and there was no solid object between the node and gateway so the line of sight condition was fulfilled. The easiest way to achieve high sensitivity in radio planning is to increase the height of the antenna. The same principle was brought under practice in the above scenario.
Interestingly the atmospheric temperature at the node was recorded at -16.5 degrees centigrade. At this temperature, it was not expected that the radio waves from LoRaWAN at 154dB would travel a distance of 766 km. However, the theoretical limit of 800 km can be met or even crossed.
Achievable data rate
Data rate depends on many factors, for example, the type of antenna, line of sight, payload, frequency, capacitance, oscillator, etc. In the case of LoRaWAN, you can look at this way. Everything comes on at cost so if power is reduced so is the data rate.
- Minimum 250 bits per second
- Maximum 50 kilobits per second
You cannot transfer files or play media over LoRaWAN. LoRaWAN is suitable only for sensor and actuators control such as tank water level monitoring, parking space or garage monitoring, wild animal detection, and security alarms.
Where the Parts can be Purchased for DIY LoRaWAN project?
BME280 : Mouser-BME280=
GPS : GPS-Mouser
LoRaWAN : LoRa Node (915Mhz-American standard)
LoRaWAN : LoRa Gateway (915Mhz-American standard)
You may also like:
Filed Under: Electronic Projects, Microcontroller Projects






Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.