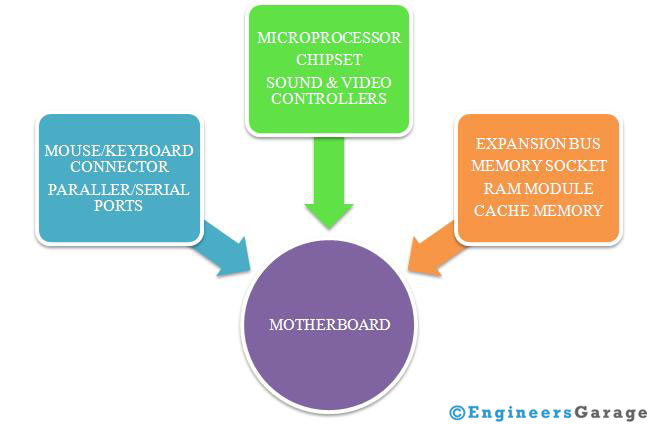
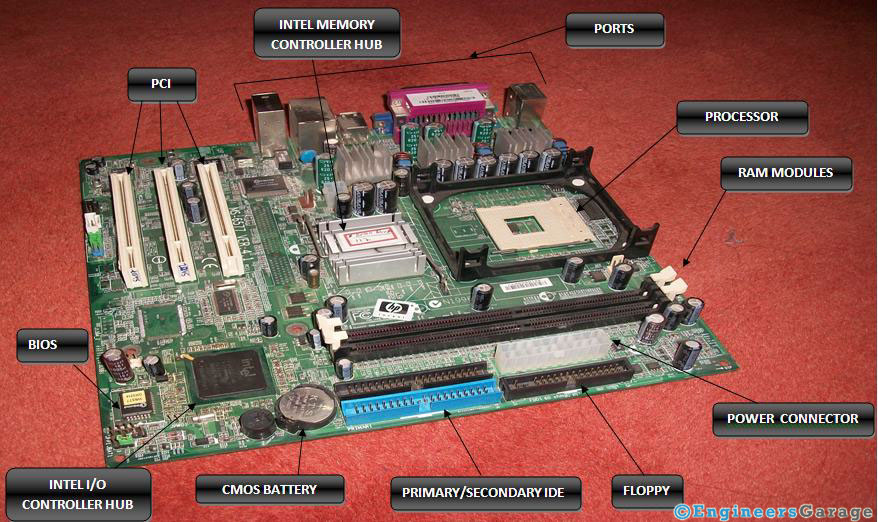
Motherboard is glue which binds all the components of a Computer. Every component directly or indirectly attached/installed/connected to a system has a connection to motherboard, because it is the base on which system & its components/peripheral devices stand and perform. Technically speaking motherboard is a PCB- Printed Circuit Board that provides an interconnect to almost every component present in a PC. It is also known as system/main board.
There are various roles that a motherboard plays. The important ones are as follows:
· It acts as glue which binds all the components together. It main job is to coordinate with the various operations performed by the various components.
· It serves as a interface for all the modular singular components of a system like Central processing Unit – CPU, Random Access Memory – RAM, Storage device – Hard Disk ( Magnetic or Solid State)
· To provide slots and expansion cards to enhance the functionality of a system. There is development of new devices with new interfaces every day. Motherboard need to provide the slots to include the functionality.
· To deliver the power to the various components and devices as per their requirements.
CHIPSET
We all understand a simple fact; to make a system run there should be a Central Processing Unit – the brain of a computer. Processor is the one which controls the functionality of the machine. But as it is clear from the above that there are many components or peripheral devices that are present in a computer. So there needs to be a proper channel or medium for an effective and efficient communication between processor and other components. This task is taken up by Chipset.
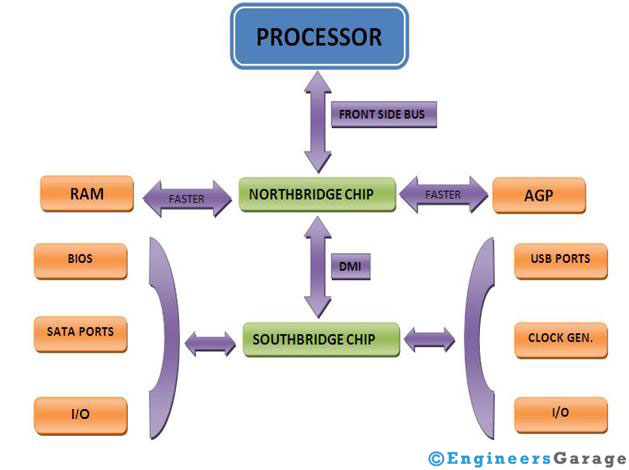
It consists of 2 parts: Northbridge and Southbridge.
These two separate units control the memory cache, external bus and loads of peripheral components/device. The fast end of the hub is known as the Northbridge, and the slow end is known as Southbridge.

The main reason that the chipset is divided into two separate units is that it is difficult to integrate the various components on a single chip. And moreover the accessing/transfer speed of instructions/commands/data between the processor and other components (some of the components processes/interprets slowly) is different, so Northbridge provides fast access as compared to Southbridge. 

Northbridge is the part of the chipset which communicates with the processor. As its interaction is with processor, so it is fast. It acts as a medium channel between processor and memory, level 2 cache, and AGP – Accelerated Graphics Port. Southbridge is slower than the Northbridge and it connects and controls computer Input output functions. It controls Universal Serial Bus – USB, the system Basic Input output System – BIOS, serial ports etc. In other words we can say they control all the functionality except that of memory and AGP.
FORM FACTOR
This is a specification format for a motherboard. Simply speaking, we know that motherboard consists of various components. Now all the components, slots, ports etc can be arranged in various forms. But this will lead to problem and chaos, as all manufacturers will follow their own convenient and suitable format. So there are specifications or set of format that define the shape and size of the motherboard. It specifies the layout of the motherboard.
The most common and most famous for factors are shown in the figure:

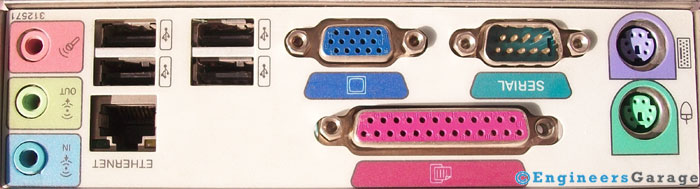
The names which are displayed are the various Form Factors. They are the standards. For example ATX was created by Intel in the year 1996. According to this standard the maximum size of the motherboard can be 12 * 9.6 in 305 * 244 mm. The main features of the ATX standard are the Back Panel Ports including parallel, serial, keyboard, mouse, USB, audio I/O, S/PDIF, and LAN. They are still one of the mostly used specifications with some advancement in form of their variants.
MEMORY
When we hear the term memory, we think of storage devices but for processor the real memory is RAM – Random Access Memory. This is where the real processing/execution/operations of data/commands/instructions take place. The speed of the execution (opening, closing, editing, copying etc.) of files depends upon this memory. More is the RAM faster is the processing.

These days the memory comes as DDR – Dual Data Rate. The one shown in the figure is 128MB DDR as seen from the RAM. These days the motherboard has multiple slots for the memory. In the motherboard diagram shown earlier, it has 2 slots for the memory. The multiple slots for the memory ensure that the advance versions of RAM can be installed and used in the system. For example if we consider the present case then there are DDR3 which are mostly used in today’s system. But most of the earlier chipset don’t have the slot for the DDR3 RAM, that is they don’t support the DDR3 RAM. So the system needs to have a new motherboard to support DDR3 RAM.
BUSES
Buses are the pair of wires or a circuitry which is used to transfer the data. So more is the capacity of the bus, faster will the execution of a process/request. The speed of the bus (rate at which data is transferred) is measured in terms of MegaHertz.
This is the most important part of the motherboard which we tend to forget. To understand this concept let us consider an example. Say that there is a road where there are 5 lanes for the movement of car. Now there is river and henceforth a bridge made over a river. But over the bridge there are only 3 lanes. So the 2 cars which are outside need to wait. This can be better understood by the figure.
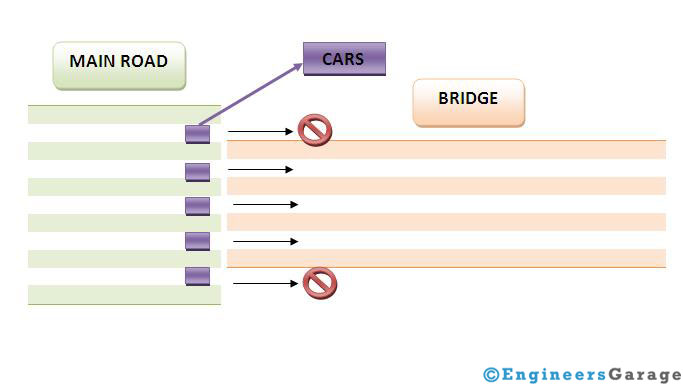
Same is the case with buses in computer. Bridge and Buses are same. What will be the use of 5 lanes on road if 5 cars can’t travel through bridge? Similarly what will be use of a component say processor which can access 5 bits simultaneously if the buses can only transfer 3 bits at a time? The processor efficiency will also be accessing 3 bits at a time. So this is important factor which should be kept in mind if we want to improve the efficiency of the system.
There are various buses that are present in the system. Some of the important are as follows.
· System Bus
· Front Side Bus
· Back Side Bus
· Control Bus
· Address Bus
· AGP Bus
· PCI Express Bus
· PATA, SATA, SCSI and its variants
· And many more…
BIOS
This is also known as the firmware. This is Read Only Memory or flash memory. When the system is powered on, then the system needs to get started by loading the operating system. But where is the operating system present. It is present in the hard disk. So somebody needs to tell that where is OS located. This is done by BIOS. At the start registers get to default value and then BIOS starts its functions. It conducts the POST power on Self Test. It checks that all the most important and necessary components for eg. Memory is present or not. It not it gives error. If not then it move on the next process that is locating the Bootloader and hence loading the Operating System.
There are many more components that are present eg. CMOS battery which keeps the clock running even when the power is down. This leads to correct time even when we power on the machine after a long time. There are also many more connections for managing other functionality. But whenever one buys a system, a motherboard should also be one of the things which should be noted carefully.
Filed Under: How to, Tech Articles


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.