The aim of the project is to build a robot which, in simple terms, is a hand and edge detecting and avoiding vehicle. When our hand comes from the top, it avoids it by moving away. Further, it will not fall off the table edge.
BLOCK DIAGRAM:

Fig. 1: Block Diagram of Obstacle Avoiding Robot
Circuit for Obstacle and Edge Detection Vehicle
The clockie consists of 4 basic modules:
i) IR Sensor Part
ii) LED & LDR Part
iii) Monostable Part
iv) Digital Logic & Motor Part
i) IR Sensor Part:
In this part, I use 2 pairs of IR LED and photodiode. I have used 2 of them for 2 reasons:
i) To detect hand coming from 2 directions
ii) To make the robot work in both day and night
During day, the photodiodes receive most of the IR radiation from the sun. So while hand comes during the day, it actually blocks the sunlight, thus reducing the amount of IR received by sensors. But during night, hand reflects the IR onto the diode.
These two are opposing behaviours. Hence to make the robot work throughout the day, I have used the XNOR logic. So when one of the sensors’ output differs from other’s the XNOR gate produces a logic low, which is used to trigger two monostables – MS1 (which decides the total time of operation of the circuit) and MS2(which causes the robot to move in the forward direction).
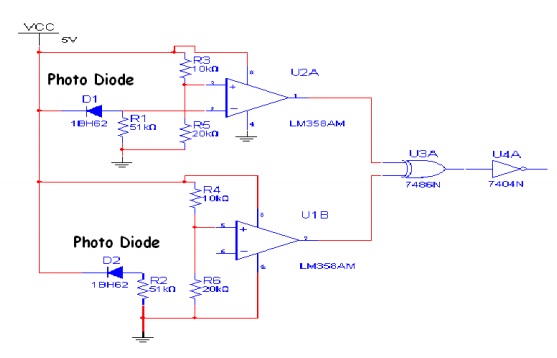
Fig. 2: Circuit Diagram of IR Sensor Module
ii) LED and LDR part:
In this part I have used 2 LED’s and 2 LDR’s and 2 comparators.
The LDRs are connected to 2 potentiometers basically for potential dividing and this potential is given to one of the comparators’ input and a reference voltage is given to the other input. I have fixed the reference so that the sensor works properly in day time as well as in the night time.
When the robot is on the table, the comparator output is logic 1(ldr receives maximum reflected light). When one of the sensors detects an edge (i.e. when ldr receives no light), the comparator output goes low. The output of both the comparators and the output of MS1 are ANDed and is given to the reset of MS2. This stops the forward motion and starts the backward motion.
The outputs of the comparators are stored in a flip-flop so that it saves the information as to which sensor has gone out of the table.
This is required because as soon as the robot moves backward, the comparator outputs become 1 again. Hence to decide the appropriate direction of turning, comparator outputs are saved.
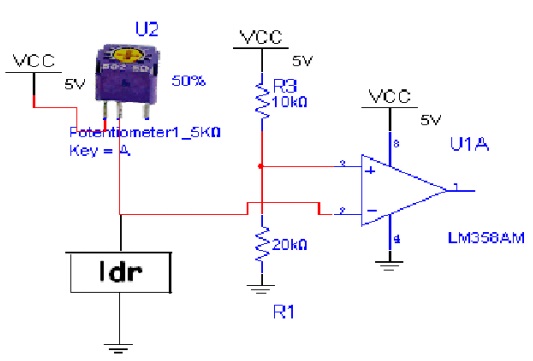
Fig. 3: Circuit Diagram of LDR Module
iii) Monostable Part:
Time for which monostable circuit using 555 gives a high pulse is given by:
TH = 1.1RC
I have used 4 monostables:
a) {C}{C}{C}{C}{C}{C}{C}{C}{C}{C}MS1 : Decides the total time of operation of the entire circuit. It is triggered when a hand comes(i.e. when IR sensor part gives a 1to 0 transition).
TH = 22s
= R = 1 Mohm , C = 22uF
b)MS2 : Makes the robot move in the forward direction. It is triggered when IR sensor part
gives a 1 to 0 transition as well as when the output of MS4 makes a transitionfrom 1 to 0.
TH = 5s
= R = 5 Mohm, C = 1uF
Hence if no edge comes in 5s, the robot will reverse and turn (just to make it interesting!!).
c)MS3 : Makes the robot move backwards. It is triggered when MS1 goes from high to low.
TH = 0.33s
= R = 330 kohm, C = 1 uF
d) MS4 : Makes the robot turn. It is triggered when MS3 goes low. It acts as the select input to the multiplexer in the module 4.
TH = 0.33s
= R = 330 kohm, C = 1 uF
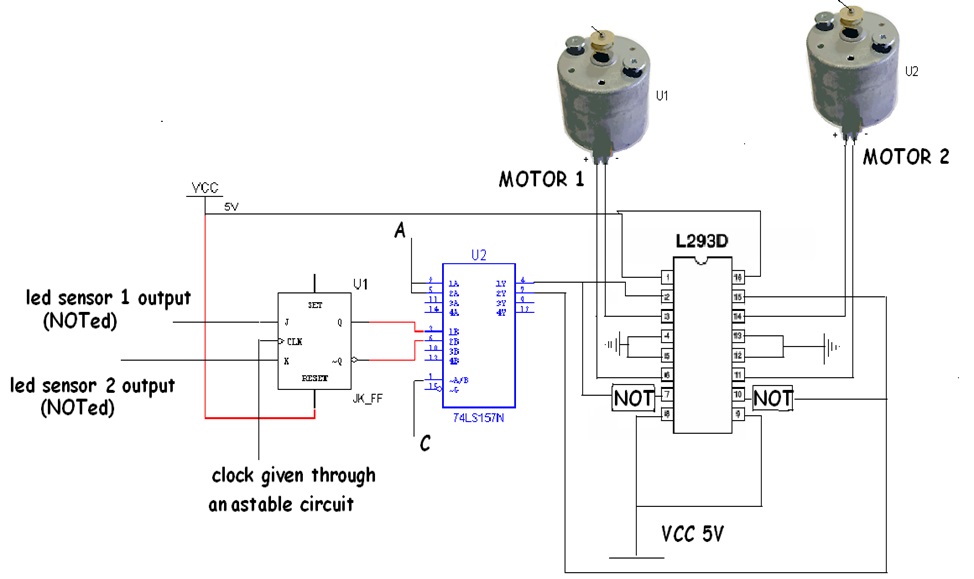
iv) Digital Logic & Motor Part:
a) Flip Flop:
A J–K flip flop is used to store the information as to which sensor has gone out.
The truth table of the J–K flip flop is as follows
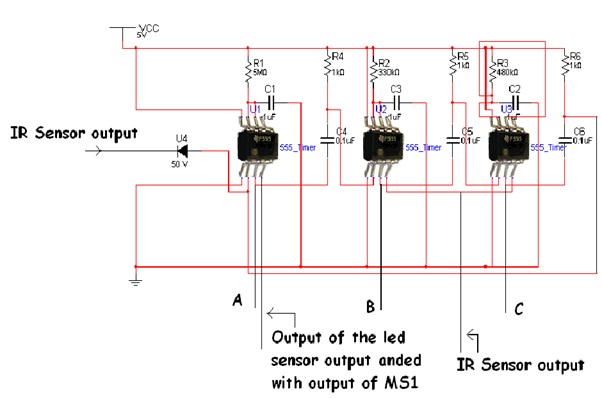
Fig. 4: Circuit Diagram of Timer Section
|
J (Noted o/p of sensor1) |
K (NOTed o/p of sensor2) |
Q (to MUX) |
|
0 |
0 |
HOLD |
|
0 |
1 |
RESET |
|
1 |
0 |
SET |
|
1 |
1 |
TOGGLE |
When the Clockie is on the table, the flip–flop is in HOLD state. When one of the sensors go out of the table, either J or K is 1. Now when the robot comes back to the table, the flip– flop is in the HOLD state thus retaining the previous information.
b) 2–iput Multiplexer:
Select input is the output of MS4(say C). When C is low, the output of the MUX is A(output of MS2). When C is high, the MUX output should be decided by the flip–flop.
Hence the below configuration:

Fig. 5:
c) H–Bridge(L293D):
|
1A |
1B |
2A |
2B |
Action |
|
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
Both forward |
|
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
Both backward |
|
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
Turn right |
|
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
Turn left |
The MUX output goes to the pins 2(1A) and 15(1B) of the h– bridge.
2A = (1A)’ and 2B = (1B)’
Hence the motors are driven. Motors used are D.C motors.
Working with sensors:
Sensors being environment dependant caused too much trouble. Everytime voltage references had to be changed. I tried my best to make it work throughout the day. So we used 2 IR sensors and made them work according to XOR logic. Moreover the photodiodes were covered.
Application:
Waking up early in the morning is very difficult to most of us. Hence to force you out of bed, Clockie is an expert. An alarm can be fixed on it. When you try to switch off the alarm to go back to sleep, the clockie avoids your hand

Fig. 6:
Circuit Diagrams
Filed Under: Electronic Projects


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.