Operating an electrical/electronic device through wireless communication is very commonly required and seems very interesting. The circuit of the project described here can operate such appliances. A few salient features of the circuit are shown below:
1. The circuit mainly comprises of a transmitter and a receiver component.
2. Whenever a signal is received by the receiver, it activates a switch which in turn turns the appliance on.
3. In this project, the transmitter component of the circuit is basically an Infrared (IR) Led which is configured to emit rays at a frequency of 38 kHz. For this purpose, NE 555 timer is used in astable mode.
To generate this frequency, a capacitor C1(.01uF), resistances R1 (1k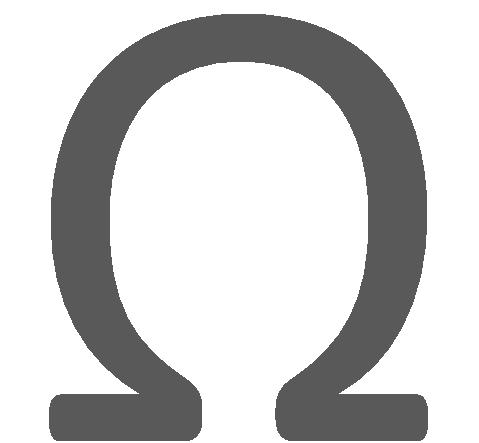 ) and R2(1394
) and R2(1394 ) are used. The R2 value is obtained through a variable resistor or preset. This frequency is to modulate the optical output of the IR Led so as to increase its transmission range. This means that the IR Led turns on and off at a frequency of 38 kHz. The receiver component uses TSOP-1738 which is tuned to the transmitted frequency. The TSOP module contains inbuilt pin diode and a pre-amplifier. Its package acts as an IR filter and the output remains normally high (5V). The transistor T1 (BC547) acts as a switch and its collector is connected to a relay. This relay can be coupled to any other circuit or electrical appliance. Whenever the TSOP module receives an IR pulse, its output drops to low (0.01V). In this state the transistor does not get the forward bias and it jumps to cut off. As a result, the collector current ceases to flow and the relay changes contact from NO to NC. Thus the appliance connected to NC turns on. The resistor R3 is used for checking the base current.
) are used. The R2 value is obtained through a variable resistor or preset. This frequency is to modulate the optical output of the IR Led so as to increase its transmission range. This means that the IR Led turns on and off at a frequency of 38 kHz. The receiver component uses TSOP-1738 which is tuned to the transmitted frequency. The TSOP module contains inbuilt pin diode and a pre-amplifier. Its package acts as an IR filter and the output remains normally high (5V). The transistor T1 (BC547) acts as a switch and its collector is connected to a relay. This relay can be coupled to any other circuit or electrical appliance. Whenever the TSOP module receives an IR pulse, its output drops to low (0.01V). In this state the transistor does not get the forward bias and it jumps to cut off. As a result, the collector current ceases to flow and the relay changes contact from NO to NC. Thus the appliance connected to NC turns on. The resistor R3 is used for checking the base current.
Project Components
Filed Under: 555 Timers, Electronic Projects


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.